The black-crowned night heron [or black-capped night heron], commonly shortened to just night heron in Eurasia, is a medium-sized heron found throughout a large part of the world, including parts of Europe, Asia, and North and South America. In Australasia it is replaced by the closely related Nankeen night heron, with which it has hybridised in the area of contact.

Nycticorax is a genus of night herons. The name Nycticorax means "night raven" and derives from the Ancient Greek νύκτος, nuktos "night" and κοραξ, korax, "raven". It refers to the largely nocturnal feeding habits of this group of birds, and the croaking crow-like call of the best known species, the black-crowned night heron.

The nankeen night heron is a heron that belongs to the genus Nycticorax and the family Ardeidae. Due to its distinctive reddish-brown colour, it is also commonly referred to as the rufous night heron. It is primarily nocturnal and is observed in a broad range of habitats, including forests, meadows, shores, reefs, marshes, grasslands, and swamps. The species is 55 to 65 cm in length, with rich cinnamon upperparts and white underparts. The nankeen night heron has a stable population size, and is classified as a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

The broad-billed parrot or raven parrot is a large extinct parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius. The species was first referred to as the "Indian raven" in Dutch ships' journals from 1598 onwards. Only a few brief contemporary descriptions and three depictions are known. It was first scientifically described from a subfossil mandible in 1866, but this was not linked to the old accounts until the rediscovery of a detailed 1601 sketch that matched both the subfossils and the accounts. It is unclear what other species it was most closely related to, but it has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. It had similarities with the Rodrigues parrot, and may have been closely related.
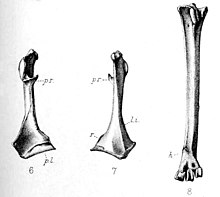
The Rodrigues night heron is an extinct species of heron that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the Indian Ocean. The species was first mentioned as "bitterns" in two accounts from 1691–1693 and 1725–1726, and these were correlated with subfossil remains found and described in the latter part of the 19th century. The bones showed that the bird was a heron, first named Ardea megacephala in 1873, but moved to the night heron genus Nycticorax in 1879 after more remains were described. The specific name megacephala is Greek for "great-headed". Two related extinct species from the other Mascarene islands have also been identified from accounts and remains: the Mauritius night heron and the Réunion night heron.

The Rodrigues rail, also known as Leguat's gelinote or Leguat's rail, is an extinct species of the rail family that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. The bird was first documented from life by two accounts from 1691–93 and 1725–26. Subfossil remains were later discovered and correlated with the old accounts in 1874, and the species was named E. leguati in Leguat's honour. It is generally kept in its own genus, Erythromachus, but has sometimes been assigned to the genus Aphanapteryx along with its close relative the red rail of Mauritius; their relationship with other rails is unclear.

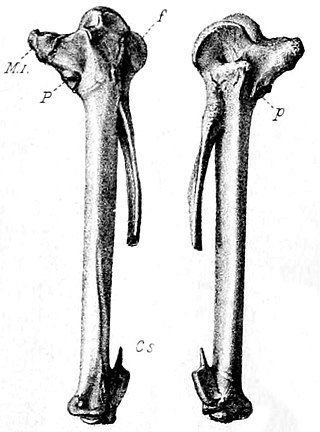
The red rail is an extinct species of rail that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. It had a close relative on Rodrigues island, the likewise extinct Rodrigues rail, with which it is sometimes considered congeneric, but their relationship with other rails is unclear. Rails often evolve flightlessness when adapting to isolated islands, free of mammalian predators, and that was also the case for this species. The red rail was a little larger than a chicken and had reddish, hairlike plumage, with dark legs and a long, curved beak. The wings were small, and its legs were slender for a bird of its size. It was similar to the Rodrigues rail, but was larger, and had proportionally shorter wings. It has been compared to a kiwi or a limpkin in appearance and behaviour.
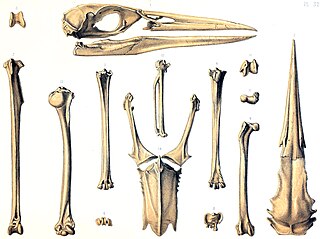
The Mauritius sheldgoose, also known as the Mauritius shelduck, is an extinct species of sheldgoose that was endemic to the island of Mauritius. While geese were mentioned by visitors to Mauritius in the 17th century, few details were provided by these accounts. In 1893, a carpometacarpus wing-bone and a pelvis from the Mare aux Songes swamp were used to name a new species of comb duck, Sarcidiornis mauritianus. These bones were connected to the contemporary accounts of geese and later determined to belong to a species related to the Egyptian goose and placed in the sheldgoose genus Alopochen. The Mauritius and Réunion sheldgoose may have descended from Egyptian geese that colonised the Mascarene Islands.

The Mascarene teal, also known as Sauzier's teal and Mauritian duck, is an extinct dabbling duck that formerly occurred on the islands of Mauritius and Réunion.

The Réunion night heron is an extinct species of heron formerly occurring on the Mascarene island of Réunion.

The Rodrigues parrot or Leguat's parrot is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. The species is known from subfossil bones and from mentions in contemporary accounts. It is unclear to which other species it is most closely related, but it is classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. The Rodrigues parrot bore similarities to the broad-billed parrot of Mauritius, and may have been related. Two additional species have been assigned to its genus, based on descriptions of parrots from the other Mascarene islands, but their identities and validity have been debated.

The extinct Mauritius scops owl, also known as Mauritius owl, Mauritius lizard owl, Commerson's owl, Sauzier's owl, or Newton's owl, was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius. It is known from a collection of subfossil bones from the Mare aux Songes swamp, a detailed sketch made by de Jossigny in 1770, a no less detailed description by Desjardins of a bird shot in 1836, and a number of brief reports about owls, the first being those of Van Westzanen in 1602 and Matelief in 1606.
Zeltornis is an extinct genus of heron. It contains a single species, Zeltornis ginsburgi.

The Rodrigues starling is an extinct species of starling that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. Its closest relatives were the Mauritius starling and the hoopoe starling from nearby islands; all three are extinct and appear to be of Southeast Asian origin. The bird was only reported by French sailor Julien Tafforet, who was marooned on the island from 1725 to 1726. Tafforet observed it on the offshore islet of Île Gombrani. Subfossil remains found on the mainland were described in 1879, and were suggested to belong to the bird mentioned by Tafforet. There was much confusion about the bird and its taxonomic relations throughout the 20th century.

The Réunion harrier, also known as Réunion marsh harrier, is a species of bird of prey belonging to the marsh harrier group of harriers. It is now found only on the Indian Ocean island of Réunion, although fossil material from Mauritius has been referred to this species. It is known locally as the papangue or pied jaune. The Malagasy harrier of Madagascar and the Comoro Islands was previously treated as a subspecies of this bird but is increasingly regarded as a separate species. The Réunion harrier appears to be declining in numbers and it is classed as an endangered species.

The Bermuda night heron is an extinct heron species from Bermuda.

The Mascarene grey parakeet, Mauritius grey parrot, or Thirioux's grey parrot, is an extinct species of parrot which was endemic to the Mascarene Islands of Mauritius and Réunion in the western Indian Ocean. It has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other parrots from the Islands.
The Rodrigues blue pigeon is an extinct species of blue pigeon which was endemic to Rodrigues. It is known only from the holotype tarsometatarsus collected in 2005, associated with remains of a Rodrigues night heron and a Rodrigues rail. A femur described in 1879 but now lost may also have belonged to the species. It was not specifically mentioned by contemporary writers, and it is therefore unknown when it became extinct.