Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name, or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name.

Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus Gadus is commonly not called cod.

Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The Sturnidae are named for the genus Sturnus, which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.

The great black-backed gull is the largest member of the gull family. Described by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology as "the king of the Atlantic waterfront", it is a very aggressive hunter, pirate, and scavenger. It breeds on the European and North American coasts and islands of the North Atlantic and is fairly sedentary, though some move farther south or inland to large lakes or reservoirs. The adult great black-backed gull has a white head, neck and underparts, dark grey wings and back, pink legs and yellow bill.

The Geoemydidae are one of the largest and most diverse families in the order Testudines (turtles), with about 70 species. The family includes the Eurasian pond and river turtles and Neotropical wood turtles. Members of this family are commonly called Leaf turtle.
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen. A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus.

Zmudowski State Beach is located on Monterey Bay, in Moss Landing, Monterey County, northern California.

The Sainte-Anne River, a north shore tributary of Saint Lawrence River, the mouth river is located at Sainte-Anne-de-la-Pérade. This river flows in the province of Quebec, Canada.
Administrative regions
Capitale-Nationale:
Mauricie:
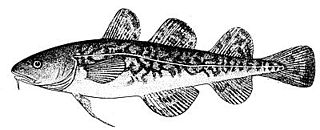
Microgadus tomcod, also commonly known as frostfish, Atlantic tomcod or winter cod, is a type of cod found in North American coastal waters from the Gulf of St. Lawrence, St. Lawrence River and northern Newfoundland, south to Virginia.

In biology, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system of biological classification (taxonomy) consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics.

Benthodesmus is a genus of fish in the family Trichiuridae. There are at least eleven species in this genus, which are known as frostfish. These are not to be confused with Microgadus tomcod and Lepidopus caudatus also known as frostfish.

Microgadus proximus, also commonly known as Pacific tomcod, is a type of cod fish found in North American coastal waters from the southeastern Bering Sea to central California. This species can reach a length of 30.5 cm (12.0 in).
The Bouleau River is a salmon river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It drains an area of the Canadian Shield plateau into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The terrain includes large areas of bare rocks, as well as forests dominated by black spruce and balsam fir.
The Véco River is a salmon river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada, that empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It has been dammed to supply a hydroelectric power plant. The shoreline around the mouth of the river is protected as part of a federal bird sanctuary.
The Véronique River is a river in the Côte-Nord region of the province of Quebec, Canada. It flows into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, opposite to Anticosti Island.

Mingan River is a 117-kilometre (73 mi) salmon river of the Côte-Nord region of Quebec. It flows from north to south and empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.













