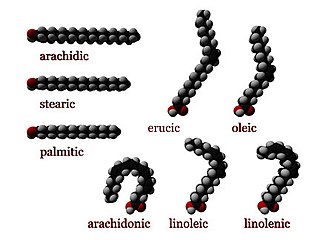
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells.

Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes involving or closely related to fatty acids, a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into (1) catabolic processes that generate energy and (2) anabolic processes where they serve as building blocks for other compounds.
Phosphatidic acids are anionic phospholipids important to cell signaling and direct activation of lipid-gated ion channels. Hydrolysis of phosphatidic acid gives rise to one molecule each of glycerol and phosphoric acid and two molecules of fatty acids. They constitute about 0.25% of phospholipids in the bilayer.
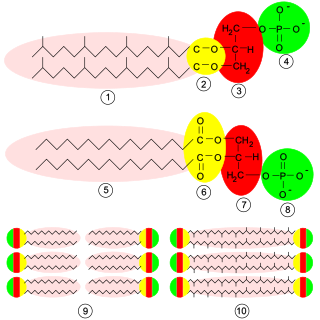
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.
Cardiolipin is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. It can also be found in the membranes of most bacteria. The name "cardiolipin" is derived from the fact that it was first found in animal hearts. It was first isolated from the beef heart in the early 1940s by Mary C. Pangborn. In mammalian cells, but also in plant cells, cardiolipin (CL) is found almost exclusively in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it is essential for the optimal function of numerous enzymes that are involved in mitochondrial energy metabolism.
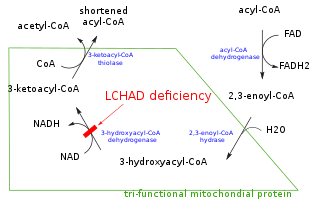
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.

Tafazzin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAFAZZIN gene. Tafazzin is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and functions as a phospholipid-lysophospholipid transacylase. It catalyzes remodeling of immature cardiolipin to its mature composition containing a predominance of tetralinoleoyl moieties. Several different isoforms of the tafazzin protein are produced from the TAFAZZIN gene. A long form and a short form of each of these isoforms is produced; the short form lacks a hydrophobic leader sequence and may exist as a cytoplasmic protein rather than being membrane-bound. Other alternatively spliced transcripts have been described but the full-length nature of all these transcripts is not known. Most isoforms are found in all tissues, but some are found only in certain types of cells. Mutations in the TAFAZZIN gene have been associated with mitochondrial deficiency, Barth syndrome, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), hypertrophic DCM, endocardial fibroelastosis, left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC), breast cancer, papillary thyroid carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, glioma, gastric cancer, thyroid neoplasms, and rectal cancer.

Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) is a protein attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane which catalyzes three out of the four steps in beta oxidation. MTP is a hetero-octamer composed of four alpha and four beta subunits:
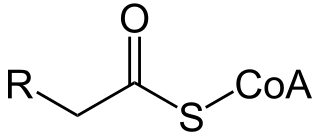
Acyl-CoA is a group of coenzymes that metabolize fatty acids. Acyl-CoA's are susceptible to beta oxidation, forming, ultimately, acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, eventually forming several equivalents of ATP. In this way, fats are converted to ATP, the universal biochemical energy carrier.
Fatty acid degradation is the process in which fatty acids are broken down into their metabolites, in the end generating acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle, the main energy supply of living organisms, including bacteria and animals. It includes three major steps:

Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) also known as carnitine acyltransferase I, CPTI, CAT1, CoA:carnitine acyl transferase (CCAT), or palmitoylCoA transferase I, is a mitochondrial enzyme responsible for the formation of acyl carnitines by catalyzing the transfer of the acyl group of a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from coenzyme A to l-carnitine. The product is often Palmitoylcarnitine, but other fatty acids may also be substrates. It is part of a family of enzymes called carnitine acyltransferases. This "preparation" allows for subsequent movement of the acyl carnitine from the cytosol into the intermembrane space of mitochondria.

α-Parinaric acid is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid. Discovered by Tsujimoto and Koyanagi in 1933, it contains 18 carbon atoms and 4 conjugated double bonds. The repeating single bond-double bond structure of α-parinaric acid distinguishes it structurally and chemically from the usual "methylene-interrupted" arrangement of polyunsaturated fatty acids that have double-bonds and single bonds separated by a methylene unit (−CH2−). Because of the fluorescent properties conferred by the alternating double bonds, α-parinaric acid is commonly used as a molecular probe in the study of biomembranes.
Sterol O-acyltransferase is an intracellular protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum that forms cholesteryl esters from cholesterol.

Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPAM gene.

Lysophosphatidylcholines, also called lysolecithins, are a class of chemical compounds which are derived from phosphatidylcholines.

2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholines are a class of phospholipids that are intermediates in the metabolism of lipids. Because they result from the hydrolysis of an acyl group from the sn-1 position of phosphatidylcholine, they are also called 1-lysophosphatidylcholine. The synthesis of phosphatidylcholines with specific fatty acids occurs through the synthesis of 1-lysoPC. The formation of various other lipids generates 1-lysoPC as a by-product.
Monolysocardiolipin acyltransferase is a mitochondrial acyltransferase that facilitates the remodeling of monolysocardiolipin (MLCL) into cardiolipin.
Acyl-CoA:lysocardiolipin acyltransferase-1 (ALCAT1) is a polyglycerophospholipid acyltransferase of the endoplasmic reticulum which is primarily known for catalyzing the acylation of monolysocardiolipin back into cardiolipin, although it does catalyze the acylation of other polyglycerophospholipids.











