
Cape Breton University (CBU) is a public university located in Sydney, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is the only post-secondary degree-granting institution within the Cape Breton Regional Municipality and on Cape Breton Island. The university is enabled by the Cape Breton University Act passed by the Nova Scotia House of Assembly. Prior to this, CBU was enabled by the University College of Cape Breton Act (amended). The University College of Cape Breton's Coat of Arms were registered with the Canadian Heraldic Authority on May 27, 1995.

Brandon University is a university located in the city of Brandon, Manitoba, Canada, with an enrolment of approximately 3,375 (2020) full-time and part-time undergraduate and graduate students. The current location was founded on July 13, 1899, as Brandon College as a Baptist institution. It was chartered as a university by then President John E. Robbins on June 5, 1967. The enabling legislation is the Brandon University Act. Brandon University is one of several predominantly undergraduate liberal arts and sciences institutions in Canada.

University College of the North (UCN)—formerly Keewatin Community College—is a post-secondary institution located in Northern Manitoba, Canada, with two main campuses in The Pas and Thompson, respectively. UCN has a student body of approximately 2,400 annually and a staff of approximately 400.
Georgian College is a College of Applied Arts and Technology in Ontario, Canada, partnered with ILAC International College. It has 13,000 full-time students, including 4,500 international students from 85 countries, across seven campuses, the largest being in Barrie.
The Gabriel Dumont Institute (GDI), formally the Gabriel Dumont Institute of Native Studies and Applied Research Inc., is a non-profit corporation serving the educational and cultural needs of the Saskatchewan Métis and Non-Status Indian community, and is the officially-designated education arm of the Métis Nation—Saskatchewan (MN-S).

St. Lawrence College (SLC) is a College of Applied Arts and Technology with three campuses in Eastern Ontario, namely Brockville (1970), Cornwall (1968) and Kingston. It is affiliated with private Alpha College of Business & Technology in Toronto and Canadian College in Vancouver. As of May, 2024, St. Lawrence College is no longer accepting new admissions to programs offered at our partner colleges. The population of St Lawrence College and it's affiliates includes a large contingent of international students. The college processed 5,421 international study permits in 2023.
Aurora College, formerly Arctic College, is a college located in the Northwest Territories, Canada with campuses in Inuvik, Fort Smith and Yellowknife. They have learning centres in 23 communities in the NWT. The head office for Aurora College is located in Fort Smith.
Olds College of Agriculture & Technology is an Alberta public post-secondary institution located in Olds, Alberta, established in 1913 as Olds Agricultural College.

Bow Valley College is a Canadian public, board-governed college located in Calgary, Alberta, operating as a comprehensive community institution under the Post-Secondary Learning Act of Alberta. The branch campuses are: Airdrie, Banff, Cochrane, Okotoks, and Strathmore. Bow Valley College is a member of the Alberta Rural Development Network and Colleges and Institutes Canada.

Northwestern Polytechnic (NWP), previously known as Grande Prairie Regional College (GPRC) is a publicly funded educational institution located in northwestern Alberta, Canada.
Keyano College is a post-secondary college located in Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada. It offers specialized training to more than 2,100 full-time students and over 4,000 part-time students. The main Clearwater Campus is located in downtown Fort McMurray with the Suncor Energy Industrial Campus located in the Gregoire Industrial Park and a new campus in Fort Chipewyan. Outreach campuses are located in Anzac, and Fort McKay. The college is also a member of the Alberta Rural Development Network.

Lakeland College is a post-secondary college in Alberta, Canada. It is publicly funded, and maintains two campuses in Vermilion and Lloydminster. Lakeland serves over 7,000 students through the academic year with 2,223 studying full- and part-time.
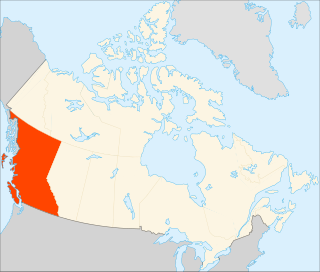
Higher education in British Columbia is delivered by 25 publicly funded institutions that are composed of eleven universities, eleven colleges, and three institutes. This is in addition to three private universities, five private colleges, and six theological colleges. There are also an extensive number of private career institutes and colleges. Over 297,000 students were enrolled in post-secondary institutions in British Columbia in the 2019-2020 academic year.
University nuhelot’įne thaiyots’į nistameyimâkanak Blue Quills (University nn Blue Quills, formerly Blue Quills Education Centre and Blue Quills First Nations College (BQFNC)) is a First Nations owned and operated university in Canada, the first of its kind in the country. The university is jointly owned by seven First Nation band governments: Beaver Lake, Cold Lake, Frog Lake, Whitefish Lake, Heart Lake, Kehewin, and Saddle Lake.
Cumberland College is a regional college based in Melfort, Nipawin and Tisdale, Saskatchewan, Canada, that provides post-secondary education in the north east region of the province.

Yellowhead Tribal College is an educational institution located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, which is run by four member nations of Treaty 6 with the four members being Alexander First Nation, O'Chiese First Nation, Sunchild First Nation and Alexis Nakota Sioux Nation.

Old Sun Community College is a community college owned and operated by First Nations that provides post-secondary education and training in Siksika 146, Alberta, Canada, to members of the Siksika Nation.

Anishinabek Educational Institute (AEI) is an First Nation-owned and controlled post-secondary institution in Canada. Indigenous institutes partner with colleges and universities to offer students degree programs, apprenticeships, certificate programs and diploma programs. AEI was founded to provide greater access to post-secondary education for First Nation peoples. AEI delivers post-secondary programs approved by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities. The educational curriculum was adapted to meet the needs of Indigenous learners to ensure it reflects community needs, cultural heritage and identity.

Seven Generations Education Institute is an Aboriginal-owned and controlled post-secondary institution, co-founded by the ten bands in the Rainy Lake Tribal area in 1985. The ten bands are: Big Grassy, Big Island, Couchiching, Lac La Croix, Naicatchewenin, Nigigoonsiminikaaning, Ojibways of Onigaming, Rainy River, Seine River and Mitaanjigamiing. Each of the bands appointed one member to the board of directors of Seven Generations Education Institute, which functions with the leadership of the Executive Director.

Iohahi:io Akwesasne Education & Training Institute is an Aboriginal-owned and controlled post-secondary institution for the Mohawks of Akwesasne.













