
The Rubiaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with interpetiolar stipules and sympetalous actinomorphic flowers. The family contains about 13,500 species in about 620 genera, which makes it the fourth-largest angiosperm family. Rubiaceae has a cosmopolitan distribution; however, the largest species diversity is concentrated in the tropics and subtropics. Economically important genera include Coffea, the source of coffee, Cinchona, the source of the antimalarial alkaloid quinine, ornamental cultivars, and historically some dye plants.

Psychotria viridis, also known as chacruna, chacrona, or chaqruy in the Quechua languages, is a perennial, shrubby flowering plant in the coffee family Rubiaceae. It is a close relative of Psychotria carthagenensis of Ecuador. It is commonly used as an ingredient of ayahuasca, a decoction with a long history of its entheogenic use and its status as a "plant teacher" among the Indigenous peoples of the Amazon rainforest.

Psychotria carthagenensis, also known as amyruca, is a South American rainforest understory shrub from the coffee family, Rubiaceae. It grows from the tropics of South America to Mexico.

Gracillariidae is an important family of insects in the order Lepidoptera and the principal family of leaf miners that includes several economic, horticultural or recently invasive pest species such as the horse-chestnut leaf miner, Cameraria ohridella.

Psychotria is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 1,582 species and is therefore one of the largest genera of flowering plants. The genus has a pantropical distribution and members of the genus are small understorey trees in tropical forests. Some species are endangered or facing extinction due to deforestation, especially species of central Africa and the Pacific.

Palicourea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 694 species, which range from shrubs to small trees, and is distributed throughout the New World tropics.

Psychotria colorata is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It has been documented in an ethnobotanical context among the Ka'apor people of Maranhão, Brazil by Dr. William Balée, the Tulane University anthropologist and historical ecologist:
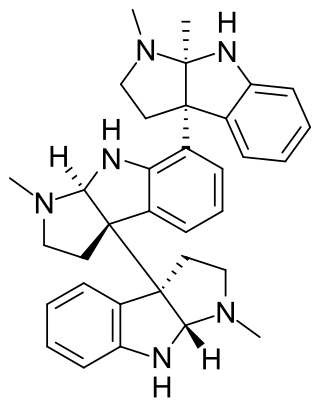
Hodgkinsine is an alkaloid found in plants of the genus Psychotria, particularly Psychotria colorata, although it is also found in Psychotria lyciiflora and probably other species in this family,

Psychotria mariniana, the forest wild coffee or kōpiko, is a tree endemic to Hawaiʻi. The plant belongs to the Rubiaceae (coffee) family, subfamily Rubioidae. It is a tree of varying size with a dark bark, shiny leaves, and orange oval fruit.
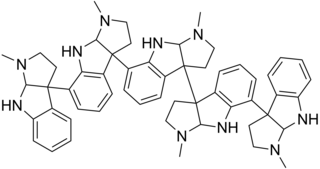
Psychotridine is an alkaloid found in some species of the genus Psychotria, namely Psychotria colorata, but also Psychotria forsteriana, Psychotria lyciiflora, Psychotria oleoides, and Psychotria beccarioides. Psychotridine has analgesic effects and dose-dependently inhibits dizocilpine binding to cortical membranes in vitro, suggesting that it acts as a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist.

Psychotria nervosa, also known as Seminole balsamo or wild coffee, is a shade tolerant medium-sized shrub native to Florida as well as the West Indies and Central and South America. It produces a "small, red, ellipsoid fruit" that resembles "the true coffee bean" in shape and attract birds. Its maximum height ranges from approximately 4–10 feet.

Psychotria ligustrifolia, the Bahama wild coffee, is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to Florida, Puerto Rico, and the Bahamas.

Xylophanes hannemanni is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is known from Mexico, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama and further south through Ecuador to Peru and Bolivia.

Xylophanes zurcheri is a moth of the family Sphingidae first described by Herbert Druce in 1894.

Gracillariinae are a subfamily of moths which was described by Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1854.

Psychotrieae is a tribe of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae and contains about 2114 species in 17 genera. Its representatives are found in the tropics and subtropics. Several genera are Myrmecophytes

Psychotria dallachiana is a rainforest plant growing in north eastern Australia. The fruit is food for the cassowary.

Psychotria tenuifolia, commonly known as velvet-leaved wild coffee, is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is endemic to southern Florida, South America and the Caribbean. The description of velvet is based on the silky appearance that the leaves display in relation to other species of the same plant family.

Psychotria serpens, the creeping psychotria, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae, native to Peninsula Malaysia, Southeast Asia, southeastern China, Hainan, Taiwan, the Ryukyu Islands, and central and southern Japan. A creeping or climbing perennial liana, it is typically found in thickets and forests, from 100 to 1,400 m above sea level. It is often substituted for "Caulis Trachelospermi" in traditional Chinese medicine preparations sold to people with cancer.

















