Force H was a British naval formation during the Second World War. It was formed in late-June 1940, to replace French naval power in the western Mediterranean removed by the French armistice with Nazi Germany. The force occupied an odd place within the naval chain of command. Normal British practice was to have naval stations and fleets around the world, whose commanders reported to the First Sea Lord via a flag officer. Force H was based at Gibraltar but there was already a flag officer at the base, Flag Officer Commanding, North Atlantic. The commanding officer of Force H did not report to this Flag Officer but directly to the First Sea Lord, Admiral of the Fleet Sir Dudley Pound.

The attack on Mers-el-Kébir on 3 July 1940, during the Second World War, was a British naval attack on neutral French Navy ships at the naval base at Mers El Kébir, near Oran, on the coast of French Algeria. The attack was the main part of Operation Catapult, a British plan to neutralise or destroy neutral French ships to prevent them from falling into German hands after the Allied defeat in the Battle of France. The British bombardment of the base killed 1,297 French servicemen, sank a battleship and damaged five other ships, for a British loss of five aircraft shot down and two crewmen killed. The attack by air and sea was conducted by the Royal Navy, after France had signed armistices with Germany and Italy, coming into effect on 25 June.

Admiral of the Fleet Sir James Fownes Somerville, was a Royal Navy officer. He served in the First World War as fleet wireless officer for the Mediterranean Fleet where he was involved in providing naval support for the Gallipoli Campaign. He also served in the Second World War as commander of the newly formed Force H: after the French armistice with Germany, Winston Churchill gave Somerville and Force H the task of neutralizing the main element of the French battle fleet, then at Mers El Kébir in Algeria. After he had destroyed the French Battle fleet, Somerville played an important role in the pursuit and sinking of the German battleship Bismarck.

The Battle of the Mediterranean was the name given to the naval campaign fought in the Mediterranean Sea during World War II, from 10 June 1940 to 2 May 1945.

Strasbourg was the second and final member of the Dunkerque class of fast battleships built for the French Navy in the 1930s. She and her sister ship Dunkerque were designed to defeat the German Deutschland class of heavy cruisers that had been laid down beginning in the late 1920s, and as such were equipped with a battery of eight 330 mm (13 in) guns to counter the six 280 mm (11 in) guns of the Deutschlands. Strasbourg was laid down in November 1934, was launched in December 1936, and was commissioned in September 1938 as the international situation in Europe was steadily deteriorating due to Nazi Germany's increasingly aggressive behavior.

The Algerian Naval Force is the naval branch of the Algerian military. The naval force operates from multiple bases along the country's nearly 1,440 km (890 mi) coastline, fulfilling its primary role of monitoring and defending Algeria's territorial waters against all foreign military or economic intrusion. Additional missions include coast guard and maritime safety missions as well a projection of marine forces. Algerian forces are an important player in the Western Mediterranean.

Provence was one of three Bretagne-class battleships built for the French Navy in the 1910s, named in honor of the French region of Provence; she had two sister ships, Bretagne and Lorraine. Provence entered service in March 1916, after the outbreak of World War I. She was armed with a main battery of ten 340 mm (13.4 in) guns and had a top speed of 20 knots.

HMS Foxhound was one of nine F-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1930s. Although she was assigned to the Home Fleet, the ship was detached as part of the Mediterranean Fleet to enforce the arms blockade imposed by Britain and France on both sides during the Spanish Civil War of 1936–39. Several weeks after the start of the Second World War in September 1939, Foxhound helped to sink a German submarine and participated in the Second Battle of Narvik during the Norwegian Campaign of April–June 1940. The ship was sent to Gibraltar in mid-1940 and formed part of Force H where she participated in the attack on Mers-el-Kébir. Foxhound escorted the aircraft carriers of Force H as they flew off aircraft for Malta and covered convoys resupplying and reinforcing the island until late 1941. During this time the ship helped to sink another German submarine.

Rigault de Genouilly (PG-80) was a Bougainville-class aviso of the French Navy. She was designed to operate from French colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific Ocean. During World War II, Rigault de Genouilly served on the side of the Allies until June 1940, and then in the naval forces of Vichy France. She was sunk in July 1940.
Méduse (NN5) was a French Navy Diane-class submarine commissioned in 1932. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. She was wrecked in November 1942.

The Spanish conquest of Oran and Mers el-Kebir took place from 15 June to 2 July 1732, between the Kingdom of Spain and the Deylik of Algiers. The great Spanish expedition led by Don José Carrillo de Albornoz, Duke of Montemar and Don Francisco Javier Cornejo defeated the Algerian troops under the command of the Bey of the Beylik of Oran, Mustapha Bouchelaghem, and the Wali of Oran, Hassan. It successfully conquered the fortress-cities of Oran and Mers el-Kebir, ruled and administered by Algiers from 1708, during the War of the Spanish Succession, when both cities were conquered by the aforementioned Bouchelaghem, who was the governor of the western regions of Algiers.
Fleuret was one of a dozen Le Hardi-class destroyers built for the Marine Nationale during the late 1930s. The ship was completed during the Battle of France in mid-1940 and her first mission was to help escort a battleship to Dakar, French West Africa, only days before the French signed an armistice with the Germans. After the British attack on Dakar in September, she was one of four destroyers ordered to attack British shipping, although there was only an inconclusive duel with a British destroyer. Fleuret helped to escort one of the battleships damaged by the British during their July attack on Mers-el-Kébir, French Algeria, back to France in November and was then reduced to reserve.
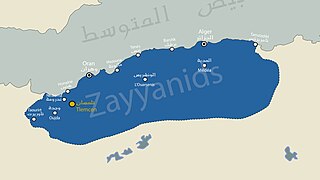
The Capture of Mers-el-Kébir on 13 September 1505 was the first campaign carried out by the Spanish Empire in its war against the Zayyanid Kingdom of Tlemcen. Mers-el-Kébir was a roadstead open to the southwest winds, and a refuge for corsairs. The port was protected by a strong and well-armed castle, and it had already been unsuccessfully attacked by Portuguese troops in 1496 and 1501.

Ariane (Q122) was a French Navy Ariane-class submarine commissioned in 1929. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. She was scuttled in November 1942.

Eurydice (Q130) was a French Navy Ariane-class submarine commissioned in 1929. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. She was scuttled in November 1942.

Danaé (Q131) was a French Navy Ariane-class submarine commissioned in 1929. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. She was scuttled in November 1942.
Diane was a French Navy Diane-class submarine commissioned in 1932, the lead ship of her class. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. She was scuttled in November 1942.
Orphée (Q163) was a French Navy Diane-class submarine commissioned in 1933. During World War II, she operated on the Allied side until 1940, when she became part of the naval forces of Vichy France. In 1942 she joined the Free French Naval Forces. She was condemned in 1946.
La Sultane (Q177) was an Argonaute-class submarine commissioned into service in the French Navy in 1935. She saw service in World War II, first on the side of the Allies from September 1939 to June 1940, then in the forces of Vichy France until November 1942, when she became part of the Free French Naval Forces. She was stricken in 1946.

US Naval Bases in North Africa were sea ports and air base used in North Africa during World War II by the United States Navy. The ports and air bases supplied the troops of the Allies armies in the flight against German and Italian forces in the North African campaign and Western Desert campaign. Later the bases supported the invasion of Italy. The ports and airfields were used after their surrender in Operation Torch. Amphibious Training Bases (ATB) were built in Algeria and Tunisia to prepare for the upcoming invasions. Seabees, United States Naval Construction Battalions, did most of the repair work, new construction, and maintaining work at the bases.