
Guiuan, officially the Municipality of Guiuan, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Eastern Samar, Philippines. It constitutes the southeastern extremity of Samar Island and some adjacent islands, surrounded by major bodies of water including the Leyte Gulf and the Philippine Sea. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 53,361 people, making it the most populous municipality in Eastern Samar and the second most populous administrative division in the entire province after the capital city Borongan.

Calicoan is a Philippine island east of Leyte Gulf, off the southeastern point of Samar. It is one of the islands that are part of the municipality of Guiuan, in the province of Eastern Samar. The island can be reached from Tacloban City by a three-hour bus ride.

USS Wildcat (AW-2), was a Stag-class tanker, built for the United States Navy during World War II, the only U.S. Naval vessel to be named for Felis silvestris.
Guiuan Airport is an airport located in the municipality of Guiuan, in the province of Eastern Samar in the Philippines. It is classified as a feeder airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines, an attached agency of the Department of Transportation that is responsible for the operations all airports in the Philippines, except the major international airports.

USS Barnwell (APA/LPA-132) was a Haskell-class attack transport in service with the United States Navy from 1945 to 1947. She was sunk as a target in 1986.

Amphibious Construction Battalion TWO is an amphibious construction battalion in the United States Navy based in Little Creek, Virginia. Amphibious Construction Battalion ONE is its sister unit based in Coronado, California.

Manicani is a small island in the Leyte Gulf, Philippines. The local governing body is the municipality of Guiuan of Eastern Samar province. Its 3,000 residents live in four barangays: San Jose, Banaag, Hamorawon and Buenavista. Housing and construction is mostly simple timber or concrete huts without power or plumbing.

The Guiuan Protected Landscape and Seascape, also known as the Guiuan Marine Reserve, is a protected area associated with the Guiuan Island Group which is located off the coast of the municipality of Guiuan on the eastern side of Leyte Gulf in the Philippines. The protected area consists of the following islands from within the group: Calicoan, Manicani, Suluan, Tubabao, Victory, Homonhon and other smaller islands and their surrounding reefs. It also includes the coastal area of mainland Guiuan in Eastern Samar covering a total area of 60,448 hectares. The land which now comprises the conservation area was previously declared as a Marine Reserve and Tourist Zone and was placed under the administration and control of the Philippine Tourism Authority in 1978. It was re-proclaimed and re-classified as a protected landscape/seascape in 1994 under the National Integrated Protected Areas System Act of 1992.
Jinamoc Seaplane Base is a former World War II seaplane base on Jinamoc Island, San Pedro Bay, Leyte Gulf, Philippines. Jinamoc Seaplane Base was part of the Leyte-Samar Naval Base.

USS ABSD-5, later redesignated as AFDB-5, was a nine-section, non-self-propelled, large auxiliary floating drydock of the US Navy. Advance Base Sectional Dock-5 was constructed in sections during 1943 and 1944 by the Chicago Bridge & Iron Company in Morgan City, Louisiana for World War II. With all nine sections joined, she was 825 feet long, 28 feet tall, and with an inside clear width of 133 feet 7 inches. ABSD-5 had two traveling 15-ton capacity crane with an 85-foot radius and two or more support barges. The two side walls were folded down under tow to reduce wind resistance and lower the center of gravity. ABSD-5 had 6 capstans for pulling, each rated at 24,000 lbf (110,000 N) at 30 ft/min (0.15 m/s), 4 of the capstans were reversible. There were also 4 ballast compartments in each section.
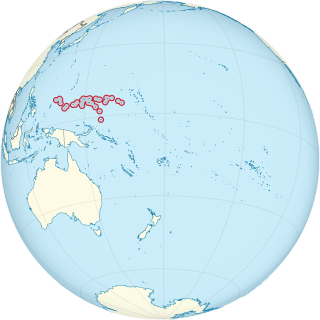
Naval Base Ulithi was major United States Navy base at the Ulithi Atoll in the Caroline Islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea during World War II. The base was built to support the island hoping Pacific war efforts of the allied nations fighting the Empire of Japan. In terms of the number of ships at one base, Naval Base Ulithi was the largest Naval Base in the world in 1944 and 1945, with over 617 ships at times.

US Naval Advance Bases were built globally by the United States Navy during World War II to support and project U.S. naval operations world-wide. A few were built on allied soil, but most were captured enemy facilities or completely new. Advance bases provided the fleet with support to keep ships tactically available with repair and supply depots of facilities, rather than return them to continental United States. Before Japan declared war on the United States the US Navy had a single fleet sized advanced base in the Territory of Hawaii. It was Naval Station Pearl Harbor. During the war the US Navy Seabees built over 400 advance bases categorized by size. Naval bases were either Lions or Cubs while airfields were either Oaks or Acorns. Lions and Oaks were major facilities while Cubs and Acorns were minor. PT Boats typically would get a Cub and airfields with single runways were Acorns. The larger bases could do refueling and overhaul; loading of troopship and cargo ships; and preparing amphibious assault ships. Some became major repair depots. The Seabees developed auxiliary floating drydocks were able to repair battle damage and do regular maintenance in the field saving ships trans-pacific trips for repair. A few bases also were developed to be R and R for all U.S. personnel. Most Advance Bases were built by the US Navy's Seabees in Naval Construction Battalions (CBs). At the start of the war some civilian contractor were employed in construction. The Seabees in World War II built most of the airfields used by the United States Army Air Forces and United States Marine Corps, as they had the ships and cranes needed to transport the vast amount of equipment needed at the advance bases. The US Army and United States Coast Guard also operated out of many of these facilities. Seabees could build new or repair damaged runways, and with advancements in heavy bomber technology lengthen runways as needed. A few Naval Advance Bases were built for the Korean War and Vietnam War.

Naval Base Trinidad, also called NAS Trinidad, NAS Port-of-Spain, was a large United States Navy Naval base built during World War II to support the many naval ships fighting and patrolling the Battle of the Atlantic. The fighting in the area became known as the Battle of the Caribbean. Naval Base Trinidad was located on the Island of Trinidad in West Indies of the Caribbean Sea.

Naval Base Okinawa, now Naval Facility Okinawa, was and is a number of bases built after the Battle of Okinawa by United States Navy on the Okinawa Island of Japan. The naval bases were built to support the landings on Okinawa on April 1, 1945, and the troops fighting on Okinawa. The Navy repaired and did expansion of the airfields on Okinawa. United States Navy Seabee built or repaired the facilities on the island. The bases on Okinawa put the United States Armed Forces only 350 miles from Japan's home islands. Most facilities closed after the war, but some are still in use today in all branches of the United States Armed Forces.

Manus Naval Base was a number of bases built after the World War II Battle of Manus by United States Navy on the Manus Island and a smaller island just east, Los Negros Island in the Admiralty Islands chain. The major naval base construction started with the Los Negros landings on February 28, 1944. The Navy repaired and did the expansion of the airfields on the Admiralty Islands. United States Navy Seabee built or repaired the facilities on the islands. The large Manus Naval Base, also called the Admiralty Island base, supported United States Seventh Fleet, Southwest Pacific command, and part of the Pacific Fleet. The base was abandoned by the US Navy after the war.

Naval Base Brisbane was a major United States Navy base built in the early part of World War II at Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. At first, operated as a base for patrol aircraft and convoy escort aircraft to protect the last leg of the Pacific War to the Southwest Pacific. As the US Navy expanded in the island hopping campaign, Naval Base Brisbane expanded to include a submarine base, repair depot, seaplane base and other facilities. US Navy operations started on April 14, 1942, and ended after the war in 1945.
Naval Base Sydney was a United States Navy base built during World War II at Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The base was built with Australian civilian contractors. As the US Navy expanded in the Island hopping campaign, Naval Base Sydney expanded to include a Naval Base Hospital, repair base and other facilities. US Navy operations started in 1943 and ended after the war in 1945.

Naval Base Puerto Princesa, Naval Base Palawan, was a United States Navy base built during World War II at Puerto Princesa on Palawan Island, Philippines, after the Invasion of Palawan on February 28, 1945. Puerto Princesa Bay offered an excellent base for fleet anchorage. At the naval base, US Navy Seabees built: a seaplane base, carrier aircraft fighter plane repair depot, land airfield and other base facilities.

US Naval Base Philippines was number of United States Navy bases in the Philippines Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Most were built by the US Navy Seabees, Naval Construction Battalions, during World War II. The US Naval Bases in Philippines were lost to the Empire of Japan in December 1941 during the Philippines campaign of 1941–1942. In February 1945 the United States Armed Forces retook the Philippines in the Battle of Manila in 1945. Before the captured US bases on Luzon were retaken the US Navy Seabees built a new large base, Leyte-Samar Naval Base, on the Philippine Island of Leyte, starting in October 1944.

Naval Base Hawaii was a number of United States Navy bases in Territory of Hawaii during World War II. At the start of the war, much of the Hawaiian Islands was converted from tourism to an United States Armed Forces base. With the loss of US Naval Base Philippines in Philippines campaign of 1941 and 1942, Hawaiian became the US Navy's main base for the early part of the island-hopping Pacific War against Empire of Japan. Naval Station Pearl Harbor was founded in 1899 with the annexation of Hawaii.
























