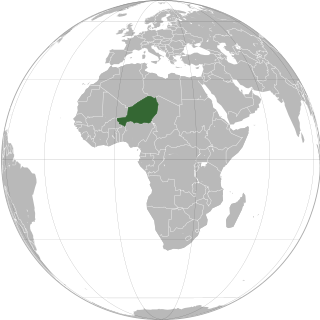
Niger or the Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state bordered by Libya to the northeast, Chad to the east, Nigeria to the south, Benin and Burkina Faso to the southwest, Mali to the west, and Algeria to the northwest. It covers a land area of almost 1,270,000 km2 (490,000 sq mi), making it the largest landlocked country in West Africa. Over 80% of its land area lies in the Sahara. Its predominantly Muslim population of about 25 million lives mostly in clusters in the south and west of the country. The capital Niamey is located in Niger's southwest corner.

The Niger River is the main river of West Africa, extending about 4,180 kilometres. Its drainage basin is 2,117,700 km2 (817,600 sq mi) in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive delta, known as the Niger Delta, into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River.

The Senegal River is a 1086 km (675 mi) long river in West Africa; much of its length marks part of the border between Senegal and Mauritania. It has a drainage basin of 270000 km2, a mean flow of 680 m3/s (24,000 cu ft/s), and an annual discharge of 21.5 km3 (5.2 cu mi). Important tributaries are the Falémé River, Karakoro River, and the Gorgol River. The river divides into two branches once it passes Kaédi The left branch, called the Doué, runs parallel to the main river to the north. After 200 km (120 mi) the two branches rejoin a few kilometers downstream of Podor.

French West Africa was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan, French Guinea, Ivory Coast, Upper Volta, Dahomey and Niger. The federation existed from 1895 until 1958. Its capital was Saint-Louis in Senegal until 1902, and then Dakar until the federation's collapse in 1960.

The Ogooué, also known as the Nazareth River, some 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) long, is the principal river of Gabon in west-central Africa and the fifth largest river in Africa by volume of discharge, trailing only the Congo, Kasai, Niger and Zambezi. Its watershed drains nearly the entire country of Gabon, with some tributaries reaching into the Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, and Equatorial Guinea.

The Gambia River is a major river in West Africa, running 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length.
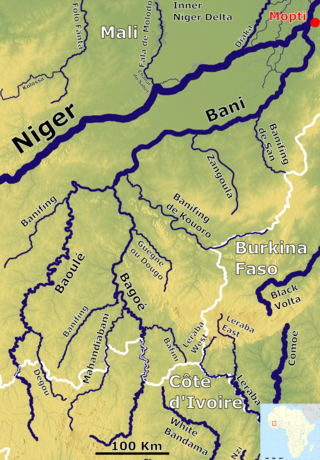
The Bani River is the principal tributary of the Niger River in Mali. The river is formed from the confluence of the Baoulé and Bagoé rivers some 160 km (99 mi) east of Bamako and it merges with the Niger near Mopti. Its length is about 1,100 km (680 mi).

The Corubal, also known as the Rio Corubal or Tomine, is a river of West Africa, a major tributary of the Geba River. For a short distance, it forms the international border between Guinea and Guinea-Bissau. It has a length of approximately 560 kilometres (350 mi).

Kankan is the largest city in Guinea in land area, and the third largest in population, with a population of 198,013 people as of 2020. The city is located in eastern Guinea about 555 kilometres east of the national capital Conakry.

Lake Faguibine was a lake in Mali on the southern edge of the Sahara Desert situated 80 km west of Timbuktu and 75 km north of the Niger River to which it is connected by a system of smaller lakes and channels. In years when the height of the annual flood of the river is sufficient, water flows from the river into the lake. Since the Sahel drought of the 1970s and 1980s the lake has been mostly dry. Water has only rarely reached the lake and even when it has done so, the lake has been only partially filled with water. This has caused a partial collapse of the local ecosystem.

The Konkouré River arises in west-central Guinea and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Several dams on the river provide the country with much of its electricity.

Lake Débo is a lake in the central part of Mali, formed by the seasonal flooding of the Niger River basin. It is in the Inner Niger Delta of the Niger River. During high water stages of the river, the delta formed by lakes, creeks, and backwaters form part of Lake Débo. The inner delta has many wide channels, which are shallow and flooded marshes; this delta extends over a length of 320 kilometres with a width of 80 km (50 mi). Lake Débo during high flow season, is at a distance of 80 km (50 mi) from Mopti on its upstream, on the southern end and 240 km (150 mi) from Timbuktu at its downstream, on the north-eastern end. It is the largest of many such seasonal wetlands and lakes which form the Inner Niger Delta, and the largest lake within Mali. Its size is largely reduced during the dry season of September to March. The existence of this lake called the "Great Lake" in the inner delta of Niger River between Jenne and Timbuktu in Mali has been established after extensive study of maps of the region extending over a period from 1000 to 1900 AD; 400 maps were studied for the period.

The Rokel River is the largest river in the Republic of Sierra Leone in West Africa. The river basin measures 10,622 square kilometres (4,101 sq mi) in size, with the drainage divided by the Gbengbe and Kabala hills and the Sula Mountains. The estuary which extends over an area of 2,950 square kilometres (1,140 sq mi) became a Ramsar wetland site of importance in 1999.

Buzi River is a river in Mozambique. The Buzi River originates in the Eastern Highlands on the border of Mozambique and Zimbabwe, and flows eastward through Manica and Sofala provinces of Mozambique. It empties to the Mozambique Channel west of Beira, forming a large estuary with the Pungwe River.
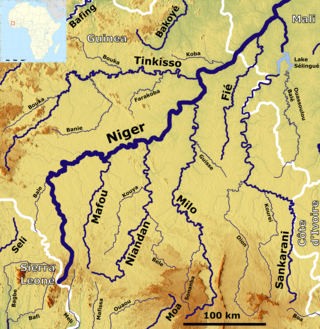
The Sankarani River is a tributary of the Niger River. Flowing northward from the Guinea Highlands of the Fouta Djallon in Guinea, it crosses into southern Mali, where it joins the Niger approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) upstream of Bamako, the capital of Mali. It forms part of the Ivory Coast-Guinea and Guinea–Mali borders.

The Sepik is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun and East Sepik, with a small section flowing through the Indonesian province of Papua.

The Pangani River, is a major river of northeastern Tanzania. It has two main sources: the Ruvu, which rises as Lumi at Kilimanjaro, passes through Lake Jipe, and empties into the Nyumba ya Mungu Reservoir, and the Kikuletwa River, coming from the west and mainly fed by rivers of Mount Meru in Arusha Region, which also enters into the Nyumba ya Mungu Reservoir in Kilimanjaro Region. Just after leaving the reservoir the stream becomes the main Pangani, which empties into the Indian Ocean in Tanga Region at the Tangan port town of Pangani.
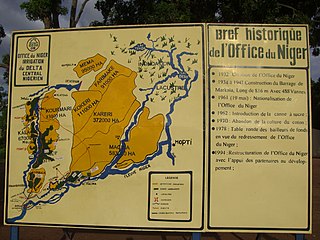
The Office du Niger is a semi-autonomous government agency in Mali that administers a large irrigation scheme in the Ségou Region of the country. Water from the Niger River is diverted into a system of canals at the Markala dam 35 kilometres (22 mi) downstream of Ségou. The water is used to irrigate nearly 100,000 hectares (390 sq mi) of the flat alluvial plains to the north and northeast of Markala that form part of the Delta mort. Although the French colonial administration constructed the system to produce cotton for the textile industry, the main agricultural product is now rice. Around 320,000 tons are grown each year representing 40 percent of the total Malian production. Large quantities of sugar cane are also grown in joint ventures between a Chinese company and the Malian state. The irrigation scheme uses 2.7 km3 (0.65 cu mi) of water each year corresponding to around 10 percent of the total flow of the Niger River.
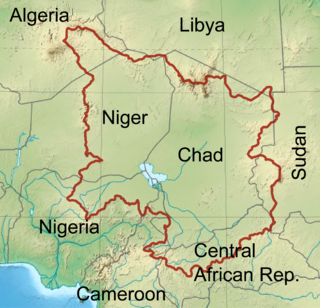
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimentary basin of the same name, but extends further to the northeast and east.

Nigerien nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Niger, as amended; the Nigerien Nationality Code, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Niger. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the state under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual within the nation. Nigerien nationality is typically obtained under the jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth in Niger or abroad to parents with Nigerien nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization.






















