
MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) is an organic compound. It is classified as a tetrahydropyridine. It is of interest as a precursor to the neurotoxin MPP+, which causes permanent symptoms of Parkinson's disease by destroying dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain. It has been used to study disease models in various animals.
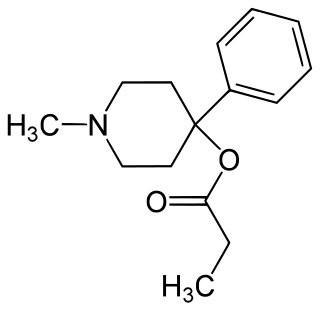
Desmethylprodine or 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1940s by researchers at Hoffmann-La Roche. Desmethylprodine has been labeled by the DEA as a Schedule I drug in the United States. It is an analog of pethidine (meperidine) a Schedule II drug. Chemically, it is a reversed ester of pethidine which has about 70% of the potency of morphine. Unlike its derivative prodine, it was not reported to exhibit optical isomerism. It was reported to have 30 times the activity of pethidine and a greater analgesic effect than morphine in rats, and it was demonstrated to cause central nervous system stimulation in mice.

Isoquinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It is a structural isomer of quinoline. Isoquinoline and quinoline are benzopyridines, which are composed of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring. In a broader sense, the term isoquinoline is used to make reference to isoquinoline derivatives. 1-Benzylisoquinoline is the structural backbone in naturally occurring alkaloids including papaverine. The isoquinoline ring in these natural compound derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine.

Phenylacetone, also known as phenyl-2-propanone, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2COCH3. It is a colorless oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of an acetone attached to a phenyl group. As such, its systematic IUPAC name is 1-phenyl-2-propanone.
J. William Langston is the founder and chief scientific officer, movement disorder specialist, and chief executive officer of the Parkinson's Institute and Clinical Center in Sunnyvale, California, the founding member of the Scientific Advisory Board for the Michael J. Fox Foundation and the Co-Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Parkinson's Disease. He is a graduate of the University of Missouri School of Medicine. Langston was formerly a faculty member at Stanford University and Chairman of Neurology at Santa Clara Valley Medical Center in San Jose, California. Langston has authored or co-authored some 360 peer-reviewed articles in the field of neurology, most of which are on Parkinson's disease and related disorders. Langston gained national and international recognition in 1982 for the discovery of the link between a "synthetic heroin" contaminant (MPTP) and parkinsonism.

The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid.

The BH3 interacting-domain death agonist, or BID, gene is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members share one or more of the four characteristic domains of homology entitled the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains, and can form hetero- or homodimers. Bcl-2 proteins act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities.

Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), also known as dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3 and trimethylamine monooxygenase, is a flavoprotein enzyme (EC 1.14.13.148) that in humans is encoded by the FMO3 gene. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction, among others:
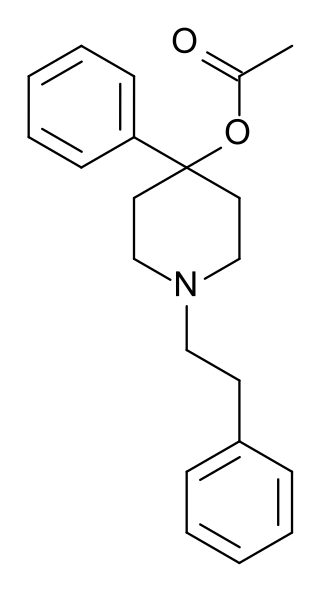
PEPAP (phenethylphenylacetoxypiperidine) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of Desmethylprodine.
In enzymology, a N-methylcoclaurine 3'-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Piroheptine is an anticholinergic and antihistamine used as an antiparkinsonian agent.

4-Benzylpiperidine is a drug and research chemical used in scientific studies. It acts as a monoamine releasing agent with 20- to 48-fold selectivity for releasing dopamine versus serotonin. It is most efficacious as a releaser of norepinephrine, with an ec50 of 109/41.4/5246nM for DA/NE/5HT, respectively. It has a fast onset of action and a short duration. It also functions as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) with preference for MAO-A.

d-Deprenyl, also known as or dextro-N-propargyl-N-methylamphetamine, is an MAO-B inhibitor that metabolizes into d-amphetamine and d-methamphetamine and is therefore also a norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent. It is the opposite enantiomer of l-deprenyl (selegiline).
The molecular formula C12H15N (molar mass: 173.25 g/mol, exact mass: 173.1204 u) may refer to:
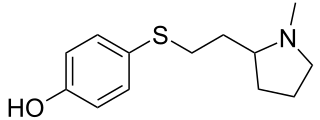
SIB-1553A is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that is selective for receptors with a β4 subunit. Administration of SIB-1553A improved memory and attention in a Parkinson's disease model.
John P. Walsh is an American academic who is an associate professor at the USC Davis School of Gerontology as well as a member of USC's Neuroscience Program. His main research interest is the physiology of basal ganglia-related brain disease.

UWA-101 is a phenethylamine derivative invented by Dr Matthew Piggott at the University of Western Australia, and researched as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease. Its chemical structure is very similar to that of the illegal drug MDMA, the only difference being the replacement of the α-methyl group with an α-cyclopropyl group. MDMA has been found in animal studies and reported in unauthorised human self-experiments to be effective in the short-term relief of side-effects of Parkinson's disease therapy, most notably levodopa-induced dyskinesia. However the illegal status of MDMA and concerns about its potential for recreational use, neurotoxicity and potentially dangerous side effects mean that it is unlikely to be investigated for medical use in this application, and so alternative analogues were investigated.

4-Methylphenethylamine (4MPEA), also known as para-methylphenethylamine, is an organic compound with the chemical formula of C9H13N. 4MPEA is a human trace amine associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonist, a property which it shares with its monomethylated phenethylamine isomers, such as amphetamine (α-methylphenethylamine), β-methylphenethylamine, and N-methylphenethylamine. 4MPEA also appears to inhibit the human cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP1A2 and CYP2A6, based upon the published literature.
1-Bromo-3-chloropropane is an organohalogen compound with the formula Br(CH2)3Cl. It is a colorless liquid, produced by free-radical addition of hydrogen bromide to allyl chloride. It is used as an alkylating agent to install the –(CH2)3Cl and –(CH2)3– groups. For example, it is a precursor to 4-chlorobutyronitrile.

Tetrahydropyridines are heterocycles with the formula C5H9N. Three isomers exist, which differ by the location of the double bond. All three are chiral. None of the parent species occur widely, so they are mainly of theoretical interest. Although the parent tetrahydropyridines are rare, many substituted tetrahydropyridines are known.















