| Leptodermis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Leptodermis |
Leptodermis is a genus of plants in the family Rubiaceae. [1]
| Leptodermis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Leptodermis |
Leptodermis is a genus of plants in the family Rubiaceae. [1]

Termites are eusocial insects that are classified at the taxonomic rank of infraorder Isoptera, or as epifamily Termitoidae within the order Blattodea. Termites were once classified in a separate order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are the sister group to wood eating cockroaches of the genus Cryptocercus. Previous estimates suggested the divergence took place during the Jurassic or Triassic. More recent estimates suggest they have an origin during the Late Jurassic, with the first fossil records in the Early Cretaceous. About 3,106 species are currently described, with a few hundred more left to be described. Although these insects are often called "white ants", they are not ants, and are not closely related to ants.

Serissa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae, containing only one species, Serissa japonica. It is native to open sub-tropical woodlands and wet meadows in southeast Asia, from India, and China to Japan. It is commonly called the snowrose, tree of a thousand stars, or Japanese boxthorn; and was formerly called Serissa foetida. 'Foetida' referres to the unpleasant, vomit-like, odour that the trees give off if their leaves are pruned or bruised. Snowrose and tree of a thousand stars are different cultivars. The only method of differentiating is measuring the difference in the shape and size of the flowers produced.

Inia is a genus of river dolphins from South America. It contains one to three species.
The Thermotogae are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogae is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.
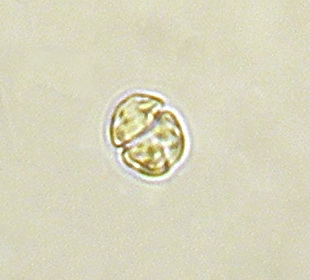
Gymnodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates, a type of marine and freshwater plankton. It is one of the few naked dinoflagellates, or species lacking armor. Since 2000, the species which had been considered to be part of Gymnodinium have been divided into several genera, based on the nature of the apical groove and partial LSU rDNA sequence data. Amphidinium was redefined later. Gymnodinium belong to red dinoflagellates that, in concentration, can cause red tides.

Raphicerus is a genus of small antelopes of the tribe Neotragini.

Scaphium affine is a tree species in the family Malvaceae, subfamily Sterculioideae. It is native to mainland Southeast Asia and no subspecies are listed in the Catalogue of Life.

The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. A food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level 3 or higher, and typically finish with apex predators at level 4 or 5. The path along the chain can form either a one-way flow or a food "web". Ecological communities with higher biodiversity form more complex trophic paths.

Schistura is a genus of fish in the stone loach family Nemacheilidae native to the streams and rivers of the southern and eastern Asia. Some of these species are troglobitic.
The Sulawesi forest turtle is a critically endangered species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is monotypic within the genus Leucocephalon. It is endemic to Sulawesi in Indonesia.

Woodfordia fruticosa is a species of plant in the family Lythraceae.

Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera. With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more manoeuvrable than birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is 29–34 millimetres in length, 150 mm (6 in) across the wings and 2–2.6 g in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes and the giant golden-crowned flying fox, Acerodon jubatus, which can weigh 1.6 kg and have a wingspan of 1.7 m.
Nitrospirae is a phylum of bacteria. It contains only one class, Nitrospira, which itself contains one order (Nitrospirales) and one family (Nitrospiraceae). It includes multiple genera, such as Nitrospira, the largest. The first member of this phylum, Nitrospira marina, was discovered in 1985. The second member, Nitrospira moscoviensis, was discovered in 1995.

The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates is a list of highly endangered primate species selected and published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature Species Survival Commission Primate Specialist Group, the International Primatological Society (IPS), and Conservation International (CI). The 2012–2014 list added the Bristol Conservation and Science Foundation (BCSF) to the list of publishers. The IUCN/SSC PSG worked with CI to start the list in 2000, but in 2002, during the 19th Congress of the International Primatological Society, primatologists reviewed and debated the list, resulting in the 2002–2004 revision and the endorsement of the IPS. The publication has since been a joint project between the three conservation organizations and has been revised every two years following the biannual Congress of the IPS. Starting with the 2004–2006 report, the title changed to "Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates". That same year, the list began to provide information about each species, including their conservation status and the threats they face in the wild. The species text is written in collaboration with experts from the field, with 60 people contributing to the 2006–2008 report and 85 people contributing to the 2008–2010 report. The 2004–2006 and 2006–2008 reports were published in the IUCN/SSC PSG journal Primate Conservation, while the 2008–2010 and 2010-2012 report were published as independent publications by all three contributing organizations.
The species Sudan ebolavirus is a virological taxon included in the genus Ebolavirus, family Filoviridae, order Mononegavirales. The species has a single virus member, Sudan virus (SUDV). The members of the species are called Sudan ebolaviruses.
Alfred Frank Millidge was a British arachnologist who wrote several works on spiders. One of his best-known might be British Spiders, volumes I and II, which he co-wrote with G. H. Locket. In 1983, he became the first person to describe the spider species Walckenaeria crocea.
The World Spider Catalog (WSC) is an online searchable database concerned with spider taxonomy. It aims to list all accepted families, genera and species, as well as provide access to the related taxonomic literature. The WSC began as a series of individual web pages in 2000, created by Norman I. Platnick of the American Museum of Natural History. After Platnick's retirement in 2014, the Natural History Museum of Bern (Switzerland) took over the catalog, converting it to a relational database.

Paederieae is a tribe of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae and contains 81 species in 4 genera. Its representatives are found in the tropics and subtropics.
Metarhizium rileyi is a species of entomopathogenic fungus in the family Clavicipitaceae; there is extensive literature under its synonym Nomuraea rileyi.
| | This Rubioideae-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |