This is a list of members of both houses of the Federal Assembly from the Canton of Schwyz.
This is a list of members of both houses of the Federal Assembly from the Canton of Schwyz.
| Councillor (Party) | Election | Councillor (Party) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaspar L. Krieg Conservative 1848–1849 | Appointed | Karl von Schorno Conservative 1848–1852 | ||
| Franz Anton Oetiker Conservative 1849–1850 | ||||
| Kaspar L. Krieg Conservative 1850–1852 | ||||
| Jos. Meinrad Benedikt Düggelin Conservative 1853–1858 | Nazar von Reding Party unknown 1853–1854 | |||
| F. Xaver J. K. Auf der Mauer Conservative 1854–1861 | ||||
| Johann Anton Steinegger Conservative 1858–1867 | ||||
| Joseph M. von Hettlingen Conservative 1862–1873 | ||||
| Johann Michael Stählin Conservative 1867–1872 | ||||
| Marianus Theiler Conservative 1872–1885 | ||||
| Karl Reichlin Conservative 1873–1874 | ||||
| Joseph M. von Hettlingen Conservative 1874–1887 | ||||
| Karl Kümin Conservative 1885–1905 | ||||
| Karl Reichlin Conservative 1887–1905 | ||||
| Nikolaus Benziger Conservative 1905–1908 | Rudolf von Reding Conservative 1905–1911 | |||
| Martin Ochsner Conservative 1908–1939 | ||||
| Josef-Maria Schuler Free Democratic Party 1911–1915 | ||||
| Joseph Räber Conservative 1915–1928 | ||||
| 1919 | ||||
| 1922 | ||||
| 1925 | ||||
| 1928 | Adolf Suter Conservative 1928–1947 | |||
| 1931 | ||||
| 1935 | ||||
| Fritz Stähli Conservative 1939–1959 | 1939 | |||
| 1943 | ||||
| 1947 | Anton Gwerder Conservative 1947–1949 | |||
| 1950 | Dominik Auf der Maur Conservative 1950–1967 | |||
| 1951 | ||||
| 1955 | ||||
| Heinrich Oechslin Christian Social Conservative Party 1959–1975 | 1959 | |||
| 1963 | ||||
| 1967 | Josef Ulrich Christian Social Conservative Party 1967–1983 | |||
| 1971 | ||||
| Alois Dobler Christian Democratic People's Party 1975–1991 | 1975 | |||
| 1979 | ||||
| 1983 | Xaver Reichmuth Christian Democratic People's Party 1983–1991 | |||
| 1987 | ||||
| Hans Bisig Free Democratic Party 1991–1999 | 1991 |  Bruno Frick Christian Democratic People's Party 1991–2011 | ||
| 1995 | ||||
| Toni Dettling Free Democratic Party 1999–2003 | 1999 | |||
 Alex Kuprecht Swiss People's Party 2003–2023 | 2003 | |||
| 2007 | ||||
| 2011 |  Peter Föhn Swiss People's Party 2011–2019 | |||
| 2015 | ||||
| 2019 |  Othmar Reichmuth Christian Democratic People's Party 2019-2023 | |||
 Pirmin Schwander Swiss People's Party 2023–present | 2023 |  Petra Gössi FDP.The Liberals 2023-present |
| Election | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1848 | Fr. Karl Schuler (Conservative) | Johann Anton Steinegger (Conservative) | 2 seats 1848–1881 | |||||
| 1851 | ||||||||
| 1852 | Karl Styger (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1854 | Meinrad Jb. Hegner (Liberal) | |||||||
| 1857 | Jos. Anton G. Büeler (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1860 | ||||||||
| 1863 | Josef Karl Benziger (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1866 | Josef Anton Eberle (Liberal) | |||||||
| 1869 | ||||||||
| 1872 | Fridolin Holdener (Conservative) | Johann Michael Stählin (Conservative) | ||||||
| 1874 | Ambros Eberle (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1875 | ||||||||
| 1878 | ||||||||
| 1881 | Vital sen. Schwander (Conservative) | 3 seats 1881–2003 | ||||||
| 1883 | Nikolaus Benziger (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1884 | ||||||||
| 1887 | ||||||||
| 1890 | ||||||||
| 1893 | ||||||||
| 1896 | Jos. Ferd. Anton Büeler (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1899 | ||||||||
| 1902 | ||||||||
| 1905 | L. Kaspar Knobel (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1908 | Anton von Hettlingen (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1910 | Martin Steinegger (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1911 | ||||||||
| 1914 | ||||||||
| 1917 | ||||||||
| 1919 | Vital jun. Schwander (Conservative) | Josef Bürgi-Gretener (PAB) | Hans Steiner (Conservative) | |||||
| 1922 | ||||||||
| 1925 | Karl von Weber (Conservative) | Johann Wattenhofer (SP/PS) | ||||||
| 1928 | Alois Ab Yberg (FDP/PRD) | Fritz Stähli (Conservative) | ||||||
| 1931 | ||||||||
| 1935 | Erhard Ruoss (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1939 | Clemenz Ulrich (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1943 | Kaspar Knobel (Conservative) | Josef Schuler (BV (SZ)*) | ||||||
| 1947 | Josef Heinzer (SP/PS) | |||||||
| 1951 | Hans Fuchs (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1953 | Josef Ulrich (Conservative) | |||||||
| 1955 | Armin Bruhin (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1959 | Karl Bachmann (CCS) | Josef Diethelm (SP/PS) | ||||||
| 1963 | ||||||||
| 1967 | Joachim Weber (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1971 | Elisabeth Blunschy-Steiner (CVP/PDC) | |||||||
| 1975 | Josef Risi (CVP/PDC) | |||||||
| 1979 | Karl Weber (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1983 | ||||||||
| 1987 | Jakob Bürgi (CVP/PDC) | Arthur Züger (SP/PS) | ||||||
| 1991 | Toni Dettling (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 1995 | Toni Eberhard (CVP/PDC) | Peter Föhn (SVP/UDC) | ||||||
| 1999 | Maya Lalive d'Épinay (FDP/PRD) | |||||||
| 2003 | Reto Wehrli (CVP/PDC) | Josy Gyr-Steiner (SP/PS) | Pirmin Schwander (SVP/UDC) | |||||
| 2007 | Andy Tschümperlin (SP/PS) | |||||||
| 2011 | Alois Gmür (CVP/PDC) | Petra Gössi (FDP/PLR) | ||||||
| 2015 | Marcel Dettling (SVP/UDC) | |||||||
| 2019 | ||||||||
| 2023 | Dominik Blunshy (The Centre) | Roman Bürgi (SVP/UDC) | ||||||

The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. The Union has a total area of 4,233,255 km2 (1,634,469 sq mi) and an estimated total population of over 448 million. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation.

The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber. The organization's strategic concepts include deterrence.

The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

The Union of European Football Associations is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs football, futsal and beach football in Europe and the transcontinental countries of Turkey, Azerbaijan, Georgia and Kazakhstan, as well as the West Asian countries of Cyprus, Armenia and Israel. UEFA consists of 55 national association members. Since 2022, due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, FIFA and UEFA suspended all Russian national teams and clubs from any FIFA and UEFA competitions.

Jehovah's Witnesses is a nontrinitarian, millenarian, restorationist Christian denomination. As of 2023, the group reported approximately 8.6 million members involved in evangelism, with around 20.5 million attending the annual Memorial of Christ's death. Jehovah's Witnesses believe that the destruction of the present world system at Armageddon is imminent, and the establishment of God's kingdom over earth is the only solution to all of humanity's problems.

The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organizations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order.

The Rajya Sabha, constitutionally the Council of States, is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. As of 2023, it has a maximum membership of 250, of which 238 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through open ballots, while the president can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social service. The total allowed capacity is 250 according to article 80 of the Indian Constitution. The current potential seating capacity of the Rajya Sabha is 245, after the Jammu and Kashmir (Reorganisation) Act, 2019, the seats came down to 245. The maximum seats of 250 members can be filled up at the discretion and requirements of the house of Rajya Sabha.

The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Parliament House, New Delhi.

The Parliament of India is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The President of India, in their role as head of the legislature, has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve the Lok Sabha, but they can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Prime Minister and their Union Council of Ministers.

A Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of an electoral district (constituency) to the legislature of State government in the Indian system of government. From each constituency, the people elect one representative who then becomes a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA). Each state has between seven and nine MLAs for every Member of Parliament (MP) that it has in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India's bicameral parliament. There are also members in three unicameral legislatures in Union Territories: the Delhi Legislative Assembly, Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly and the Puducherry Legislative Assembly. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can work as a minister for more than 6 months. If a non-Member of the Legislative Assembly becomes a Chief Minister or a minister, he must become an MLA within 6 months to continue in the job. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can become the Speaker of the Legislature
An independent, non-partisan politician or non-affiliated politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party or bureaucratic association. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent.

The Schengen Area is an area encompassing 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

NATO is an international military alliance consisting of 32 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary. Article 6 of the treaty limits the scope of Article 5 to the islands north of the Tropic of Cancer, the North American and European mainlands, the entirety of Turkey, and French Algeria, the last of which has been moot since July 1962. Thus, an attack on Hawaii, Puerto Rico, French Guiana, the Falkland Islands, Ceuta or Melilla, among other places, would not trigger an Article 5 response.

The United States House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together, they comprise the national bicameral legislature of the United States. The House is charged with the passage of federal legislation, known as bills; those that are also passed by the Senate are sent to the president for signature or veto. The House's exclusive powers include initiating all revenue bills, impeaching federal officers, and electing the president if no candidate receives a majority of votes in the Electoral College.

The Commonwealth of Nations, often simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire from which it developed. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations among member states. Numerous organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth.

The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Crystal City, Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educational programs to public television stations in the United States, distributing shows such as Frontline, Nova, PBS NewsHour, Masterpiece, Sesame Street, and This Old House.
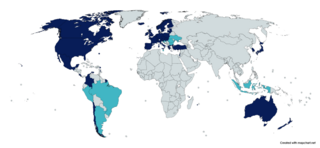
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members.