
Gentianaceae is a family of flowering plants of 103 genera and about 1600 species.

The Monimiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It is closely related to the families Hernandiaceae and Lauraceae. It consists of shrubs, small trees, and a few lianas of the tropics and subtropics, mostly in the southern hemisphere. The largest center of diversity is New Guinea, with about 75 species. Lesser centres of diversity are Madagascar, Australia, and the neotropics. Africa has one species, Xymalos monospora, as does Southern Chile. Several species are distributed through Malesia and the southwest Pacific.
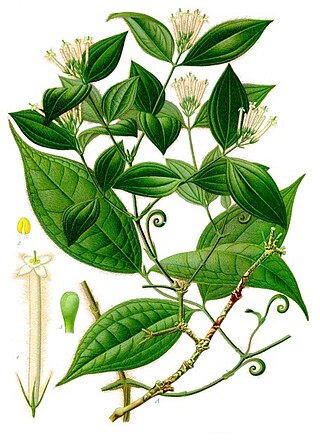
Strychnos is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae. The genus includes about 100 accepted species of trees and lianas, and more than 200 that are as yet unresolved. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare.

The Rapateaceae are a family of flowering plants. The botanical name has been recognized by most taxonomists.

Rhabdodendron is a genus of flowering plant in the family Rhabdodendraceae. It comprises three species of tropical South American trees.

Otto Stapf FRS was an Austrian born botanist and taxonomist, the son of Joseph Stapf, who worked in the Hallstatt salt-mines. He grew up in Hallstatt and later published about the archaeological plant remains from the Late Bronze- and Iron Age mines that had been uncovered by his father.
Hoplestigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Boraginaceae, although this is disputed, and it has been placed in its own family Hoplestigmataceae. Its two species are native to Cameroon, Gabon, Ivory Coast and Liberia in western tropical Africa.

Monotes is a genus of flowering plants in the family Dipterocarpaceae. Its name, meaning "unity" or "uniqueness" was chosen because it was the only genus of dipterocarp then known to occur in Africa. The Zambezian region is the centre of diversity for the genus.

Ludwig Adolph Timotheus Radlkofer, was a Bavarian taxonomist and botanist.

Hans Schinz was a Swiss explorer and botanist who was a native of Zürich.
Bachmannia is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the family Capparaceae with the sole member being Bachmannia woodii, the four-finger bush. It is native to southeastern Africa.

Chytranthus is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Sapindaceae. It includes 32 species of small trees and shrubs native to tropical Africa, ranging from Guinea eastwards to Kenya and Tanzania and south to Angola. Most species have a palm-like habit, with large pinnate leaves and unbranched trunks.
Deinbollia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Sapindaceae.
Englerodaphne is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Thymelaeaceae.
Lindackeria is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Achariaceae.
Sarcodraba is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Brassicaceae.








