
Cuxhaven is a town and seat of the Cuxhaven district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town includes the northernmost point of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the shore of the North Sea at the mouth of the Elbe River. Cuxhaven has a footprint of 14 kilometres (east–west) by 7 km (4 mi) (north–south). Its town quarters Duhnen, Döse and Sahlenburg are especially popular vacation spots on the North Sea and home to about 52,000 residents.

Buxtehude, officially the Hanseatic City of Buxtehude, is a town on the Este River in Northern Germany, belonging to the district of Stade in Lower Saxony. It is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region and attached to the city's S-Bahn rapid transit network. Buxtehude is a medium-sized town and the second largest municipality in the Stade district. It lies on the southern border of the Altes Land in close proximity to the city-state of Hamburg. To the west lie the towns of Horneburg and Stade and to the south there are a number of incorporated villages featuring mostly upscale housing; e.g., Ottensen and Apensen.

The Hamburg S-Bahn is a rapid transit railway system in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Together, the S-Bahn, the Hamburg U-Bahn, the AKN railway and the regional railway form the backbone of railway public transport in the city and the surrounding area. The network has operated since 1907 as a commuter rail system, under the direction of the state railway, and is a member of the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund. There are four lines, serving 68 stations, on 147 kilometres (91 mi) of route. On an average working day the S-Bahn transports about 590,000 passengers; in 2010 about 221 million people used the S-Bahn.
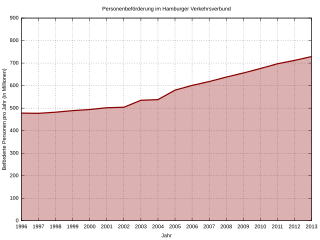
The Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV) is a transport association coordinating public transport in and around Hamburg, Germany. Its main objectives are to provide a unified fare system, requiring only a single ticket for journeys with transfers between different operating companies, and to facilitate and speed up travel by harmonising the individual companies' schedules. At its inception in 1965, the HVV was the first organisation of its kind worldwide.

Hamburg Hauptbahnhof, or Hamburg Central Railway Station in English, is the main railway station of the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1906 to replace four separate terminal stations, today Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is operated by DB Station&Service AG. With an average of 550,000 passengers a day, it is Germany's busiest railway station and the second-busiest in Europe after the Gare du Nord in Paris. It is classed by Deutsche Bahn as a category 1 railway station.
The Bremen–Bremerhaven railway line is a railway line connecting the German cities Bremen and Bremerhaven. It is an entirely two-track and electrified mainline railway that is operated Deutsche Bahn. It is designed for speeds of up to 160 km/h. In section from Bremen Hauptbahnhof to Bremerhaven Hauptbahnhof is 62.0 km long, but its extension via Bremerhaven-Lehe to the Bremerhaven-Speckenbüttel marshalling yard and on to Columbus quay is also often included. The most important intermediate station is Osterholz-Scharmbeck, where Regional-Express trains also stop.

The Metronom railway company is a German non-entirely-state-owned railway company based in the Lower Saxon town of Uelzen since December 2005. The company's activities focus exclusively on passenger transport, operating services from Hamburg to Bremen, Lüneburg and Uelzen, and from Uelzen to Hanover and Göttingen. Services listed on the timetables are abbreviated ME. Furthermore, the company operates services from Wolfsburg to Hanover and Hildesheim under its other brand Enno.

Buxtehude is a railway station in northwestern Germany. The station is located in the town of Buxtehude. It is located on two railway lines: the Lower Elbe Railway, which runs between Cuxhaven and Hamburg, and the Bremerhaven–Buxtehude line of the Eisenbahnen und Verkehrsbetriebe Elbe-Weser (EVB) to Bremervörde.

Neu Wulmstorf is a railway station in northwestern Germany. The station is situated in the municipality of Neu Wulmstorf on the Cuxhaven to Hamburg Niederelbebahn railway line. The station was built on an enclave of land belonging to Daerstorf and thus was called Daerstorf until Daerstorf joined the municipality of Neu Wulmstorf in 1970.

Cuxhaven is a railway station located in Cuxhaven, Germany. The station is located on the Lower Elbe Railway and Bremerhaven–Cuxhaven railway. The Cuxhaven-Bremerhaven service is operated by EVB. The Cuxhaven to Hamburg service, which was operated by Deutsche Bahn, became a Metronom service at the end of 2007. In December 2018, Start Unterelbe GmbH, a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn, took over the service. Today the station building is owned by a cooperative.
The Bremerhaven–Cuxhaven railway is a railway line between Bremerhaven and Cuxhaven, opened in 1899. Since December 14, 2003, passenger trains on the line are operated by the company with the same name, a joint venture of DB Regio AG and EVB.

Hamburg-Harburg or Harburg is one of four operational main-line railway stations (Fernbahnhöfe) in the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened on 1 May 1897, it is situated on the Hannover-Hamburg, Wanne-Eickel-Hamburg and Lower Elbe lines as well as the Harburg S-Bahn line. Train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn and Metronom with the rapid transit station being served by the Hamburg S-Bahn. The station is managed by DB Station&Service.

Hammerbrook is an elevated railway station on the Harburg S-Bahn line, served by the city trains of Hamburg S-Bahn. The railway station is located in Hammerbrook, Hamburg-Mitte, Hamburg, Germany.
Transport in Hamburg comprises an extensive, rail system, subway system, airports and maritime services for the more than 1.8 million inhabitants of the city of Hamburg and 5.3 million people in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region.
The Hanover–Hamburg railway is one of the most important railway lines in Lower Saxony and Germany. It links the Lower Saxon state capital of Hanover with Hamburg, running through Celle, Uelzen and Lüneburg.

The region between the Elbe and Weser rivers forms the Elbe–Weser triangle, also rendered Elbe-Weser Triangle, in northern Germany. It is also colloquially referred to as the Nasses Dreieck or "wet triangle".

The DBAG Class 474/874 is a three-car electric multiple unit train for the Hamburg S-Bahn. The class 474 were built to replace the nearly-60-year-old class 471 trains. Some units have a pantograph (474.3) to service the 2007 opened line to Stade on an overhead catenary track.

Stade is a railway station which opened in 1881 and is located in the town of Stade, Lower Saxony, Germany. Stade station is the terminus for the rapid transit trains of Hamburg S-Bahn line S5 from Elbgaustraße station via central station, and a through station for the Metronom line from Hamburg to Cuxhaven. For the Metronom, Stade is the last station within the Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV).

The rapid transit railway station Horneburg is located in the Horneburg village, Lower Saxony. The trains of the Hamburg S-Bahn serve the station with the line S5 from Elbgaustraße station via central station to Stade. It is also a station for the Niederelbebahn line from Hamburg to Cuxhaven.

The Harburg S-Bahn line is a railway line in southern Hamburg, Germany. It starts at Hamburg Hauptbahnhof and runs via Harburg to Stade. It mostly runs parallel with the line to Hanover and the Lower Elbe line and is now part of the Hamburg S-Bahn lines S3 and S31.




















