
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaves, short internodes and leaf orientation which is parallel or oblique to direct sunlight. The word comes from the Greek sklēros (hard) and phyllon (leaf). The term was coined by A.F.W. Schimper in 1898, originally as a synonym of xeromorph, but the two words were later differentiated.

A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of grasses. According to Britannica, there exists four savanna forms; savanna woodland where trees and shrubs form a light canopy, tree savanna with scattered trees and shrubs, shrub savanna with distributed shrubs, and grass savanna where trees and shrubs are mostly nonexistent.

The Top End of Australia's Northern Territory is a geographical region encompassing the northernmost section of the Northern Territory, which aside from the Cape York Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Australian continent. It covers a rather vaguely defined area of about 245,000 km² behind the northern coast from the Northern Territory capital of Darwin across to Arnhem Land with the Indian Ocean on the west, the Arafura Sea to the north, and the Gulf of Carpentaria to the east, and with the almost waterless semi-arid interior of Australia to the south, beyond the huge Kakadu National Park.

The Madagascar subhumid forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion that covers most of the Central Highlands of the island of Madagascar. They are included in the WWF's Global 200 list of outstanding ecoregions. Most of the original habitats have been lost due to human pressure.

The East Sudanian savanna is a hot, dry, tropical savanna ecoregion of Central and East Africa.
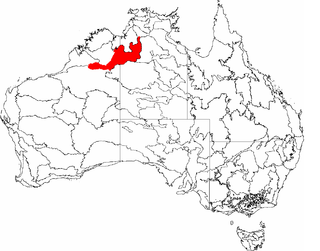
The Ord Victoria Plain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory and Western Australia, comprising 12,540,703 hectares.

Pakistan's native flora reflects its varied climatic zones, which range from arid and semi-arid to temperate and tropical.

The Arnhem Land tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in Australia's Northern Territory.

The Carpentaria tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northern Australia.

The Kimberley tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northwestern Australia, covering portions of Western Australia and the Northern Territory south of the Timor Sea.

The Victoria Plains tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northwestern Australia.

Persoonia falcata, commonly known as the wild pear, is a shrub native to northern Australia.

The Mandara Plateau mosaic, also known as the Mandara Plateau woodlands, is a tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion located in the Mandara Mountains of northern Nigeria and Cameroon.

Macropteranthes is a genus containing five species of woody shrub native to northern Australia.

The Southern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets is a tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in Tanzania and Kenya. It includes portions of Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area, which are designated World Heritage Sites and biosphere reserves for their outstanding wildlife and landscapes. It is one of three Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets ecoregions in eastern Africa.

Teucrium integrifolium, commonly known as teucry weed or green germander, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae and is endemic to northern Australia. It is a perennial herb with broadly elliptic to broadly egg-shaped leaves and white or cream-coloured flowers.

Hibbertia dilatata is a species of flowering plant in the family Dilleniaceae and is endemic to the Northern Territory. It is a sub-shrub with flattened stems and pale to bright pink, purplish or white flowers with seven to ten stamens.
Hibbertia juncea is a species of flowering plant in the family Dilleniaceae and is endemic to the Northern Territory. It is a small shrub with leaves reduced to minute scales, and white to cream-coloured or pink flowers arranged in leaf axils with seven to ten stamens.
Hibbertia scabra is a species of flowering plant in the family Dilleniaceae and is endemic to the north of the Northern Territory. It is a small shrub with hairy foliage, linear to narrow elliptical leaves and yellow flowers arranged singly near the ends of branches with about fifty stamens arranged around two densely scaly carpels.

Rainforests and vine thickets are a major vegetation group in Australia. It consists of temperate to tropical rainforests, monsoon forests, and vine thickets. Rainforests and vine thickets are generally found in small pockets across the eastern and northern portions of the continent, including western Tasmania, eastern New South Wales, eastern Queensland, the northern portion of the Northern Territory, and the Kimberley Region of northeastern Western Australia.


















