
Vaccinium is a common and widespread genus of shrubs or dwarf shrubs in the heath family (Ericaceae). The fruits of many species are eaten by humans and some are of commercial importance, including the cranberry, blueberry, bilberry (whortleberry), lingonberry (cowberry), and huckleberry. Like many other ericaceous plants, they are generally restricted to acidic soils.

Vaccinium vitis-idaea, the lingonberry, partridgeberry, mountain cranberry or cowberry, is a small evergreen shrub in the heath family Ericaceae, that bears edible fruit. It is native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from Europe and Asia to North America. Lingonberries are picked in the wild and used to accompany various dishes, primarily in the Nordics. Commercial cultivation is undertaken in the U.S. Pacific Northwest and in the Netherlands.

Bilberries or blueberries are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus Vaccinium, bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is Vaccinium myrtillus L., but there are several other closely related species.
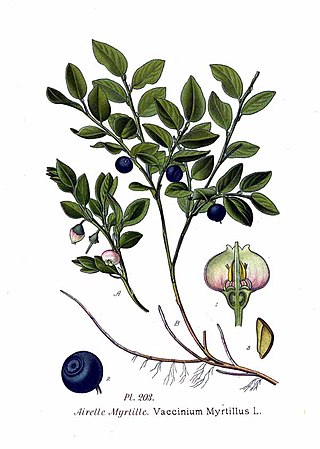
Vaccinium myrtillus or European blueberry is a holarctic species of shrub with edible fruit of blue color, known by the common names bilberry, blaeberry, wimberry, and whortleberry. It is more precisely called common bilberry or blue whortleberry to distinguish it from other Vaccinium relatives.

Vaccinium corymbosum, the northern highbush blueberry, is a North American species of blueberry which has become a food crop of significant economic importance. It is native to eastern Canada and the eastern and southern United States, from Ontario east to Nova Scotia and south as far as Florida and eastern Texas. It is also naturalized in other places: Europe, Japan, New Zealand, the Pacific Northwest of North America, etc. Other common names include blue huckleberry, tall huckleberry, swamp huckleberry, high blueberry, and swamp blueberry.

Vaccinium arboreum is a species of Vaccinium native to the southeastern and south-central United States, from southern Virginia west to southeastern Nebraska, south to Florida and eastern Texas, and north to Illinois.

Vaccinium uliginosum is a Eurasian and North American flowering plant in the genus Vaccinium within the heath family.

Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section Cyanococcus within the genus Vaccinium. Vaccinium also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s.

Metaxmeste is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

Huckleberry is a name used in North America for several plants in the family Ericaceae, in two closely related genera: Vaccinium and Gaylussacia.

Glacies is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Pierre Millière in 1874.

Metaxmeste phrygialis is a species of moth of the family Crambidae described by Jacob Hübner in 1976. It is found in mountainous areas of Europe, including the Alps.

Dysstroma infuscata is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Johan Martin Jakob von Tengström in 1869. It is found from Scandinavia, Poland and the Czech Republic to the Amur River and Sakhalin.

Odontiinae is a subfamily of moths of the family Crambidae. The subfamily was described by Achille Guenée in 1854.

Ancylis myrtillana is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It was described by Treitschke in 1830. It is found in most of Europe and across the Palearctic.It has also been recorded in North America. The habitat consists of moorland.

Ceruchus is a genus of stag beetles in the family Lucanidae. There are about 19 described species in Ceruchus.

Ibalia leucospoides, the knife-shaped ibalia, is a species of ibaliid wasp in the family Ibaliidae.

Ibalia is a genus of ibaliid wasps in the family Ibaliidae. There are about 14 described species in Ibalia. All species are parasitoids of Siricidae species, which they seek out by detecting volatiles emitted by the fungi Siricidae larvae feed on, Amylostereum.
Sigmund von Hochenwarth was an Austrian botanist and entomologist. von Hochenwarth was a Domherr in Gurk, Carinthia. He described Ibalia leucospoides. He wrote:

Ceruchus chrysomelinus is a species of beetle belonging to the family Lucanidae.

















