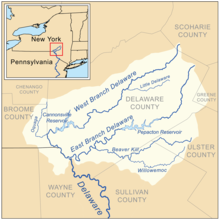
The West Branch Delaware River is one of two branches that form the Delaware River. It is approximately 90 mi (144 km) long, and flows through the U.S. states of New York and Pennsylvania. It winds through a mountainous area of New York in the western Catskill Mountains for most of its course, before joining the East Branch along the northeast border of Pennsylvania with New York. Midway or so it is empounded by the Cannonsville Dam to form the Cannonsville Reservoir, both part of the New York City water supply system for delivering drinking water to the City.

Schoharie Creek is a river in New York that flows north 93 miles (150 km) from the foot of Indian Head Mountain in the Catskills through the Schoharie Valley to the Mohawk River. It is twice impounded north of Prattsville to create New York City's Schoharie Reservoir and the Blenheim-Gilboa Power Project.

The Sacandaga River is a 64-mile-long (103 km) river in the northern part of New York in the United States. Its name comes from the Native American Sa-chen-da'-ga, meaning "overflowed lands".

The Cranberry River is a tributary of the Gauley River located in southeastern West Virginia in the United States. It is a part of the Mississippi River watershed, by way of the Gauley, Kanawha, and Ohio Rivers, draining an area of 74 square miles (192 km2).

The West Canada Creek is a 76-mile-long (122 km) river in upstate New York, United States. West Canada Creek is an important water way in Hamilton, Oneida, and Herkimer counties, draining the south part of the Adirondack Mountains before emptying into the Mohawk River near the Village of Herkimer. The name "Canada" is derived from an Iroquoian word for "village" (Kanata).

Esopus Creek is a 65.4-mile-long (105.3 km) tributary of the Hudson River that drains the east-central Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. From its source at Winnisook Lake on the slopes of Slide Mountain, the Catskills' highest peak, it flows across Ulster County to the Hudson at Saugerties. Many tributaries extend its watershed into neighboring Greene County and a small portion of Delaware County. Midway along its length, it is impounded at Olive Bridge to create Ashokan Reservoir, the first of several built in the Catskills as part of New York City's water supply system. Its own flow is supplemented 13 miles (21 km) above the reservoir by the Shandaken Tunnel, which carries water from the city's Schoharie Reservoir into the creek.

Fishing Creek is a 29.98-mile (48.25 km) long tributary of the Susquehanna River in Columbia County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It joins the Susquehanna River near the census-designated place of Rupert and the town of Bloomsburg. The watershed has an area of 385 square miles (1,000 km2).

Raccoon Creek is a 114-mile-long (183 km) stream that drains parts of five Ohio counties in the United States. It originates in Hocking County, Ohio. It flows through Vinton County and Gallia County and a corner of Meigs County. Its largest tributary, Little Raccoon Creek, arises in Jackson County. The watershed also includes part of Athens County, drained by another tributary, Hewett Fork. The other major tributaries are Elk Fork, located entirely in Vinton County, and Brushy Fork, which is mostly in Vinton County with a small area in Hocking County.
Sauquoit Creek is a 17.0-mile-long (27.4 km) river in New York, United States. It lies within the southern part of Oneida County. The creek flows eastward, then turns sharply and flows generally northward through the Sauquoit Valley to the Mohawk River, entering the river on the east side of Whitesboro. It is therefore part of the Hudson River watershed.

Oaks Creek is a river that drains Canadarago Lake, which is situated in the north central region of Otsego County, New York. The creek begins by the Hamlet of Schuyler Lake and flows southeast approximately 9.32 miles (15.00 km), dropping only 105 feet (32 m) in elevation, before converging with the Susquehanna River south of the Village of Cooperstown, by the Hamlet of Index. From the source to Oaksville the creek flows along Panther Mountain. Fly Creek is a main tributary, that converges with Oaks Creek south of the Hamlet of Fly Creek.
Ocquionis Creek, also known as Fish Creek, is a river in southern Herkimer County and northern Otsego County in the State of New York. It begins northeast of the Hamlet of Jordanville and flows generally southward before flowing into the northern end of Canadarago Lake south of the Village of Richfield Springs. Ocquionis is an Iroquois word that translates to "he is a bear".

Otsquago Creek is a river that enters the Mohawk River in Fort Plain, New York. Otsquago is a Mohawk Indian word meaning 'under the bridge,' probably referring to an early bridge of felled trees along the creek, a way of making small bridges. It is also referred to as Otsquage on old maps, which is an Indian word for 'healing waters'.

The Canajoharie Creek is a river that flows into the Mohawk River in the Village of Canajoharie in the U.S. State of New York. The name "Canajoharie" is a Mohawk language term meaning "the pot that washes itself", referring to the "Canajoharie Boiling Pot", a 20-foot (6.1 m) wide and 10-foot (3.0 m) deep pothole in the Canajoharie Creek, just south of the village of Canajoharie. Bowmans Creek is one main tributary that enters the creek east of the Hamlet of Sprout Brook. The other main tributary is Brimstone Creek which enters the creek north-northwest of the Village of Ames.
Fulmer Creek is an 11.5-mile-long (18.5 km) river that flows into the Mohawk River in Mohawk, New York. The creek derives its name from the "Fulmer" family, who bought land through the Burnetsfield patent of 1725, in which lands on the present village site were granted out.

Steele Creek is a river in Herkimer County in the state of New York. The creek begins in an unnamed swamp south of Cedarville, and flows in a northeast direction before emptying into the Mohawk River in the village of Ilion. Steele Creek travels through the Ilion Gorge and alongside NY-51 for most of its length. Steele Creek derives its name from Rudolph Stahl, who built the first grist mill in Ilion along the creek.
Little Schoharie Creek is a river in Schoharie and Albany counties in the state of New York. It converges with the Schoharie Creek in Middleburgh.

The West Kill, an 11-mile-long (18 km) tributary of Schoharie Creek, flows through the town of Lexington, New York, United States, from its source on Hunter Mountain, the second-highest peak of the Catskill Mountains. Ultimately its waters reach the Hudson River via the Mohawk. Since it drains into the Schoharie upstream of Schoharie Reservoir, it is part of the New York City water supply system. It lends its name to both a mountain to its south and a small town midway along its length.

Batavia Kill is a 21-mile-long (34 km) tributary of Schoharie Creek, that flows across the towns of Windham, Ashland and Prattsville in the U.S. state of New York. Its waters reach the Hudson River via Schoharie Creek and the Mohawk River. Since it drains into the Schoharie upstream of Schoharie Reservoir, it is part of the New York City water supply system. From the source to Maplecrest, Batavia Kill drains the northern slopes of the Blackhead Mountains, which include Thomas Cole Mountain, Black Dome, and Blackhead Mountain, the fourth-, third-, and fifth-highest peaks in the Catskills, respectively.

Mine Kill is a river in Schoharie County in the state of New York. It flows into the Schoharie Creek by Gilboa, New York. Mine Kill Falls is located on the creek where it passes under State Route 30.
West Brook flows into the West Branch Delaware River by Walton, New York.