Related Research Articles

Svalbard, also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen.

Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean roughly centered on 78° north latitude and 20° east longitude. The archipelago is the northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway. The three main islands in the group consist of Spitsbergen, Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. There are also a number of smaller islands, such as Barents Island (Barentsøya), Kvitøya, Prins Karls Forland, Kongsøya, Bear Island, Svenskøya, Wilhelm Island and other smaller islands or skerries.
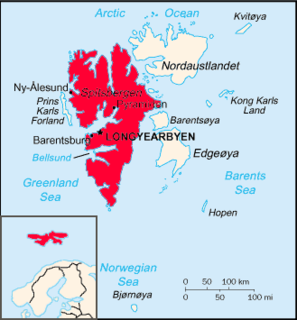
Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway.

Bear Island is the southernmost island of the Norwegian Svalbard archipelago. The island is located in the western part of the Barents Sea, approximately halfway between Spitsbergen and the North Cape.

Svalbard and Jan Mayen is a statistical designation defined by ISO 3166-1 for a collective grouping of two remote jurisdictions of Norway: Svalbard and Jan Mayen. While the two are combined for the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) category, they are not administratively related. This has further resulted in the country code top-level domain .sj being issued for Svalbard and Jan Mayen, and ISO 3166-2:SJ. The United Nations Statistics Division also uses this code, but has named it the Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands.

Longyearbyen is the world's northernmost settlement and largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank of the Longyear Valley and on the shore of Adventfjorden, the short estuary leading into Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the island's broadest inlet. As of 2002 Longyearbyen Community Council became an official Norwegian municipality. It is the seat of the Governor of Svalbard. The town's mayor is Arild Olsen.
The polar archipelago of Svalbard was first discovered by Willem Barentsz in 1596, although there is disputed evidence of use by Pomors or Norsemen. Whaling for bowhead whales started in 1611, dominated by English and Dutch companies, though other countries participated. At that time there was no agreement about sovereignty. Whaling stations, the largest being Smeerenburg, were built during the 17th century, but gradually whaling decreased. Hunting was carried out from the 17th century by Pomors, but from the 19th century it became more dominated by Norwegians.

The Svalbard Treaty recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty regulates the demilitarisation of the archipelago. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities on the islands. As of 2012, Norway and Russia make use of this right.

The Norwegian Polar Institute is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica.

Hopen is an island in the southeastern part of the Svalbard archipelago (Norway). Hopen was discovered in 1596 by Jan Cornelisz Rijp during the third expedition by Willem Barentsz, trying to find the Northeast Passage. Later, in 1613, its name was given by Thomas Marmaduke of Hull, who named it after his former command, the Hopewell.
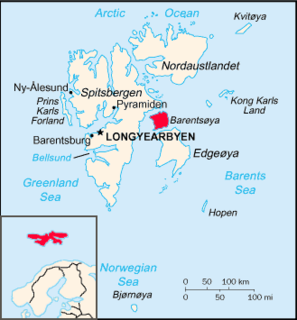
Barentsøya, sometimes anglicized as Barents Island, is an island in the Svalbard archipelago of Norway, lying between Edgeøya and Spitsbergen. Barents Island has no permanent human inhabitants. Named for the Dutch explorer Willem Barents, it is a part of Søraust-Svalbard Nature Reserve.

Svalbard lies under the sovereignty of Norway, but the Svalbard Treaty places several restrictions. Norway cannot use the archipelago for warlike purposes, cannot discriminate economic activity based on nationality and is required to conserve the natural environment. Uniquely, Svalbard is an entirely visa-free zone. Everybody may live and work in Svalbard indefinitely regardless of country of citizenship. Svalbard Treaty grants treaty nationals equal right of abode as Norwegian nationals. Non-treaty nationals may live and work indefinitely visa-free as well. "Regulations concerning rejection and expulsion from Svalbard" is in force on non-discriminatory basis.

Kvitøya is an island in the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean, with an area of 682 square kilometres (263 sq mi). It is the easternmost part of the Kingdom of Norway. The closest Russian Arctic possession, Victoria Island, lies only 62 kilometres (39 mi) to the east of Kvitøya.

Orion's Belt is a 1985 Norwegian dual-language, political action thriller film, directed by Ola Solum and Tristan de Vere Cole. It is based on Jon Michelet's 1977 novel by the same name. The film follows three Svalbard-based shabby seamen, played by Helge Jordal, Sverre Anker Ousdal and Hans Ola Sørlie, who discover a Soviet bearing station. They are subsequently targets of Soviet liquidation and American interrogation in an attempt to quiet them and retain the political status quo. The Cold War topics were a critique of the Norwegian policy of allowing a Soviet presence on Svalbard.

Svenskøya is an island in Svalbard. It is the second largest island of Kong Karls Land with an area of 137 km².

Sjuøyane is the northernmost part of the Svalbard archipelago north of mainland Norway, and some 20 km north of the eastern major island Nordaustlandet. The islands are the northernmost landmass reachable by normal means, being 1024.3 kilometers south of the North Pole. In comparison, Robert Falcon Scott started his ill-fated Terra Nova Expedition 1374 km from the South Pole. Many of the islands are named after English explorers, most notably Captain Nelson.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Svalbard:

Indre Wijdefjorden National Park is located in a steep fjord landscape in northern Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It covers the inner part of Wijdefjorden—the longest fjord on Svalbard. The national park was established on 9 September 2005 and covers 1,127 km2 (435 sq mi), of which 745 km2 (288 sq mi) is on land and 382 km2 (147 sq mi) is sea. The marine environment changes vastly from the mouth of the fjord, through a still, cold, water basin, becoming deeper before reaching the glacier Mittag-Lefflerbreen at the inner-most sections of the fjord.

Cannabis in Svalbard is illegal. Practically functioning as ungoverned terra nullius prior to the Svalbard Treaty of 1920, the Arctic Ocean archipelago dominated by glaciers and barren rock, is part of Norway, and hence Norwegian law applies. Under it, there is a sliding scale approach to cannabis legislation. Possession for personal use, defined as up to 15 grams, is punished with a fine of between roughly 1,500 and 15,000 Norwegian kroner. Possession of amounts larger than that is punished by jail, ranging from 6 months all the way up to 21 years. These laws are enforced by the Norwegian Police Service, the small Svalbard district of which is run by the Governor of Svalbard.
Uniquely, the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard, located in the High Arctic, is an entirely visa-free zone. However, travelers who have a visa requirement to enter mainland Norway/the Schengen area must have a Schengen visa if they travel via mainland Norway/the Schengen area. This must be a double-entry visa so they can return to mainland Norway/the Schengen area.
References
- ↑ Higgins, Andrew (9 July 2014). "A Harsh Climate Calls for Banishment of the Needy". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331.