This list of places in Scotland is a complete collection of lists of places in Scotland.

Local government in Scotland comprises thirty-two local authorities, commonly referred to as councils. Each council provides public services, including education, social care, waste management, libraries and planning. Councils receive the majority of their funding from the Scottish Government, but operate independently and are accountable to their local electorates. Councils raise additional income via the Council Tax, a locally variable domestic property tax, and Business rates, a non-domestic property tax.

Lieutenancy areas, officially counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, are the separate areas of the United Kingdom appointed to a lord-lieutenant – a representative of the British monarch. In many cases they have similar demarcation and naming to, but are not necessarily coterminate with, the counties of the United Kingdom.
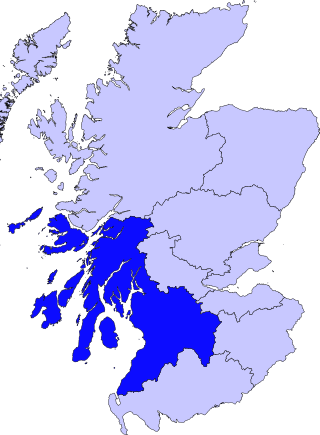
Strathclyde was one of nine former local government regions of Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and abolished in 1996 by the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994. The Strathclyde region had 19 districts. The region was named after the early medieval Kingdom of Strathclyde centred on Govan, but covered a broader geographic area than its namesake.

The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that created the current local government structure of 32 unitary authorities covering the whole of Scotland.
Chapman codes are a set of 3-letter codes used in genealogy to identify the administrative divisions in the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.

The Central Belt of Scotland is the area of highest population density within Scotland. Depending on the definition used, it has a population of between 2.4 and 4.2 million, including multiple Scottish cities such as Greater Glasgow, Ayrshire, Falkirk, Edinburgh and Lothian.
A local enterprise company (LEC) was a public-sector organisation in Scotland with responsibility for local economic development activities. The LECs formed part of the two enterprise networks, Scottish Enterprise and Highlands and Islands Enterprise. The 22 LECs were abolished in September 2007 and replaced with enterprise regions (ERs).
Community Health Partnerships, known as CHPs were subdivisions of Health Boards in Scotland, from 2005 to 2015, after which their functions were fully taken over by Health and Social Care Partnerships in April 2015.

The Fortified House in Scotland is a five-volume book by the Scottish author Nigel Tranter.
Scouting in Scotland is largely represented by Scouts Scotland, a registered Scottish Charity No. SC017511 that is affiliated to the Scout Association of the United Kingdom. The Baden-Powell Scouts' Association also has a presence in Scotland.

The 2012 Scottish local elections were held on 3 May 2012 in all 32 local authorities. The Scottish National Party (SNP) overtook Labour to win the highest share of the vote, and retained and strengthened its position as the party with most councillors. Labour also made gains, while the Liberal Democrats experienced meltdown, losing over half their seats and falling behind the Conservatives. For the first time since the introduction of the Single Transferable Vote system, the SNP won majority control of 2 councils, from no overall control. Labour also won majority control of 2 councils from no overall control, while retaining majority control over 2 councils.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the United Kingdom.
This is a list of listed buildings in Scotland. The list is split out by council area.
Health and Social Care Partnerships, (HSCPs) are organisations formed to integrate services provided by Health Boards and Councils in Scotland. Each partnership is jointly run by the NHS and local authority. There are 31 HSCPs across Scotland. These are statutory bodies, which took over responsibilities from Community Health Partnerships. They are responsible for £8.5 billion of funding for local services.

Bowls Scotland is the governing body for the sport of bowls in Scotland. A subsidiary of World Bowls, it is responsible for the leadership, development and management of lawn bowls in Scotland. It is headquartered in Ayr.