Related Research Articles

The Nürburgring is a 150,000-person capacity motorsports complex located in the town of Nürburg, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It features a Grand Prix race track built in 1984, and a long Nordschleife "North loop" track, built in the 1920s, around the village and medieval castle of Nürburg in the Eifel mountains. The north loop is 20.830 km (12.943 mi) long and contains more than 300 metres of elevation change from its lowest to highest points. Scottish racing driver Jackie Stewart nicknamed the track "The Green Hell".

Denis Clive Hulme was a New Zealand racing driver, who competed in Formula One from 1965 to 1974. Nicknamed "The Bear", Hulme won the Formula One World Drivers' Championship in 1967 with Brabham, and won eight Grands Prix across 10 seasons.

Watkins Glen International, nicknamed "The Glen", is an automobile race track in the northeastern United States, located in Dix, New York, just southwest of the village of Watkins Glen, at the southern tip of Seneca Lake. It is long known around the world as the former home of the Formula One United States Grand Prix, which it hosted for twenty consecutive years (1961–1980). In addition, the site has also been home to road racing of nearly every class, including the World Sportscar Championship, Trans-Am, Can-Am, NASCAR Cup Series, the International Motor Sports Association, and the IndyCar Series. The facility is currently owned by NASCAR.

Sonoma Raceway is a road course and dragstrip located at Sears Point in the southern Sonoma Mountains of Sonoma County, California. The road course features 12 turns on a hilly course with 160 ft (49 m) of total elevation change. It is host to one of the few NASCAR Cup Series races each year that are run on road courses. It has also played host to the IndyCar Series, the NHRA Mission Foods Drag Racing Series, and several other auto races and motorcycle races such as the American Federation of Motorcyclists series. Sonoma Raceway continues to host amateur, or club racing events with some open to the public. The largest such car club is the Sports Car Club of America. The track is 30 mi (48 km) north of San Francisco and Oakland.
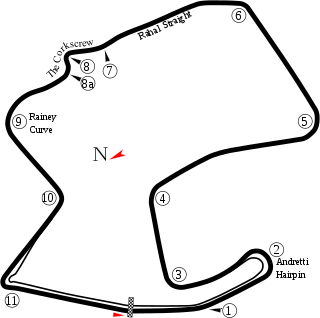
Laguna Seca Raceway is a paved road racing track in central California used for both auto racing and motorcycle racing, built in 1957 near both Salinas and Monterey, California, United States.

Alfred Unser Jr. – nicknamed "Little Al" to distinguish him from his father, Al Unser – is an American retired racing driver. Known primarily for his Championship car career, Unser won two CART championships, and is a two-time winner of the Indianapolis 500.
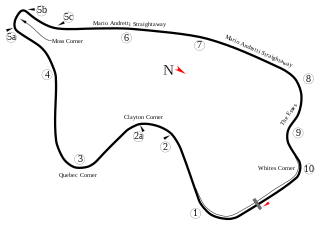
Canadian Tire Motorsport Park is a multi-track motorsport venue located north of Bowmanville, in Ontario, Canada, approximately 75 kilometers east of Toronto. The facility features a 3.957 km (2.459 mi), 10-turn road course; a 2.9 km (1.8 mi) advance driver and race driver training facility with a 0.402 km (0.250 mi) skid pad and a 1.5 km (0.93 mi) kart track. The name "Mosport", a portmanteau of Motor Sport, came from the enterprise formed to build the track.

The Caesars Palace Grand Prix was an annual car race held in Las Vegas, US from 1981 to 1984. In 1981 and 1982 the race was part of the Formula One World Championship and featured a 2.268 mile, 14 turn Grand Prix layout; in 1983 and 1984 it became a round of the CART Indy car series and featured a 5 turn 1.125 mile distorted oval layout. Nissan/Datsun was a presenting sponsor of the races. The races were held on a temporary circuit in the parking lot of the Caesars Palace hotel.

The Circuit Gilles Villeneuve, also spelled Circuit Gilles-Villeneuve, is a 4.361 km (2.710 mi) motor racing circuit on Notre Dame Island in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is the venue for the FIA Formula One Canadian Grand Prix. It has previously hosted the World Sportscar Championship, the Champ Car World Series, the NASCAR Pinty’s Series, the NASCAR Nationwide Series, and the Grand-Am Rolex Sports Car Series.

Riverside International Raceway was a motorsports race track and road course established in the Edgemont area of Riverside County, California, just east of the city limits of Riverside and 50 mi (80 km) east of Los Angeles, in 1957. In 1984, the raceway became part of the newly incorporated city of Moreno Valley. Riverside was noted for its hot, dusty environment, which was a dangerous challenge for drivers. It was also considered one of the finest tracks in the United States. The track was in operation from September 22, 1957, to July 2, 1989, with the last race, The Budweiser 400, won by Rusty Wallace, held in 1988. After that final race, a shortened version of the circuit was kept open for car clubs and special events until 1989.

Lime Rock Park is a natural-terrain motorsport road racing venue located in Lakeville, Connecticut, United States, a hamlet in the town of Salisbury, in the state's northwest corner. Built in 1956, it is the nation's third oldest continuously operating road racing venue, behind Road America (1955) and Willow Springs International Motorsports Park (1953). The track was owned by Skip Barber from 1984 to April 2021, a former race car driver who started the Skip Barber Racing School in 1975. Now, it is owned by Lime Rock Group, LLC. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2009.

Road Atlanta is a 2.540 mi (4.088 km) road course located just north of Braselton, Georgia, United States. The facility is utilized for a wide variety of events, including professional and amateur sports car and motorcycle races, racing and driving schools, corporate programs and testing for motorsports teams. The track has 12 turns, including the famous "esses" between turns three and five; and Turn 12, a downhill, diving turn. The track is owned by IMSA Holdings, LLC through its subsidiary Road Atlanta, LLC, and is the home to the Petit Le Mans, as well as AMA motorcycle racing, and smaller events throughout the year. Michelin acquired naming rights to the facility in 2018.

Road America is a motorsport road course located near Elkhart Lake, Wisconsin on Wisconsin Highway 67. It has hosted races since the 1950s and currently hosts races in the IndyCar Series, IMSA SportsCar Championship, Sports Car Club of America GT World Challenge America and Trans-Am Series and the MotoAmerica Superbike Championship.

Portland International Raceway (PIR) is a motorsport facility in Portland in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is part of the Delta Park complex on the former site of Vanport, just south of the Columbia River. It lies west of the Delta Park/Vanport light rail station and less than a mile west of Interstate 5.

Mid-Ohio Sports Car Course is a road course auto racing facility located in Troy Township, Morrow County, Ohio, United States, just outside the village of Lexington. It hosts a number of racing series such as IndyCar, IMSA WeatherTech Sportscar Championship, and the NASCAR Craftsman Truck Series, along with other club events such has SCCA and National Auto Sport Association.

Brainerd International Raceway is a road course, and dragstrip racing complex northwest of the city of Brainerd, Minnesota. The complex has a 0.25 mi (0.40 km) dragstrip, and overlapping 2.500 mi (4.023 km) and 3.100 mi (4.989 km) road courses. The complex also includes a kart track. The raceway hosts the National Hot Rod Association's Lucas Oil Nationals. It is a popular racetrack for the Trans Am Series. The spectator seating capacity of the circuit is 20,000.
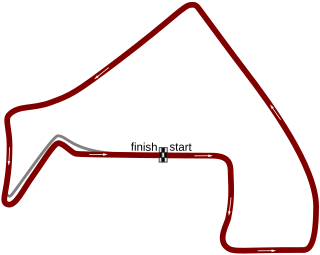
The Circuit Trois-Rivières is a street circuit in Trois-Rivières, Quebec, Canada. The circuit has been the home of the annual Grand Prix de Trois-Rivières, the longest-running street race in North America, since 1967. The circuit is located on the Terrain de l'Exposition (fairgrounds) and is unusual in that it passes through Porte Duplessis, the narrow concrete gateway of the grounds at turn 3.

Edmonton International Speedway, also known as Speedway Park, was a 251-acre (1.02 km2) multi-track auto racing facility located in the present Cumberland and Hudson neighbourhoods of Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. The facility featured a 1⁄4-mile (400 m) dragstrip, a 2.53-mile (4.07 km) 14-turn road course, and a 1⁄4-mile short oval. At its peak, it had capacity for over 30,000 fans.
The March 817 was a British sports prototype racing car, built by March Engineering in 1981 for the Can-Am series. As with all other full-size Can-Am cars of the time, it used a mid-mounted 5-litre, naturally-aspirated Chevrolet V8 engine. Two cars are known to have been built. Paul Newman Racing won the Team's championship of the Can-Am series in 1981 with the March 817, whilst their main driver, Teo Fabi took second in the driver's standings.
The March 847 was a British sports prototype racing car, built by March Engineering in 1984 for the Can-Am series. As with all other full-size Can-Am cars of the time, it used a mid-mounted 5-litre, naturally-aspirated Chevrolet V8 engine. It was driven by Jim Crawford for RK Racing/United Breweries, scoring 3 wins. Jim Crawford and the March 847 chassis would both successfully finish the championship as runner-up at the end of the season.
References
- ↑ "March 827" . Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ↑ "March 827" . Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ↑ "March 827" . Retrieved 26 June 2022.