
The government of Switzerland is a federal state with direct democracy.

The federal chancellor is the head of the Federal Chancellery of Switzerland, the oldest Swiss federal institution, established at the initiative of Napoleon in 1803. The officeholder acts as the general staff of the seven-member Federal Council. The Chancellor is not a member of the government and the office is not at all comparable to that of the Chancellor of Germany or the Chancellor of Austria, or to the United Kingdom's Chancellor of the Exchequer.

The Federal Council is the federal cabinet of the Swiss Confederation. Its seven members also serve as the collective head of state and government of Switzerland. Since after World War II, the Federal Council is by convention a permanent grand coalition government composed of representatives of the country's major parties and language regions.

The National Council is the lower house of the Federal Assembly, with the upper house being the Council of States. Containing 200 seats, the National Council is the larger of the two houses.

The Council of States is the upper house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, and the lower house being the National Council. It comprises 46 members.

The Swiss People's Party, also known as the Democratic Union of the Centre, is a national-conservative and right-wing populist political party in Switzerland. Chaired by Marcel Dettling, it is the largest party in the Federal Assembly, with 62 members of the National Council and 6 of the Council of States.

The Christian Democratic People's Party of Switzerland, also called the Christian Democratic Party, Democratic People's Party and Swiss Christian Democratic Party, was a Christian democratic political party in Switzerland. On 1 January 2021, it merged with the Conservative Democratic Party of Switzerland (BDP/PBD) to form The Centre, which now operates at the federal level. The Christian Democratic People's Party will continue to exist at the cantonal level as individual local and regional parties determine their status. Its 28 seats in the National Council and 13 seats in the Council of States were transferred to the new party, as was its sole seat on the Federal Council, held by Viola Amherd.
Switzerland elects on national level a collective head of state, the Federal Council, and a legislature, the Federal Assembly.

The Federal Assembly is the federal bicameral parliament of Switzerland. It comprises the 200-seat National Council and the 46-seat Council of States. It meets in Bern in the Federal Palace.

Elections to the Swiss Federal Assembly, the federal parliament of Switzerland, were held on Sunday, 21 October 2007. In a few cantons, a second round of the elections to the Council of States was held on 11 November, 18 November, and 25 November 2007. For the 48th legislative term of the federal parliament (2007–2011), voters in 26 cantons elected all 200 members of the National Council as well as 43 out of 46 members of the Council of States. The other three members of the Council of States for that term of service were elected at an earlier date.

The tables below show information and statistics about the members of the Swiss Federal Council, or Federal Councilors.

The Conservative Democratic Party of Switzerland was a conservative political party in Switzerland from 2008 to 2020. After the 2019 federal election, the BDP had three members in the National Council.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 18 October 2015 for the National Council and the first round of elections to the Council of States, with runoff elections to the Council of States being held in various cantons until 22 November.
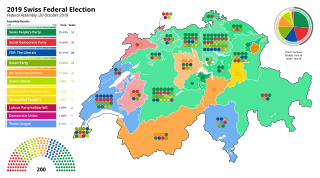
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 20 October 2019 to elect all members of both houses of the Federal Assembly. This was followed by the 2019 election to the Swiss Federal Council, the federal executive, by the United Federal Assembly.

The Centre is a centre to centre-right political party in Switzerland. It was formed through the merger of the Christian Democratic People's Party of Switzerland (CVP/PDC) and the Conservative Democratic Party of Switzerland (BDP/PBD). Following the formal merger of the parties on 1 January 2021, it has 29 of 200 seats in the National Council and 15 of 46 seats in the Council of States. Viola Amherd is the party's representative on the Federal Council and served as the President of the Swiss Confederation in 2024.

















