
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.

Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Harpacticoida is an order of copepods, in the subphylum Crustacea. This order comprises 463 genera and about 3,000 species; its members are benthic copepods found throughout the world in the marine environment and in fresh water. A few of them are planktonic or live in association with other organisms. Harpacticoida represents the second-largest meiofaunal group in marine sediments, after nematodes. In Arctic and Antarctic seas, Harpacticoida are common inhabitants of sea ice. The name Harpacticoida comes from the Greek noun harpacticon and the suffix -oid and means reminiscent of a predator.

Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them.

The least auklet is a seabird and the smallest species of auk. It is the most abundant seabird in North America, and one of the most abundant in the world, with a population of around nine million birds. They breed on the islands of Alaska and Siberia, and spend the winter close to the edge of the ice sheet. Their largest colonies are on the Aleutian Islands, St. Lawrence Island and Little Diomede Island.

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.

Calanidae is the largest taxonomic family of calanoid copepods. It includes the genus Calanus, which may be the most abundant metazoan genus on Earth.

Dracunculus medinensis, or Guinea worm, is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at up to 80 centimetres in length, is among the longest nematodes infecting humans. In contrast, the longest recorded male Guinea worm is only 4 cm.

Poecilostomatoida are an suborder of copepods. Although it was previously considered a separate order, recent research showed it to be nested within the Cyclopoida

The Cyclopidae are a family of copepods containing more than half of the 1,200 species in the order Cyclopoida in over 70 genera.
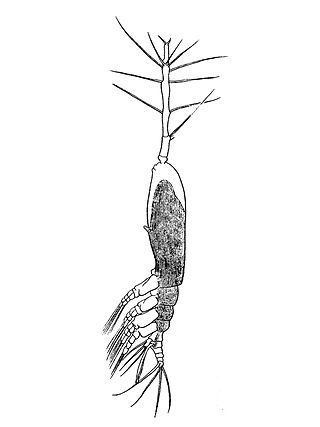
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae. The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.

Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding. They include particularly fishes of the order Clupeiformes, but also other small fish, including halfbeaks, silversides, smelt such as capelin and goldband fusiliers.
Diphyllobothrium mansonoides is a species of tapeworm (cestodes) that is endemic to North America. Infection with D. mansonoides in humans can result in sparganosis. Justus F. Mueller first reported this organism in 1935. D. mansonoides is similar to D. latum and Spirometra erinacei. When the organism was discovered, scientist did not know if D. mansonoides and S. erinacei were separate species. PCR analysis of the two worms has shown the two to be separate but closely related organisms.
Syndinium is a cosmopolitan genus of parasitic dinoflagellates that infest and kill marine planktonic species of copepods and radiolarians. Syndinium belongs to order Syndiniales, a candidate for the uncultured group I and II marine alveolates. The lifecycle of Syndinium is not well understood beyond the parasitic and zoospore stages.
Metridinidae is a family of copepods, comprising three genera – Gaussia, Metridia and Pleuromamma. It has also been referred to as "Metridiidae", but following a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature, that name has been restricted to the family Metridiidae Carlgren, 1893, based on the anthozoan genus Metridium. All species in the family can produce blue-green bioluminescence; the light is produced in glands, whose position varies between genera.
Ellobiopsis is a genus of unicellular, ectoparasitic eukaryotes causing disease in crustaceans. This genus is widespread and has been found infecting copepods from both marine and freshwater ecosystems. parasitism has been seen to interfere with fertility in both sexes of copepods.

Crustaceans form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans.

Temora is a genus of copepods in the family Temoridae. The World Register of Marine Species lists the following species:
Mesocyclops longisetus is a species of freshwater copepod in the family Cyclopidae. Two subspecies are accepted, Mesocyclops longisetus curvatus Dussart, 1987, and Mesocyclops longisetus longisetus. It has a neotropical distribution.















