
The Arthoniales is the second largest order of mainly crustose lichens, but fruticose lichens are present as well. The order contains around 1500 species, while the largest order with lichenized fungi, the Lecanorales, contains more than 14000 species.

The Physciaceae are a family of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. A 2016 estimate placed 19 genera and 601 species in the family.

The Baeomycetales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the subclass Ostropomycetidae, in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains 8 families, 33 genera and about 170 species. As a result of molecular phylogenetics research published in the late 2010s, several orders were folded into the Baeomycetales, resulting in a substantial increase in the number of taxa.

The Graphidaceae are a family of lichen-forming fungi in the order Graphidales. The family contains nearly a hundred genera and more than 2000 species. Although the family has a cosmopolitan distribution, most Graphidaceae species occur in tropical regions, and typically grow on bark.

Verrucariaceae is a family of lichens and a few non-lichenised fungi in the order Verrucariales. The lichens have a wide variety of thallus forms, from crustose (crust-like) to foliose (bushy) and squamulose (scaly). Most of them grow on land, some in freshwater and a few in the sea. Many are free-living but there are some species that are parasites on other lichens, while one marine species always lives together with a leafy green alga.
Speerschneidera is a single-species genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Leprocaulaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Italian botanist Vittore Benedetto Antonio Trevisan de Saint-Léon in 1861, with Speerschneidera euploca as the type species. This lichen was originally described by Edward Tuckerman in 1858 as Physcia euploca. It is a crustose lichen found in the southern United States and Mexico.
Gyrophthorus is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the phylum Ascomycota. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the phylum is unknown, and it has not yet been placed with certainty into any class, order, or family. The genus was circumscribed in 1990 by Josef Hafellner and Leopoldo Sancho, with Gyrophthorus perforans assigned as the type species.

The Lecideaceae are a family of lichens in the order Lecideales. It contains about 30 genera about roughly 250 species. A major distinguishing characteristic of the family is the lecanoroid form of the fruiting bodies: typically circular, dark, and without a thalline margin. Most species in the family are lichenised with green algae, although a few species, scattered amongst several genera, are lichenicolous–they live on other lichens. Lecideaceae lichens tend to grow on rocks, wood, and soil. The largest genus in the family, Lecidea, was once a loosely circumscribed wastebasket taxon containing hundreds of morphologically similar species with generally crustose thalli, photobiont-free apothecial margins and translucent, single-celled ascospores. The overall taxonomy and classification within the family has been made more accurate with recent molecular phylogenetics studies.

Phacopsis is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi. They are parasites of members of the large lichen family Parmeliaceae, of which they are also a member. Originally proposed by Edmond Tulasne in 1852 to contain 3 species, Phacopsis now contains 10 species, although historically, 33 taxa have been described in the genus. Many of the species are poorly known, some of them having been documented only from the type specimen.

Leprocaulon is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Leprocaulaceae. Members of the genus Leprocaulon are commonly called mealy lichens.

Trapeliaceae is a family of lichens in the order Baeomycetales. The family contains 12 genera and about 125 species.

Varicellaria is a genus of crustose lichens. It is the only genus in the family Varicellariaceae.
Paralecia is a monotypic fungal genus in the family Cladoniaceae. It contains a single species, the lichenicolous fungus Paralecia pratorum, found in Europe.

Loxospora is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Sarrameanaceae. It has 13 species. The genus was circumscribed by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1852, with Loxospora elatina assigned as the type species. This crustose lichen was originally named Lecanora elatina by Erik Acharius in 1810.

Halecania is a genus of fungi in the family Leprocaulaceae. It has 22 species. The genus was circumscribed by Austrian lichenologist Michaela Mayrhofer in 1987, with Halecania alpivaga assigned as the type species. She created Halecania to contain species, formerly placed in Lecania, with the following characteristics: uniformly amyloid apical domes, paraphyses with dark brown apical caps, and halonate ascospores.

Andreiomyces is the sole genus in Andreiomycetaceae, a family in the order Arthoniales. Andreiomyces contains two lichen-forming fungi, both of which were previously classified in the genus Lepraria.

Sarrameanaceae is a family of lichen-forming fungi in the monotypic order Sarrameanales. It contains two genera, Loxospora, and Sarrameana, the type genus. The family was circumscribed by Josef Hafellner in 1984. The order Sarrameanales was proposed by Brendan Hodkinson and James Lendemer in 2011, as they had noted that previously published large-scale molecular phylogenetic studies had shown that the group of species contained in the family Sarrameanaceae were distinct and separate from the clade containing all of the other orders of the Ostropomycetidae. However, the name Sarrameanales was not validly published according to the rules of botanical nomenclature, because it was not accompanied by a suitable description. Despite this, the order continues to be used in lichenological literature.

Thelenellaceae is a family of lichen-forming fungi. It is the sole family in the monotypic order Thelenellales, and contains three genera and about 50 species.
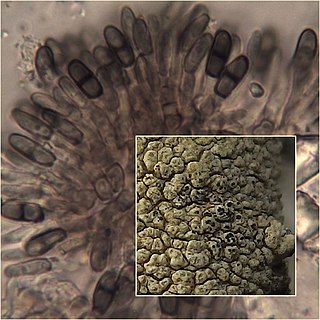
Minutoexcipula is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi of uncertain familial placement in the order Chaetothyriales. It has eight species. The genus was circumscribed in 1994 by M. Violeta Atienza Tamarit and David Leslie Hawksworth, with Minutoexcipula tuckerae assigned as the type species. The genus is characterized both by its black convex sporodochia-like conidiomata, as well as the well-differentiated exciple on these structures.
Protothelenella is a genus of fungi in the family Protothelenellaceae. It contains 11 species, some of which form lichens. Protothelenella species have a crustose thallus with spherical to pear-shaped, dark brown to blackish perithecia. Microscopic characteristics of the genus include bitunicate asci with an amyloid tholus, and ascospores that are colourless and contain multiple internal partitions. Some species grow on acidic substrates including rocks, soil, bryophytes, plant detritus or rotten wood. Other species are lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling), growing on species of Solorina, Peltigera, Pseudocyphellaria, or Cladonia.















