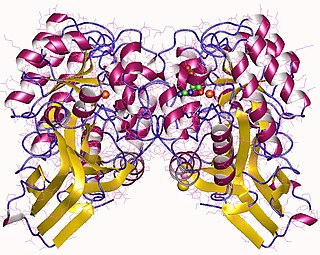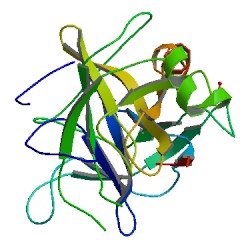
Chymotrypsin (EC 3.4.21.1, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly those containing leucine at the P1 position.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
2,4-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one-glucoside dioxygenase (EC 1.14.20.2, BX6 (gene), DIBOA-Glc dioxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (2R)-4-hydroxy-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl beta-D-glucopyranoside:oxygen oxidoreductase (7-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-Hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl glucoside beta-D-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.182, DIMBOAGlc hydrolase, DIMBOA glucosidase) is an enzyme with systematic name (2R)-4-hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl beta-D-glucopyranoside beta-D-glucosidase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.17, tesD (gene), hsaD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase ( (2Z,4Z)-2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-dienoate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction