This is a list of members of both houses of the Federal Assembly from the Canton of Thurgau.
This is a list of members of both houses of the Federal Assembly from the Canton of Thurgau.
| Councillor (Party) | Election | Councillor (Party) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johann Karl Kappeler Party unknown 1848–1881 | Appointed | Johann Baptist von Streng Liberal Party 1848–1850 | ||
| Johann Keller Liberal Party 1850–1851 | ||||
| Jakob Albrecht Liberal Party 1851–1851 | ||||
| K. Eduard Häberlin Liberal Party 1851–1855 | ||||
| Johann Conrad Kern Liberal Party 1855–1857 | ||||
| K. Eduard Häberlin Liberal Party 1857–1860 | ||||
| K. Eduard Häberlin Liberal Party 1860–1869 | ||||
| Paul Nagel Liberal Party 1869–1880 | ||||
| Johannes Altwegg Free Democratic Party 1880–1888 | ||||
| Jak. Albert Scherb Swiss Democrats 1881–1908 | ||||
| Johann Ulrich Baumann Swiss Democrats 1889–1890 | ||||
| Joh. Georg Leumann Free Democratic Party 1890–1918 | ||||
| G. Adolf Deucher Swiss Democrats 1908–1910 | ||||
| Albert Böhi Free Democratic Party 1910–1935 | ||||
| A. Otto Aepli Free Democratic Party 1919–1921 | ||||
| Rudolf Huber Free Democratic Party 1921–1928 | ||||
| 1922 | ||||
| 1925 | ||||
| 1928 | Anton Schmid Paysans, Artisans et Bourgeois 1928–1935 | |||
| 1931 | ||||
| Paul Altwegg Free Democratic Party 1935–1951 | 1935 | Eduard Pfister Paysans, Artisans et Bourgeois 1935–1939 | ||
| 1939 | Erich Ullmann Paysans, Artisans et Bourgeois 1939–1963 | |||
| 1943 | ||||
| 1947 | ||||
| Jakob Müller Free Democratic Party 1951–1967 | 1951 | |||
| 1955 | ||||
| 1959 | ||||
| 1963 | Heinrich Herzog Paysans, Artisans et Bourgeois 1963–1979 | |||
| Hans Munz Free Democratic Party 1967–1983 | 1967 | |||
| 1971 | ||||
| 1975 | ||||
| 1979 | Franco Matossi Swiss People's Party 1979–1987 | |||
| Heinz Moll Free Democratic Party 1983–1987 | 1983 | |||
| Thomas Onken Social Democratic Party 1987–1999 | 1987 | Hans Uhlmann Swiss People's Party 1987–1999 | ||
| 1991 | ||||
| 1995 | ||||
 Philipp Stähelin Christian Democratic People's Party 1999–2011 | 1999 |  Hermann Bürgi Swiss People's Party 1999–2011 | ||
| 2003 | ||||
| 2007 | ||||
 Brigitte Häberli-Koller Christian Democratic People's Party 2011–2023 The Centre 2023–present | 2011 |  Roland Eberle Swiss People's Party 2011–2019 | ||
| 2015 | ||||
| 2019 |  Jakob Stark Swiss People's Party 2019–present | |||
| 2023 |
| Election | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | Councillor (Party) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1848 | Johann Conrad Kern (Liberal) | Johann Georg Kreis (Liberal) | Philipp Gottlieb Labhardt (Liberal) | Johann Georg Rauch (Liberal) | 4 seats 1848–1863 | |||||||||
| 1851 | K. Eduard Häberlin (Liberal) | Johann Ludwig Sulzberger (Liberal) | ||||||||||||
| 1854 | Johann Baptist von Streng (Liberal) | |||||||||||||
| 1857 | Johann Messmer (Liberal) | |||||||||||||
| 1860 | ||||||||||||||
| 1863 | Jos. Fridolin Anderwert (SD/DS) | Johann Joachim Lüthi (Liberal) | Augustin Ramsperger (Conservative) | 5 seats 1863–1902 | ||||||||||
| 1865 | Philipp Gottlieb Labhardt (Liberal) | |||||||||||||
| 1866 | ||||||||||||||
| 1869 | Adolf K. W. Deucher (SD/DS) | Johann Jakob Häberlin (Liberal) | Jak. Albert Scherb (SD/DS) | |||||||||||
| 1872 | Severin Stoffel (SD/DS) | |||||||||||||
| 1873 | Fr. Heinrich Häberlin (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1875 | Gustave Merkle (Liberal) | |||||||||||||
| 1878 | ||||||||||||||
| 1879 | Adolf K. W. Deucher (SD/DS) | |||||||||||||
| 1880 | Joh. Philipp Heitz (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1881 | Jakob H. Bachmann (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1883 | Johann Jakob Schümperlin (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1884 | ||||||||||||||
| 1887 | ||||||||||||||
| 1889 | Karl Alfred Fehr (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1890 | Josef Anton Koch (Grut*) | |||||||||||||
| 1893 | ||||||||||||||
| 1896 | Adolf Germann (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1897 | Joh. Konrad Egloff (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1898 | Emil Hofmann (SD/DS) | |||||||||||||
| 1899 | Carl Eigenmann (PAB) | |||||||||||||
| 1902 | Jakob Müller (FDP/PRD) | 6 seats 1902–1911 | ||||||||||||
| 1904 | Heinrich Häberlin (FDP/PRD) | Alfons von Streng (Conservative) | ||||||||||||
| 1905 | ||||||||||||||
| 1908 | ||||||||||||||
| 1911 | Oskar Ullmann (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1914 | Jakob Zingg (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1917 | ||||||||||||||
| 1919 | Otto Höppli (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1920 | A. Eduard Fehr (FDP/PRD) | Jakob Meili (PAB) | ||||||||||||
| 1922 | Eduard Pfister (PAB) | |||||||||||||
| 1925 | ||||||||||||||
| 1927 | Johann Lymann (SD/DS) | |||||||||||||
| 1928 | August Roth (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1931 | Jakob Zingg (PAB) | 6 seats 1931-present | ||||||||||||
| 1935 | Carl Eder (Conservative) | August Roth (SP/PS) | Otto Wartmann (PAB) | Alfred Müller (FDP/PRD) | ||||||||||
| 1939 | ||||||||||||||
| 1941 | Gottlieb Meier (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1942 | Otto (senior) Hess (PAB) | |||||||||||||
| 1943 | Rudolf Schümperli (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1947 | August Roth (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1951 | Albert Bauer (SP/PS) | Walter Tuchschmid (FDP/PRD) | ||||||||||||
| 1954 | Ernst Rodel (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1955 | ||||||||||||||
| 1959 | Hermann Graf (FDP/PRD) | Albert Schläpfer (FDP/PRD) | ||||||||||||
| 1963 | Hanspeter Fischer (BP*) | Alfred Abegg (SP/PS) | Josef Harder (CCS) | |||||||||||
| 1964 | Otto Keller (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||||
| 1967 | Walter Ballmoos (PAB) | |||||||||||||
| 1968 | Alois Bommer (CCS) | |||||||||||||
| 1970 | Rolf Weber (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 1971 | Paul Tanner (SVP/UDC) | Wilfried Naegeli (N) | ||||||||||||
| 1975 | Franco Matossi (SVP/UDC) | Hermann Wellauer (CVP/PDC) | ||||||||||||
| 1979 | Paul Rutishauser (SVP/UDC) | Hans Frei (CVP/PDC) | Willy Messmer (FDP/PRD) | |||||||||||
| 1983 | Ernst Mühlemann (FDP/PRD) | Hans Uhlmann (SVP/UDC) | ||||||||||||
| 1986 | Margrit Camenzind (CVP/PDC) | |||||||||||||
| 1987 | Peter Schmid (GPS/PES) | Menga Danuser (SP/PS) | Otto Hess (SVP/UDC) | |||||||||||
| 1991 | Hansueli Raggenbass (CVP/PDC) | |||||||||||||
| 1995 | J. Alexander Baumann (SVP/UDC) | Wilfried Ernest Gusset (0) | Jost Gross (SP/PS) | |||||||||||
| 1999 | Werner Messmer (FDP/PRD / FDP.The Liberals) | Peter Spuhler (SVP/UDC) | Hansjörg Walter (SVP/UDC) | |||||||||||
| 2003 | Brigitte Häberli-Koller (CVP/PDC) | |||||||||||||
| 2005 | Edith Graf-Litscher (SP/PS) | |||||||||||||
| 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||
| 2011 | Thomas Böhni (GLP/PVL) | Markus Hausammann (SVP/UDC) | Christian Lohr (CVP/PDC/ The Centre) | |||||||||||
| 2013 | Verena Herzog (SVP/UDC) | |||||||||||||
| 2015 | Hermann Hess (FDP/PLR) | |||||||||||||
| 2017 | Hansjörg Brunner (FDP/PLR) | Diana Gutjahr (SVP/UDC) | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | Kurt Egger (GP/PV) | Manuel Strupler (SVP/UDC) | ||||||||||||
| 2023 | Kristiane Vietze (FDP.The Liberals) | Pascal Schmid (SVP/UDC) | Nina Schläfli (SP/PS) | |||||||||||

The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. The Union has a total area of 4,233,255 km2 (1,634,469 sq mi) and an estimated total population of over 448 million. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation.

The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved.

The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 190 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of last resort to national governments, and a leading supporter of exchange-rate stability. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world." Established in July 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference, primarily according to the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it started with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary system after World War II. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises. Through a quota system, countries contribute funds to a pool from which countries can borrow if they experience balance of payments problems. As of 2016, the fund had SDR 477 billion.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber. The organization's strategic concepts include deterrence.

The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

Jehovah's Witnesses is a nontrinitarian, millenarian, restorationist Christian denomination. As of 2023, the group reported approximately 8.6 million members involved in evangelism, with around 20.5 million attending the annual Memorial of Christ's death. Jehovah's Witnesses believe that the destruction of the present world system at Armageddon is imminent, and the establishment of God's kingdom over earth is the only solution to all of humanity's problems.

The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organizations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order.

The Rajya Sabha, constitutionally the Council of States, is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. As of 2023, it has a maximum membership of 250, of which 238 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through open ballots, while the president can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social service. The total allowed capacity is 250 according to article 80 of the Indian Constitution. The current potential seating capacity of the Rajya Sabha is 245, after the Jammu and Kashmir (Reorganisation) Act, 2019, the seats came down to 245. The maximum seats of 250 members can be filled up at the discretion and requirements of the house of Rajya Sabha.

The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Parliament House, New Delhi.

The Parliament of India is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The President of India, in their role as head of the legislature, has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve the Lok Sabha, but they can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Prime Minister and their Union Council of Ministers.

A Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of an electoral district (constituency) to the legislature of State government in the Indian system of government. From each constituency, the people elect one representative who then becomes a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA). Each state has between seven and nine MLAs for every Member of Parliament (MP) that it has in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India's bicameral parliament. There are also members in three unicameral legislatures in Union Territories: the Delhi Legislative Assembly, Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly and the Puducherry Legislative Assembly. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can work as a minister for more than 6 months. If a non-Member of the Legislative Assembly becomes a Chief Minister or a minister, he must become an MLA within 6 months to continue in the job. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can become the Speaker of the Legislature
An independent, non-partisan politician or non-affiliated politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party or bureaucratic association. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent.

The Schengen Area is an area encompassing 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

NATO is an international military alliance consisting of 32 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary. Article 6 of the treaty limits the scope of Article 5 to the islands north of the Tropic of Cancer, the North American and European mainlands, the entirety of Turkey, and French Algeria, the last of which has been moot since July 1962. Thus, an attack on Hawaii, Puerto Rico, French Guiana, the Falkland Islands, Ceuta or Melilla, among other places, would not trigger an Article 5 response.

The United States House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together, they comprise the national bicameral legislature of the United States. The House is charged with the passage of federal legislation, known as bills; those that are also passed by the Senate are sent to the president for signature or veto. The House's exclusive powers include initiating all revenue bills, impeaching federal officers, and electing the president if no candidate receives a majority of votes in the Electoral College.

The Commonwealth of Nations, often simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire from which it developed. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations among member states. Numerous organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth.

The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Crystal City, Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educational programs to public television stations in the United States, distributing shows such as Frontline, Nova, PBS NewsHour, Masterpiece, Sesame Street, and This Old House.
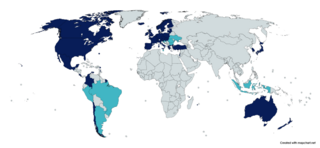
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members.