
Sequoiadendron giganteum, also known as the giant sequoia, giant redwood or Sierra redwood is a coniferous tree, classified in the family Cupressaceae in the subfamily Sequoioideae. Giant sequoia specimens are the most massive trees on Earth. They occur naturally only in groves on the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California.

The Douglas fir is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir, Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir and Mexican Douglas-fir.

Spanish moss is an epiphytic flowering plant that often grows upon large trees in tropical and subtropical climates. It is native to much of Mexico, Bermuda, the Bahamas, Central America, South America, the Southern United States, and West Indies. It has been naturalized in Queensland (Australia). It is known as "grandpa's beard" in French Polynesia.

Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophytasensu stricto. Bryophyta may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically 0.2–10 cm (0.1–3.9 in) tall, though some species are much larger. Dawsonia, the tallest moss in the world, can grow to 50 cm (20 in) in height. There are approximately 12,000 species.

Banana slugs are North American terrestrial slugs comprising the genus Ariolimax.

Quercus garryana is an oak tree species of the Pacific Northwest, with a range stretching from southern California to southwestern British Columbia. It is commonly known as the Garry Oak, Oregon white oak or Oregon oak. It grows from sea level to an altitude of 690 feet in the northern part of its range, and from 980 to 5,900 ft in the south of the range in California. The eponymous Nicholas Garry was deputy governor of the Hudson's Bay Company.

Muir Woods National Monument is a United States National Monument managed by the National Park Service and named after naturalist John Muir. It is located on Mount Tamalpais near the Pacific coast in southwestern Marin County, California. The Monument is part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area, and is 12 miles (19 km) north of San Francisco. It protects 554 acres (224 ha), of which 240 acres (97 ha) are old growth coast redwood forests, one of a few such stands remaining in the San Francisco Bay Area.

Alnus rubra, the red alder, is a deciduous broadleaf tree native to western North America.

Ficus microcarpa, also known as Chinese banyan, Malayan banyan, Indian laurel, curtain fig, or gajumaru (ガジュマル), is a tree in the fig family Moraceae. It is native in a range from China through tropical Asia and the Caroline Islands to Australia. It is widely planted as a shade tree and frequently misidentified as F. retusa or as F. nitida.

Taxodium distichum is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a wide range of soil types, whether wet, salty, dry, or swampy. It is noted for the russet-red fall color of its lacy needles.

Pandanus tectorius is a species of Pandanus (screwpine) that is native to Malesia, Papuasia, eastern Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It grows in the coastal lowlands typically near the edge of the ocean. Common names in English include thatch screwpine, Tahitian screwpine, hala tree and pandanus. The fruit is edible and sometimes known as hala fruit.

Moresby Island is one of the Gulf Islands of British Columbia, located on the west side of Swanson Channel and east of the southern end of Saltspring Island. It is not to be confused with Moresby Island, the second largest of the Haida Gwaii Islands off the north coast of BC. It is currently a privately owned island, and is used by its current owners to raise beef cattle. The island is not open to the general public. Its current population is 2 people, a manager and his wife.
Rhytidiadelphus triquetrus, the big shaggy-moss or rough goose neck moss, is a species of moss in the family Hylocomiaceae. It is often the dominating moss species in moderately rich forest habitats in the boreal regions and the Pacific Northwest. Because of its fuzzy appearance and tail-like shape it is also called the 'electrified cat's tail moss'. Not to be confused with square goose-necked moss, Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus.

Sequoia sempervirens is the sole living species of the genus Sequoia in the cypress family Cupressaceae. Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood, and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to 115.9 m (380.1 ft) in height and up to 8.9 m (29 ft) in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the longest-living organisms on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated 810,000 ha along much of coastal California and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States.
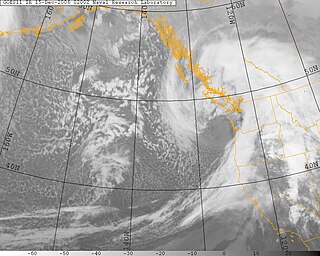
Pacific Northwest windstorms, sometimes colloquially known as Big Blows, are extratropical cyclones which form in the Pacific basin, and affect land areas in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and British Columbia, Canada. They form as cyclonic windstorms associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure that track across the North Pacific Ocean towards western North America. Deep low pressure areas are relatively common over the North Pacific. They are most common in the winter months. On average, the month when most windstorms form is November or December.

Antitrichia curtipendula is a species of feather-moss found predominantly in western North America and the western coast of Europe.

Mniaceae is a moss family in the order Bryales.

Leucolepis is a genus of mosses in the family Mniaceae.

Plagiomnium insigne, the badge moss or coastal leafy moss, is a species of moss found on humus in moist, shaded, lowland forests. It can also be found on soil along trails and other shaded, open areas. The moss sometimes forms lush, extensive mats.
Lejeunea mandonii, also known as Atlantic lejeunea is a species of liverwort from the Lejeuneaceae family.


















