
Eomaia is a genus of extinct fossil mammals containing the single species Eomaia scansoria, discovered in rocks that were found in the Yixian Formation, Liaoning Province, China, and dated to the Barremian Age of the Lower Cretaceous about 125 million years ago. The single fossil specimen of this species is 10 centimetres (3.9 in) in length and virtually complete. An estimate of the body weight is 20–25 grams (0.71–0.88 oz). It is exceptionally well-preserved for a 125-million-year-old specimen. Although the fossil's skull is squashed flat, its teeth, tiny foot bones, cartilages and even its fur are visible.

Catopsbaatar is a genus of multituberculate, an extinct order of rodent-like mammals. It lived in what is now Mongolia during the late Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 72 million years ago. The first fossils were collected in the early 1970s, and the animal was named as a new species of the genus Djadochtatherium in 1974, D. catopsaloides. The specific name refers to the animal's similarity to the genus Catopsalis. The species was moved to the genus Catopsalis in 1979, and received its own genus in 1994. Five skulls, one molar, and one skeleton with a skull are known; the last is the genus' most complete specimen. Catopsbaatar was a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae.

Eutheria, also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placentals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.
Ferugliotherium is a genus of fossil mammals in the family Ferugliotheriidae from the Campanian and/or Maastrichtian period of Argentina. It contains a single species, Ferugliotherium windhauseni, which was first described in 1986. Although originally interpreted on the basis of a single brachydont (low-crowned) molar as a member of Multituberculata, an extinct group of small, rodent-like mammals, it was recognized as related to the hypsodont (high-crowned) Sudamericidae following the discovery of additional material in the early 1990s. After a jaw of the sudamericid Sudamerica was described in 1999, these animals were no longer considered to be multituberculates and a few fossils that were previously considered to be Ferugliotherium were assigned to unspecified multituberculates instead. Since 2005, a relationship between gondwanatheres and multituberculates has again received support. A closely related animal, Trapalcotherium, was described in 2009 on the basis of a single tooth.

Metatheria is a mammalian clade that includes all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. First proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1880, it is a more inclusive group than the marsupials; it contains all marsupials as well as many extinct non-marsupial relatives. It is one of two groups placed in the clade Theria alongside Eutheria, which contains the placentals. Remains of metatherians have been found on all of Earth’s continents.

Lama is a genus containing the South American camelids: the wild guanaco and vicuña and the domesticated llama, alpaca, and the extinct chilihueque. Before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, llamas, alpacas, and chilihueques were the only domesticated ungulates of the continent. They were kept not only for their value as beasts of burden, but also for their flesh, hides, and wool.
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammalian order. The best-known representative of Ferugliotheriidae is the genus Ferugliotherium from the Late Cretaceous epoch in Argentina. A second genus, Trapalcotherium, is known from a single tooth, a first lower molariform, from a different Late Cretaceous Argentinean locality. Another genus known from a single tooth, Argentodites, was first described as an unrelated multituberculate, but later identified as possibly related to Ferugliotherium. Finally, a single tooth from the Paleogene of Peru, LACM 149371, perhaps a last upper molariform, and a recent specimen from Mexico, may represent related animals.

Plesiadapis is one of the oldest known primate-like mammal genera which existed about 58–55 million years ago in North America and Europe. Plesiadapis means "near-Adapis", which is a reference to the adapiform primate of the Eocene period, Adapis. Plesiadapis tricuspidens, the type specimen, is named after the three cusps present on its upper incisors.
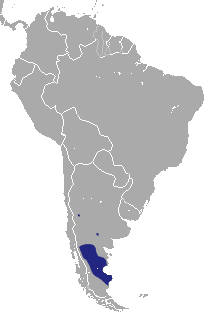
The Patagonian opossum(Lestodelphys halli) is the sole species in genus Lestodelphys.

Gobiconodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammals belonging to the family Gobiconodontidae. Undisputed records of Gobiconodon are restricted to the Early Cretaceous of Asia and North America, but isolated teeth attributed to the genus have also been described from formations in England and Morocco dating as far back as the Middle Jurassic. Species of Gobiconodon varied considerably in size, with G. ostromi, one of the larger species, being around the size of a modern Virginia opossum. Like other gobiconodontids, it possessed several speciations towards carnivory, such as shearing molariform teeth, large canine-like incisors and powerful jaw and forelimb musculature, indicating that it probably fed on vertebrate prey. Unusually among predatory mammals and other eutriconodonts, the lower canines were vestigial, with the first lower incisor pair having become massive and canine-like. Like the larger Repenomamus there might be some evidence of scavenging.

Tillodontia is an extinct suborder of eutherian mammals known from the Early Paleocene to Late Eocene of China, the Late Paleocene to Middle Eocene of North America where they display their maximum species diversity, the Middle Eocene of Pakistan, and the Early Eocene of Europe. Leaving no descendants, they are most closely related to the pantodonts, another extinct group. The tillodonts were medium- to large-sized animals that probably fed on roots and tubers in temperate to subtropical habitats.

Pipistrellus raceyi, also known as Racey's pipistrelle, is a bat from Madagascar, in the genus Pipistrellus. Although unidentified species of Pipistrellus had been previously reported from Madagascar since the 1990s, P. raceyi was not formally named until 2006. It is apparently most closely related to the Asian species P. endoi, P. paterculus, and P. abramus, and its ancestors probably reached Madagascar from Asia. P. raceyi has been recorded at four sites, two in the eastern and two in the western lowlands. In the east, it is found in open areas and has been found roosting in a building; in the west it occurs in dry forest. Because of uncertainties about its ecology, it is listed as "Data Deficient" on the IUCN Red List.
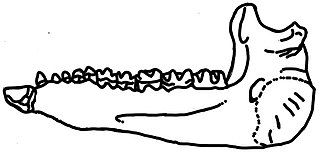
Urtinotherium is an extinct genus of paracerathere mammals. It was a large animal that was closely related to Paraceratherium, and found in rocks dating from the Late Eocene to Early Oligocene period. The remains were first discovered in the Urtyn Obo region in Inner Mongolia, which the name Urtinotherium is based upon. Other referred specimens are from northern China.
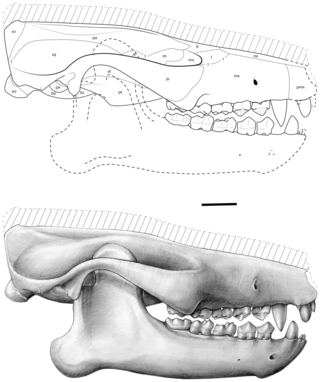
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.
Azilestes is a genus of probable zhelestid eutherian mammal, a family consisting of small herbivores, that was discovered in the early Maastrichtian Grès de Labarre Formation of France. It is a monotypic genus, with only type species A. ragei being known. Only one specimen, the holotype described in 2021, is known. It consists of a partial dentary with teeth.

Gypsonictops is an extinct genus of leptictidan mammals of the family Gypsonictopidae, which was described in 1927 by George Gaylord Simpson. Species in this genus were small mammals and the first representatives of the order Leptictida, that appeared during the Upper Cretaceous.
Ambolestes is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Ambolestes zhoui, known from a single complete skeleton recovered from the Yixian Formation, part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. Ambolestes is one of the most basal eutherians, presenting a combination of features from both early eutherians (stem-placentals) and early metatherians (stem-marsupials). This is responsible for the generic name of Ambolestes: "ambo" is Latin for "both", while "-lestes" is a popular suffix for fossil mammals. The species name honors influential Jehol paleontologist Zhou Zhonghe.
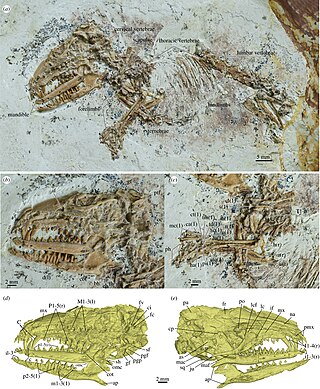
Cokotherium is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Cokotherium jiufotangensis, known from a single partial skeleton, missing a portion of the hindlimbs and tail. It was recovered from the Jiufotang Formation, the upper part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. The generic name of Cokotherium honors the nickname of the late paleontologist Chuan-Kui Li, a specialist on the Jiufotang Formation. The specific name refers to the formation in question. Cokotherium is one of the youngest and most well-preserved Early Cretaceous eutherians, illustrating an array of transitional conditions between Early Cretaceous and Late Cretaceous members of Eutheria.
Chaoyangodens is an extinct genus of eutriconodont mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Chaoyangodens lii, known from a single complete skeleton recovered from the Dawangzhangzi bed of the Yixian Formation, part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. Chaoyangodens was a moderate-sized Mesozoic mammal. The generic name refers to Chaoyang Prefecture while the specific name honors the collector of the fossil, Hai-Jun Li. Chaoyangodens is intermediate in age between Liaoconodon and a diverse fauna of eutriconodonts from older beds of the Yixian Formation. Like Liaoconodon, it is not easily equated with other eutriconodonts, since it bears distinctive dental traits relative to recognized eutriconodont subgroups.
Hadrogeneios is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal recovered from the Khouribga Phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin dating from the Selandian to the Thanetian. Only the type species H. phosphaticus is known for this genus, with the material being of dental and jaw specimens. The placement of Hadrogeneios recovered it to be the most basal stem-paenungulate, the clade that includes elephants, sea cows, and hyraxes. Despite this Hadrogeneios was a contemporary of more derived members of the group such as Abdounodus, Ocepeia, and the early proboscideans Eritherium, Phosphatherium, and Daouitherium.













