Paraconger is a genus of eels in the family Congridae. It currently contains the following species:
Pythonichthys sanguineus is an eel in the family Heterenchelyidae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1868. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Suriname, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It leads a benthic lifestyle, dwelling in reefs or rocky regions at a maximum depth of 37 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 41.9 centimetres.

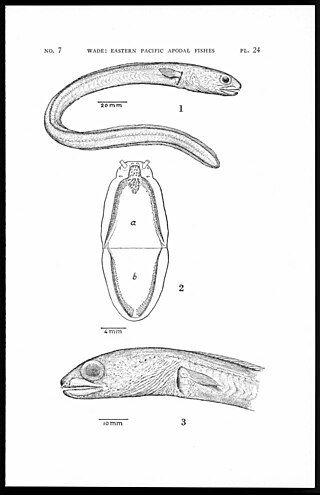
The shorttail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Charles Barkley Wade in 1946, originally under the genus Chiloconger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, the Galapagos Islands, Panama, and Revillagigedo. It dwells at a depth range of 108–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres.
The sea conger, also known as the big-eye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1853, originally under the genus Conger. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western Pacific Ocean, including Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan; the eastern China Sea, and the East Indies. It leads a benthic lifestyle and dwells in sand and mud. Males can reach a maximum total length of 51 centimeters.
The longtrunk conger, also known as the short-tail conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1860, originally under the genus Conger. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including southern Florida, Panama, the Guianas, and the Gulf of Guinea. It leads a benthic lifestyle, and inhabits sand and rock at a depth range of 11–63 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.3 centimeters.

The bandtooth conger, also known as the Baleares conger or the Balearic conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by François Étienne Delaroche in 1809, originally under the genus Muraena. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic and the western Indian Ocean, including North Carolina, United States; the northern Gulf of Mexico, northern South America, Canada, Portugal, Angola, the Mediterranean, and the Red Sea. It inhabits reefs and littoral shelves, and burrows into sand and mud. It dwells at a depth range of 1–732 meters (3–2,402 ft), but most frequently between 20–100 m (66–328 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length (TL) of 35 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 25 centimetres (9.8 in)
The large-eye conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Léon Vaillant and Henri Émile Sauvage in 1875, originally under the genus Congrogadus. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the northwestern and eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Hawaii and the Ladd Seamount. It typically dwells at a depth range of 2–420 metres, and leads a benthic, nocturnal lifestyle, burrowing into sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 38 centimetres.
The slope conger, also known as the black-fin conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1891, originally under the genus Ophisoma. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the southeastern and eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Honduras, El Salvador, Mexico, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Panama, and Peru. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 380–740 metres, and inhabits substrates. Males can reach a maximum total length of 35 centimetres.
The Californian conger, also known as the ringeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, and Peru. It is known to dwell at a depth of 50 metres. Males reach an average total length of 40 centimetres, but can reach a maximum TL of 60 cm.
Paraconger guianensis is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from French Guiana and northern Brazil, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 73 metres.
The blackspot conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Conger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira and Azores. It dwells at a depth range of 30–100 meters and burrows into sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 50 centimetres.
The Guinean conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Senegal to Angola, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 25–50 metres, and inhabits benthic sand, which it burrows into backwards. Males can reach a maximum total length of 62.7 centimetres.
Paraconger ophichthys is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Cocos Island, in the eastern central Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 1953 metres.
The neighbor conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Uroconger. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel that is known from the southwestern and western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Bahamas, Brazil, Cuba, and Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 101–503 metres (331–1,650 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 46.2 centimetres (18.2 in).
The grey conger, also known as the Antillean conger or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1861. It is a tropical and subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including Cuba, Jamaica, and throughout northern South America. It dwells at a depth range of 120–400 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting coral reefs and rocky regions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 160 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 90 centimetres.
The manytooth conger, also known as the manytooth conger eel or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bermuda, the Antilles, the western Caribbean, and Brazil. It dwells at a depth range of 3–55 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting rocky regions and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimeters, but more commonly reach a TL of 80 cm.
Gnathophis bracheatopos, the longeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the United States and the eastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 55–110 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 35 centimeters.

Gnathophis mystax, the thinlip conger or blacktailed conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by François Étienne Delaroche in 1809, originally under the genus Muraena. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including southern Portugal, the Mediterranean, and Morocco. It dwells at a depth range of 75–800 metres, and inhabits mud and sand on the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 35 centimetres.
The whiptail conger, also known as the conger eel in Cuba, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951, originally under the genus Congrina. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States in the northern Gulf of Mexico and northern South America. It is known to dwell at a depth of 203 meters (666 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 61 centimeters (24 in).

Cynoponticus savanna,, the Guayana pike-conger, pike-headed eel or sapphire eel, is an eel in the family Muraenesocidae. It was described by Edward Nathaniel Bancroft in 1831, originally under the genus Conger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including Central America, the Caribbean and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 100 metres (330 ft), and inhabits muddy substrates in bays and estuaries. Males can reach a maximum total length of 150 centimetres (59 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 50 centimetres (20 in).




