
Acanthaceae is a family of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing almost 250 genera and about 2500 species. Most are tropical herbs, shrubs, or twining vines; some are epiphytes. Only a few species are distributed in temperate regions. The four main centres of distribution are Indonesia and Malaysia, Africa, Brazil, and Central America. Representatives of the family can be found in nearly every habitat, including dense or open forests, scrublands, wet fields and valleys, sea coast and marine areas, swamps, and mangrove forests.

Cyperus papyrus, better known by the common names papyrus, papyrus sedge, paper reed, Indian matting plant, or Nile grass, is a species of aquatic flowering plant belonging to the sedge family Cyperaceae. It is a tender herbaceous perennial, native to Africa, and forms tall stands of reed-like swamp vegetation in shallow water.

Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests (TSMF), also known as tropical moist forest, is a subtropical and tropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature.

Heliconia, derived from the Greek word Ἑλικώνιος, is a genus of flowering plants in the monotypic family Heliconiaceae. Most of the ca 194 known species are native to the tropical Americas, but a few are indigenous to certain islands of the western Pacific and Maluku. Many species of Heliconia are found in the tropical forests of these regions. Most species are listed as either vulnerable or data deficient by the IUCN Red List of threatened species. Several species are widely cultivated as ornamentals, and a few are naturalized in Florida, Gambia, and Thailand. Common names for the genus include lobster-claws, toucan beak, wild plantain, or false bird-of-paradise. The last term refers to their close similarity to the bird-of-paradise flowers (Strelitzia). Collectively, these plants are also simply referred to as "heliconias".

Strophanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1802. It is native primarily to tropical Africa, extending to South Africa, with a few species in Asia from southern India to New Guinea and southern China. The genus name is a compound of the Greek words στροφος (strophos) "twisted" and ανθοσ (anthos) "flower", in reference to the corolla lobes which, in some species - notably S. petersianus - resemble long twisted ribbons or threads and can reach a length of 30–35 cm. This trait, in addition to colouring involving combinations of bright pinks, purples and oranges, combine to make the flowers among the most ornamental in the plant kingdom.

Acanthus is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae, native to tropical and warm temperate regions, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean Basin and Asia. This flowering plant is nectar producing and is susceptible to predation by butterflies, such as Anartia fatima, and other nectar feeding organisms. Common names include Acanthus and Bear's breeches. The generic name derives from the Greek term ἄκανθος (akanthos) for Acanthus mollis, a plant that was commonly imitated in Corinthian capitals.
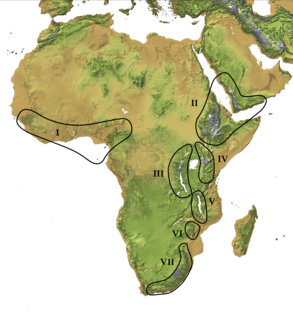
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.
Terminalia schimperiana is a species of Terminalia, native to tropical Africa from Guinea and Sierra Leone east to Uganda and Ethiopia.

The copper sunbird is a species of passerine bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is native to tropical Africa, its range extending from Senegal and Guinea in the west to South Sudan and Kenya in the east, and southwards to Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe and Mozambique.

Monodora myristica, the calabash nutmeg, is a tropical tree of the family Annonaceae or custard apple family of flowering plants. It is native to Angola, Benin, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Liberia, Nigeria, the Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo and Uganda. In former times, its seeds were widely sold as an inexpensive nutmeg substitute. This is now less common outside its region of production. Other names of calabash nutmeg include Jamaican nutmeg, African nutmeg, ehuru, ariwo, awerewa, ehiri, airama, African orchid nutmeg, muscadier de Calabash and lubushi.

Aneilema is a genus of monocotyledonous plants of approximately 60 species. The vast majority of the species are native to sub-Saharan Africa, but a few are found in Oceania and one, Aneilema brasiliense, is from South America. It is the third largest genus in the family Commelinaceae after Commelina and Tradescantia, and it is one of only six genera in the family to occur in both the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.

Impatiens sakeriana is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Balsaminaceae. It is native to Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea and grows in mountain forest understory habitat at altitudes up to 3000 meters. I. sakeriana is most often cited for its role in sunbird pollination. It can be locally common in parts of its range, but its habitat is threatened by agriculture.
Mimulopsis arborescens is a tree from the family Acanthaceae and a species of the genus Mimulopsis. This tree is one of the species that can be found at Rwenzori Mountains.
Mimulopsis elliotii is a flowering shrub from the family Acanthaceae and a species of the genus Mimulopsis. This flowering shrub is one of the species that can be found at Rwenzori Mountains.

Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands, shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply.

Metarungia pubinervia is an Afrotropical plant species in the acanthus family, which is native to forest understorey in the Afromontane archipelago. It is widespread in eastern Africa, with isolated populations in southern Africa and Nigeria. The species is named for the fine down that covers the main leaf veins (-nervia).

Costus spectabilis, commonly known as the yellow trumpet, is an African, gregarious species of herb; low and perennial, it is found from Sierra Leone to Sudan to as far south as Angola and Zimbabwe.

Cycnium tubulosum, also known as the vlei ink-flower and the tissue paper flower, is a slender hemiparasitic perennial plant of the broomrape family. Its range includes much of southern and eastern Africa, from South Africa to Ethiopia, including Madagascar. It has creeping, straggling or upright stems, with few narrow, entire leaves and erect, white or pinkish, slightly zygomorph flowers on a long tube, with five lobes, reminiscent of a Phlox-flower. It may not always be fully dependent on the supply of minerals by other plants, but usually makes connections with the roots of grasses. It can be found in moist, short grasslands, reaching altitudes of about 1,550 m (5,090 ft). Its conservation status in South-Africa is "least concern".

Craterostigma plantagineum, is a resurrection plant species in the genus Craterostigma. It is a dwarf growing plant and can be found to make a 'carpet' across the ground, with blooms in shades of blue and purple. It is a well-studied desiccation-tolerant species known for its extreme vegetative tolerance against dehydration and desiccation. It is native to parts of Africa and to India. It is known as a resurrection plant.

Ruspolia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Acanthaceae.
















