
The North Shore is one of the major geographical regions of Auckland, the largest city in New Zealand. The area is defined as the northern shores of the Waitematā Harbour as far north as the Ōkura River.

Waitematā Harbour is the main access by sea to Auckland, New Zealand. The harbour forms the northern and eastern coasts of the Auckland isthmus and is crossed by the Auckland Harbour Bridge. It is matched on the southern side of the city by the shallower waters of the Manukau Harbour.

Panmure is an east Auckland suburb, in the North Island of New Zealand. It is located 11 kilometres southeast of the Auckland CBD, close to the western banks of the Tāmaki River and the northern shore of the Panmure Basin. To the north lies the suburb of Tāmaki, and to the west is the cone of Maungarei / Mount Wellington.

Waitematā railway station, formerly known as Britomart Transport Centre, is the public transport hub in the central business district of Auckland and the northern terminus of the North Island Main Trunk railway line. It combines a railway station in a former Edwardian post office, extended with expansive modernist architectural elements, with a bus interchange. It is at the foot of Queen Street, the main commercial thoroughfare of the CBD, with the main ferry terminal just across Quay Street.

Parnell is a suburb of Auckland, New Zealand. It is one of New Zealand's most affluent suburbs, consistently ranked within the top three wealthiest, and is often billed as Auckland's "oldest suburb" since it dates from the earliest days of the European settlement of Auckland in 1841. It is characterised by its mix of tree-lined streets with large estates; redeveloped industrial zones with Edwardian town houses and 1920s bay villas; and its hilly topography that allows for views of the port, the Waitematā Harbour, Rangitoto Island and the Auckland Domain. To its west lies the Auckland Domain, to the south Newmarket, and to the north the Ports of Auckland.

Saint Marys Bay is an inner suburb of Auckland, New Zealand.

Riverhead is a small, historically predominantly working-class town located at the head of the Waitematā Harbour in the north-west of Auckland, New Zealand. It is located on the northwestern shores of the Upper Waitematā Harbour, north-east of the towns of Kumeū and Huapai.

The Strand Station, also referred to as Auckland Strand Station, is a railway station located on the eastern edge of the Auckland CBD. It serves as the long-distance railway station for Auckland. It is the northern terminus of the Northern Explorer service between Auckland and Wellington, and the northern terminus for the Te Huia service between Auckland and Hamilton. Suburban services are not scheduled to pass through the station, however, it serves as a backup for Waitematā railway station during times of disruption.

Huapai is a locality north-west of Auckland, New Zealand. State Highway 16 and the North Auckland Railway Line pass through it. Kumeū is adjacent to the east, Riverhead is to the north-east, and Waimauku to the west.

Takaparawhau / Bastion Point is a coastal piece of land in Ōrākei, Auckland, New Zealand, overlooking the Waitematā Harbour. The area is significant in New Zealand history as the site of protests in the late 1970s by Māori against forced land alienation by Pākehā. Takaparawhau is now the site of the private Ōrākei Marae, the public Michael Joseph Savage Memorial, and privately-owned reserve land that is accessible to the public.

The Auckland isthmus, also known as the Tāmaki isthmus, is a narrow stretch of land on the North Island of New Zealand in the Auckland Region, and the location of the central suburbs of the city of Auckland, including the CBD. The isthmus is located between two rias : the Waitematā Harbour to the north, which opens to the Hauraki Gulf / Tīkapa Moana and Pacific Ocean, and the Manukau Harbour to the south, which opens to the Tasman Sea. The isthmus is the most southern section of the Northland Peninsula.
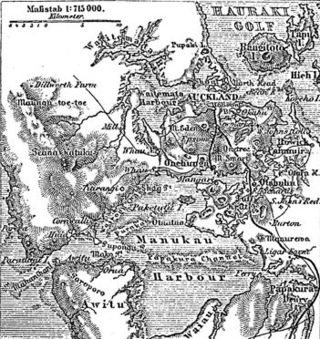
The human history of the Auckland metropolitan area stretches from early Māori settlers in the 14th century to the first European explorers in the late 18th century, over a short stretch as the official capital of (European-settled) New Zealand in the middle of the 19th century to its current position as the fastest-growing and commercially dominating metropolis of the country.

Commercial Bay was a historic bay on the southern side of the Waitematā Harbour that defined the original extent of the Auckland waterfront in Auckland, New Zealand. Today, the name Commercial Bay refers to the heavily developed area around lower Queen Street and Viaduct Harbour.

The Auckland Central Business District (CBD), or Auckland city centre, is the geographical and economic heart of the Auckland metropolitan area. It is the area in which Auckland was established in 1840, by William Hobson on land gifted by mana whenuahapū Ngāti Whātua Ōrākei. It is New Zealand's leading financial hub, and the centre of the country's economy; the GDP of the Auckland Region was NZD$139 billion in the year ending September 2023.

Point Britomart was a headland in the Waitematā Harbour, in Auckland, New Zealand. Located between Commercial Bay and Official Bay, the point was later quarried away to produce fill for land reclamation in Mechanics Bay, and almost no physical trace remains at street level in what is today an area of the Auckland CBD and the Auckland waterfront.

Achilles Point is a rocky point on the headland at the eastern end of the small sandy beach named Ladies Bay, Auckland, New Zealand. The name 'Te Pane o Horoiwi' can also sometimes refer to the whole headland between St Heliers and Tamaki River estuary. Achilles Point is named after a ship called HMNZS Achilles (70) which defeated the German pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee in 1939. The headland, from the point round to the Tamaki heads, was previously known as Te Pane o Horoiwi, named after Horoiwi who arrived in New Zealand on the Tainui canoe (waka).

Tamaki Drive is the coastal road which follows the contours of the Waitematā Harbour, Auckland, New Zealand. The road links the suburbs Ōrākei, Mission Bay, and Kohimarama ending in Saint Heliers providing easy access to the local beaches. Tamaki Drive was completed in 1932 and incorporates The Strand, Bice Esplanade and, what was once part of the old Kohimarama Road. It is also referred to as the Waterfront Road. Tamaki Drive is a flat road around 8 km long and popular with walkers, runners and roller skaters, and includes a dedicated cycle lane. Those travelling along Tamaki Drive can find scenic highlights and peaceful views across the harbour to the volcanic island Rangitoto. The cliffs backing onto Tamaki Drive are made of Waitematā Sandstone strata clothed in places with pōhutukawa. These trees seem to flower out of season, because these are actually Kermadec pōhutukawa with small distinctive roundish leaves.

West Auckland is one of the major geographical areas of Auckland, the largest city in New Zealand. Much of the area is dominated by the Waitākere Ranges, the eastern slopes of the Miocene era Waitākere volcano which was upraised from the ocean floor, and now one of the largest regional parks in New Zealand. The metropolitan area of West Auckland developed between the Waitākere Ranges to the west and the upper reaches of the Waitematā Harbour to the east. It covers areas such as Glen Eden, Henderson, Massey and New Lynn.

Portages in New Zealand, known in Māori as Tō or Tōanga Waka, are locations where waka (canoes) could easily be transported overland. Portages were extremely important for early Māori, especially along the narrow Tāmaki isthmus of modern-day Auckland, as they served as crucial transportation and trade links between the east and west coasts. Portages can be found across New Zealand, especially in the narrow Northland and Auckland regions, and the rivers of the Waikato Region.

Shoal Bay is a bay of the Waitematā Harbour in Auckland, New Zealand. It is located on the North Shore.

























