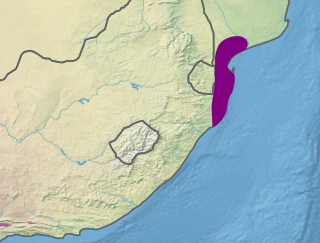
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Swaziland, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.

Chromolaena odorata is a tropical and subtropical species of flowering shrub in the sunflower family. It is native to the Americas, from Florida and Texas in the United States south through Mexico and the Caribbean to South America. It has been introduced to tropical Asia, West Africa, and parts of Australia.

The Barberton groundsel or succulent bush senecio is an evergreen succulent shrub of the family Asteraceae and genus Senecio, native to Southern Africa, named after one of its native localities Barberton and is now also being cultivated elsewhere for its drought resistance, clusters of sweetly scented, golden-yellow, tufted flower heads in winter and attractiveness to butterflies, the painted lady butterfly in particular.

Senecio tamoides, also known as Canary creeper, is a climbing member of the genus Senecio of the family Asteraceae that is native to Southern Africa. It is used as an ornamental plant for its showy yellow, daisy-like flowers in autumn.

The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot (MPA) is a biodiversity hotspot, a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity, in Southern Africa. It is situated near the south-eastern coast of Africa, occupying an area between the Great Escarpment and the Indian Ocean. The area is named after Maputaland, Pondoland and Albany. It stretches from the Albany Centre of Plant Endemism in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, through the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and KwaZulu-Natal Province, the eastern side of Eswatini and into southern Mozambique and Mpumalanga. The Maputaland Centre of Plant Endemism is contained in northern KwaZulu-Natal and southern Mozambique.

Isoglossa woodii, commonly known as buckweed, is a monocarpic shrub of the family Acanthaceae, growing up to 4 m tall. It grows in colonies in coastal forest areas of KwaZulu-Natal and marginally into Eastern Cape, South Africa.

Deinbollia oblongifolia is a shrub or small tree in the family Sapindaceae. It is commonly known as the dune soap-berry and is found in coastal vegetation from the Eastern Cape of South Africa, through KwaZulu-Natal to southern Mozambique and Swaziland. It is named after Peter Vogelius Deinboll (1783-1876), a Danish botanist and plant collector.

Sclerocroton integerrimus, the duiker berry, is a tree in the family Euphorbiaceae, from Southern Africa.

Bridelia micrantha, the mitzeeri or the coastal golden-leaf, is a tree in the family Phyllanthaceae and is native to tropical and southern Africa as well as to the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean.

Capparis fascicularis, the zigzag caper-bush, is a plant in the Capparaceae family and is native to Africa.

Dalbergia obovata is a robust shrub or climber in the family Fabaceae, and is native to Southern Africa.

Tragia durbanensis, the stinging nettle creeper, is a twining herb in the family Euphorbiaceae, with a restricted distribution in southern Africa. There are some 150 species in the genus Tragia.

Erianthemum dregei is a species of parasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, and is commonly known as the hairy mistletoe or wood flower.

Thamnocalamus tessellatus is a species of bamboo belonging to the family Poaceae, and endemic to the high mountains of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland, lying along the south-eastern part of the country. It is found in the Amatola Mountains, the Bamboesberg, which is named after it, and the Drakensberg. Its generic name means "bushy reed", while the specific name means "tiled", an allusion to the rectangular pattern of veins on the leaves. Its common names include Bergbamboes, Wildebamboes and Mountain Bamboo.

Actinote thalia is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in the 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found in most of South America. An attempt was made by the South African programme to defoliate the Chromolaena odorata, a shrub of Neotropical origin, by this species, but was disqualified due to an unacceptably wide host range.

Maerua cafra (DC.) Pax is a small Southern African tree belonging to Capparaceae, the caper family, occurring eastwards along the coast from Knysna, then further inland and northwards through KwaZulu-Natal and Swaziland to the Transvaal, southern Mozambique and southern Zimbabwe. The genus Maerua comprises about 60 species found in Africa and Asia.

Protorhus longifolia, the red beech, is a medium to large, mostly dioecious species of tree in the family Anacardiaceae. It is native to South Africa and Eswatini, where it occurs in well-watered situations from coastal elevations to 1,250 m. The leafy, evergreen trees have rounded crowns and usually grow between 6 and 10 m tall, but regularly taller in forest.

Felicia rosulata is a hairy, perennial, herbaceous plant of up to 30 cm (1 ft) high, that is assigned to the daisy family. It has a rosette of elliptic 8 cm × 2 cm leaves with 3–5 veins, and long, hairy stalks, each topped with one floral head consisting of about thirty middle blue ray florets encircling many yellow disc florets. It can be found in the mountains of Lesotho, eastern South Africa and Swaziland.

Allophylus natalensis, commonly known as the dune false crowberry or dune false currant, is a species of plant in the genus Allophylus native to south-eastern Africa.
Drypetes gerrardii is a species of small tree or large shrub in the family Putranjivaceae. Common names include forest ironplum, bastard white ironwood, and forest ironwood. It is native to tropical and subtropical central and eastern Africa. It was first described in 1920 by the English botanist John Hutchinson, who named it after the English botanist William Tyrer Gerrard who collected plants and seeds in southern Africa in the 1860s.




















