Related Research Articles

Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fluid to the bloodstream. Lymphedema is most frequently a complication of cancer treatment or parasitic infections, but it can also be seen in a number of genetic disorders. Though incurable and progressive, a number of treatments may improve symptoms. Tissues with lymphedema are at high risk of infection because the lymphatic system has been compromised.
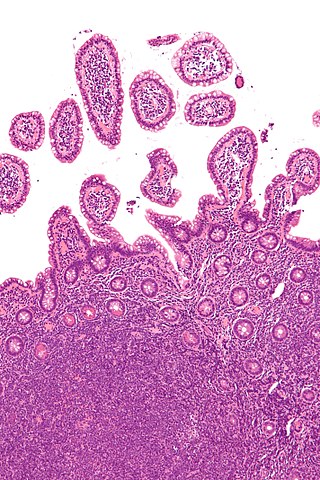
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow-growing while others are fast-growing.

Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes. In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night.

The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph back towards the heart, for re-circulation.
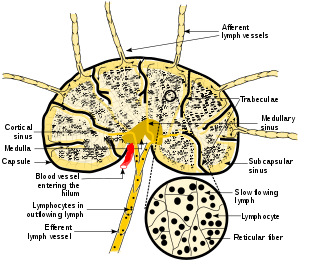
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.

Elephantiasis is the enlargement and hardening of limbs or body parts due to tissue swelling. It is characterised by edema, hypertrophy, and fibrosis of skin and subcutaneous tissues, due to obstruction of lymphatic vessels. It may affect the genitalia. The term elephantiasis is often used in reference to parasitic worm infections, but may refer to a variety of diseases where parts of a person's body swell to massive proportions.
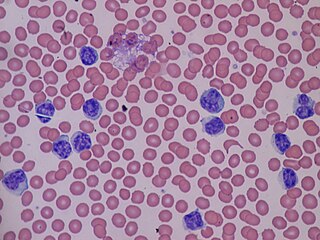
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the condition where the proportion of lymphocytes relative to white blood cell count is above the normal range. In adults, absolute lymphocytosis is present when the lymphocyte count is greater than 5000 per microliter (5.0 x 109/L), in older children greater than 7000 per microliter and in infants greater than 9000 per microliter. Lymphocytes normally represent 20% to 40% of circulating white blood cells. When the percentage of lymphocytes exceeds 40%, it is recognized as relative lymphocytosis.

Lymphogranuloma venereum is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the invasive serovars L1, L2, L2a, L2b, or L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis.

Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula.

Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that starts in the endothelial cells that line the walls of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. Since they are made from vascular lining, they can appear anywhere and at any age, but older people are more commonly affected, and the skin is the most affected area, with approximately 60% of cases being cutaneous. Specifically, the scalp makes up ~50% of angiosarcoma cases, but this is still <0.1% of all head and neck tumors. Since angiosarcoma is an umbrella term for many types of tumor that vary greatly in origin and location, many symptoms may occur, from completely asymptomatic to non-specific symptoms like skin lesions, ulceration, shortness of breath and abdominal pain. Multiple-organ involvement at time of diagnosis is common and makes it difficult to ascertain origin and how to treat it.

Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.
Ann Arbor staging is the staging system for lymphomas, both in Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It was initially developed for Hodgkin's, but has some use in NHL. It has roughly the same function as TNM staging in solid tumors.
Lymph node biopsy is a test in which a lymph node or a piece of a lymph node is removed for examination under a microscope.

Lymphangitis is an inflammation or an infection of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. The most common cause of lymphangitis in humans is Streptococcus pyogenes, hemolytic streptococci, and in some cases, mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, tuberculosis, syphilis, and the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. Lymphangitis is sometimes mistakenly called "blood poisoning". In reality, "blood poisoning" is synonymous with sepsis.

T-cell lymphoma is a rare form of cancerous lymphoma affecting T-cells. Lymphoma arises mainly from the uncontrolled proliferation of T-cells and can become cancerous.

Milroy's disease (MD) is a familial disease characterized by lymphedema, commonly in the legs, caused by congenital abnormalities in the lymphatic system. Disruption of the normal drainage of lymph leads to fluid accumulation and hypertrophy of soft tissues.

Elephantiasis nostras, is a disease that usually affects the lower legs or scrotum. Swelling is accompanied by rough nodules or wart-like plaques on the skin. If the disease is not treated, it eventually results in pain and immobility.

Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to lymphadenopathy of the cervical lymph nodes. The term lymphadenopathy strictly speaking refers to disease of the lymph nodes, though it is often used to describe the enlargement of the lymph nodes. Similarly, the term lymphadenitis refers to inflammation of a lymph node, but often it is used as a synonym of lymphadenopathy.
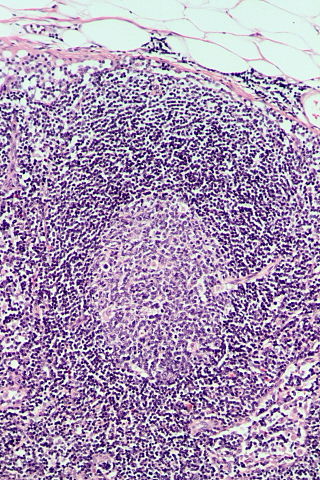
Follicular hyperplasia (FH) is a type of lymphoid hyperplasia and is classified as a lymphadenopathy, which means a disease of the lymph nodes. It is caused by a stimulation of the B cell compartment and by abnormal cell growth of secondary follicles. This typically occurs in the cortex without disrupting the lymph node capsule. The follicles are pathologically polymorphous, are often contrasting and varying in size and shape. Follicular hyperplasia is distinguished from follicular lymphoma in its polyclonality and lack of bcl-2 protein expression, whereas follicular lymphoma is monoclonal, and expresses bcl-2.

Indolent lymphoma, also known as low-grade lymphoma, is a group of slow-growing non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs). Because they spread slowly, they tend to have fewer signs and symptoms when first diagnosed and may not require immediate treatment. Symptoms can include swollen but painless lymph nodes, unexplained fever, and unintended weight loss.