Mammalian vision is the process of mammals perceiving light, analyzing it and forming subjective sensations, on the basis of which the animal's idea of the spatial structure of the external world is formed. Responsible for this process in mammals is the visual sensory system, the foundations of which were formed at an early stage in the evolution of chordates. Its peripheral part is formed by the eyes, the intermediate (by the transmission of nerve impulses) - the optic nerves, and the central - the visual centers in the cerebral cortex.
The recognition of visual stimuli in mammals is the result of the joint work of the eyes and the brain. At the same time, a significant part of the visual information is processed already at the receptor level, which allows to significantly reduce the amount of such information received by the brain. Elimination of redundancy in the amount of information is inevitable: if the amount of information delivered to the receptors of the visual system is measured in millions of bits per second (in humans - about 1×107 bits/s), the capabilities of the nervous system to process it are limited to tens of bits per second.
The organs of vision in mammals are, as a rule, well developed, although in their life they are of less importance than for birds: usually mammals pay little attention to immovable objects, so even cautious animals such as a fox or a hare may come close to a human who stands still without movement. The size of the eyes in mammals is relatively small; in humans, eye weight is 1% of the mass of the head, while in a starling it reaches 15%. Nocturnal animals (for example, tarsiers) and animals that live in open landscapes have larger eyes. The vision of forest animals is not so sharp, and in burrowing underground species (moles, gophers, zokors), eyes are reduced to a greater extent, in some cases (marsupial moles, mole rats, blind mole), they are even covered by a skin membrane.

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information and the coordination of motor control.

The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.

In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes, it is located within the brain.

An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.

Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions

Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity.

The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception. The system detects, transduces and interprets information concerning light within the visible range to construct an image and build a mental model of the surrounding environment. The visual system is associated with the eye and functionally divided into the optical system and the neural system.
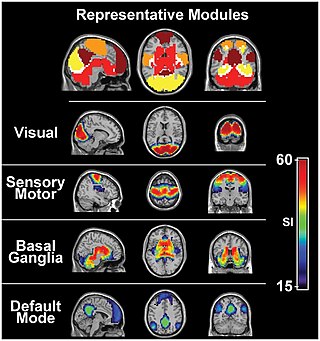
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons, neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception and interoception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, balance and visceral sensation. Sense organs are transducers that convert data from the outer physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them.

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.
Stimulus modality, also called sensory modality, is one aspect of a stimulus or what is perceived after a stimulus. For example, the temperature modality is registered after heat or cold stimulate a receptor. Some sensory modalities include: light, sound, temperature, taste, pressure, and smell. The type and location of the sensory receptor activated by the stimulus plays the primary role in coding the sensation. All sensory modalities work together to heighten stimuli sensation when necessary.

In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form tectal is commonly used for both structures.

The star-nosed mole is a small semiaquatic mole found in moist, low elevation areas in the northern parts of North America. It is the only extant member of the tribe Condylurini and genus Condylura, and it has more than 25,000 minute sensory receptors in touch organs, known as Eimer's organs, with which this hamster-sized mole feels its way around. With the help of its Eimer's organs, it may be perfectly poised to detect seismic wave vibrations.
In medicine and anatomy, the special senses are the senses that have specialized organs devoted to them:
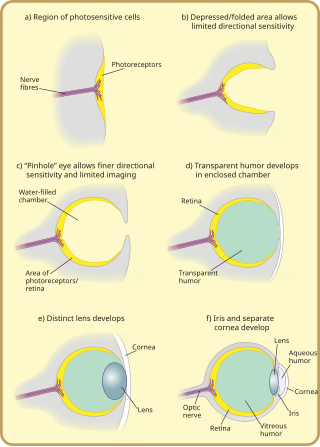
Many scientists have found the evolution of the eye attractive to study because the eye distinctively exemplifies an analogous organ found in many animal forms. Simple light detection is found in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants and animals. Complex, image-forming eyes have evolved independently several times.

Cat senses are adaptations that allow cats to be highly efficient predators. Cats are good at detecting movement in low light, have an acute sense of hearing and smell, and their sense of touch is enhanced by long whiskers that protrude from their heads and bodies. These senses evolved to allow cats to hunt effectively at dawn and dusk.

Vision is the most important sense for birds, since good eyesight is essential for safe flight. Birds have a number of adaptations which give visual acuity superior to that of other vertebrate groups; a pigeon has been described as "two eyes with wings". Birds are theropods, and the avian eye resembles that of other sauropsids, with ciliary muscles that can change the shape of the lens rapidly and to a greater extent than in the mammals. Birds have the largest eyes relative to their size in the animal kingdom, and movement is consequently limited within the eye's bony socket. In addition to the two eyelids usually found in vertebrates, bird's eyes are protected by a third transparent movable membrane. The eye's internal anatomy is similar to that of other vertebrates, but has a structure, the pecten oculi, unique to birds.
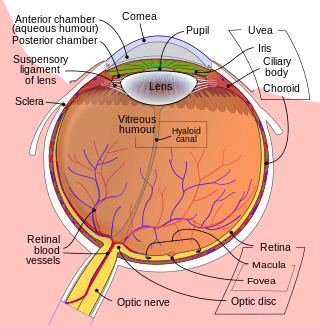
Mammals normally have a pair of eyes. Although mammalian vision is not as excellent as bird vision, it is at least dichromatic for most of mammalian species, with certain families possessing a trichromatic color perception.

Visual perception in animals plays an important role in the animal kingdom, most importantly for the identification of food sources and avoidance of predators. For this reason, blindness in animals is a unique topic of study.
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as such, many more are now recognized. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli for transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought.
Odor molecules are detected by the olfactory receptors in the olfactory epithelium of the nasal cavity. Each receptor type is expressed within a subset of neurons, from which they directly connect to the olfactory bulb in the brain. Olfaction is essential for survival in most vertebrates; however, the degree to which an animal depends on smell is highly varied. Great variation exists in the number of OR genes among vertebrate species, as shown through bioinformatic analyses. This diversity exists by virtue of the wide-ranging environments that they inhabit. For instance, dolphins that are secondarily adapted to an aquatic niche possess a considerably smaller subset of genes than most mammals. OR gene repertoires have also evolved in relation to other senses, as higher primates with well-developed vision systems tend to have a smaller number of OR genes. As such, investigating the evolutionary changes of OR genes can provide useful information on how genomes respond to environmental changes. Differences in smell sensitivity are also dependent on the anatomy of the olfactory apparatus, such as the size of the olfactory bulb and epithelium.

















