Related Research Articles

Alpha-thalassemia is a form of thalassemia involving the genes HBA1 and HBA2. Thalassemias are a group of inherited blood conditions which result in the impaired production of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood. Normal hemoglobin consists of two alpha chains and two beta chains; in alpha-thalassemia, there is a quantitative decrease in the amount of alpha chains, resulting in fewer normal hemoglobin molecules. Furthermore, alpha-thalassemia leads to the production of unstable beta globin molecules which cause increased red blood cell destruction. The degree of impairment is based on which clinical phenotype is present.
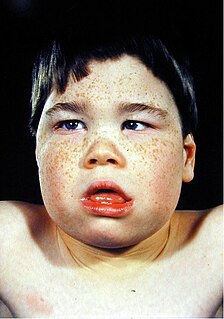
Alpha-thalassemia mental retardation syndrome (ATRX), also called alpha-thalassemia X-linked mental retardation, nondeletion type or ATR-X syndrome, is an X-linked recessive condition associated with a mutation in the ATRX gene. Males with this condition tend to be moderately intellectually disabled and have physical characteristics including coarse facial features, microcephaly, hypertelorism, a depressed nasal bridge, a tented upper lip and an everted lower lip. Mild or moderate anemia, associated with alpha-thalassemia, is part of the condition. Females with this mutated gene have no specific signs or features, but if they do, they may demonstrate skewed X chromosome inactivation.
The human β-globin locus is composed of five genes located on a short region of chromosome 11, responsible for the creation of the beta parts of the oxygen transport protein Haemoglobin. This locus contains not only the beta globin gene but also delta, gamma-A, gamma-G, and epsilon globin. Expression of all of these genes is controlled by single locus control region (LCR), and the genes are differentially expressed throughout development.
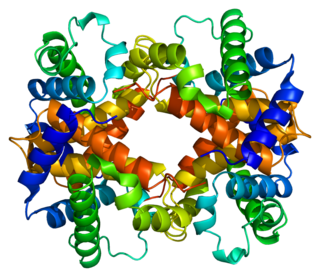
Hemoglobin subunit beta, is a globin protein, coded for by the HBB gene, which along with alpha globin (HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, hemoglobin A (HbA). It is 147 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains.
Hemoglobin Barts, abbreviated Hb Barts, is an abnormal type of hemoglobin that consists of four gamma globins. It is moderately insoluble, and therefore accumulates in the red blood cells. Hb Barts has an extremely high affinity for oxygen, so it cannot release oxygen to the tissue. Therefore, this makes it an inefficient oxygen carrier. As an embryo develops, it begins to produce alpha-globins at weeks 5–6 of development. When both of the HBA1 and HBA2 genes which code for alpha globins becomes dysfunctional, the affected fetuses will have difficulty in synthesizing a functional hemoglobin. As a result, gamma chains will accumulate and form four gamma globins. These gamma globins bind to form hemoglobin Barts. It is produced in the disease alpha-thalassemia and in the most severe of cases, it is the only form of hemoglobin in circulation. In this situation, a fetus will develop hydrops fetalis and normally die before or shortly after birth, unless intrauterine blood transfusion is performed.

Krueppel-like factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF1 gene. The gene for KLF1 is on the human chromosome 19 and on mouse chromosome 8. Krueppel-like factor 1 is a transcription factor that is necessary for the proper maturation of erythroid cells.

Hemoglobin subunit alpha , also known as HBA1, is a hemoglobin protein that in humans is encoded by the HBA1 gene.

Hemoglobin subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBG2 gene.

Poly(rC)-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PCBP2 gene.

Hemoglobin subunit delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBD gene.

Hemoglobin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBG1 gene.
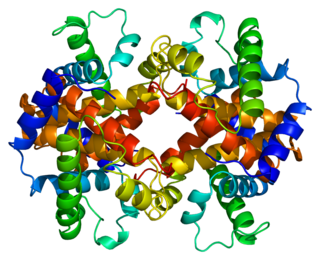
Hemoglobin subunit epsilon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBE1 gene.

Glycoprotein Ib (platelet), beta polypeptide (GP1BB) also known as CD42c, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BB gene.

Krüppel-like Factor 2 (KLF2), also known as lung Krüppel-like Factor (LKLF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF2 gene on chromosome 19. It is a member of the Krüppel-like factor family of zinc finger transcription factors, and it has been implicated in a variety of biochemical processes in the human body, including lung development, embryonic erythropoiesis, epithelial integrity, T-cell viability, and adipogenesis.

Hemoglobin subunit zeta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBZ gene.

Transcription factor NF-E2 45 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFE2 gene.
Hemoglobin, alpha pseudogene 1, also known as HBAP1, is a human gene.

Hemoglobin subunit theta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBQ1 gene.

Hemoglobin, alpha 2 also known as HBA2 is a gene that in humans codes for the alpha globin chain of hemoglobin.

Nitrogen permease regulator-like 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPRL3 gene.
References
- ↑ Higgs DR, Vickers MA, Wilkie AO, Pretorius IM, Jarman AP, Weatherall DJ (April 1989). "A review of the molecular genetics of the human alpha-globin gene cluster". Blood. 73 (5): 1081–104. doi: 10.1182/blood.V73.5.1081.1081 . PMID 2649166.
- ↑ Fischel-Ghodsian N, Nicholls RD, Higgs DR (November 1987). "Unusual features of CpG-rich (HTF) islands in the human alpha globin complex: association with non-functional pseudogenes and presence within the 3' portion of the zeta gene". Nucleic Acids Res. 15 (22): 9215–25. doi:10.1093/nar/15.22.9215. PMC 306463 . PMID 2825132.
- ↑ Goh SH, Lee YT, Bhanu NV, et al. (August 2005). "A newly discovered human alpha-globin gene". Blood. 106 (4): 1466–72. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-03-0948. PMC 1895206 . PMID 15855277.