
Uttara Kannada is a fifth largest district in the Indian state of Karnataka, It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belagavi districts to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shivamogga District, and Udupi District to the south, and the Laccadive Sea to the west. Karwar is the district headquarters, Kumta and Sirsi are the major commercial centers in the district. The district's agroclimatic divisions include the coastal plain consisting of Karwar, Ankola, Kumta, Honnavar Bhatkal taluks and Malenadu consisting of Sirsi, Siddapur, Yellapur, Haliyal, Dandeli, Joida, Mundgod taluks.
Ankola is a town municipal council and taluka in the Uttara Kannada district of the Indian state of Karnataka. The town is around 33 km (21 mi) from district headquarters Karwar.

Sirsi is a city in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state in India. It was also known as "Kalyana Pattana" during the Sonda Dynasty. It is a tourist destination with evergreen forest and waterfalls and is also a commercial centre. The main businesses around the city are mostly subsistence and agriculture-based. Areca nut or betel nut, locally known as Adike, is the primary crop grown in the nearby villages, making it one of the major trading centres for areca nut. The region is also known for spices such as cardamom, pepper, betel leaves, and vanilla. The major food crop is paddy.

North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from 300 to 730 metres elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 14 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra.

Holenarasipura is a town and taluk in Hassan district of Karnataka. The town is situated on the banks of the Hemavati, one of the tributaries of the Kaveri.
Shiggaon, also known as Shiggavi is a municipal town in Haveri district in the Indian state of Karnataka.
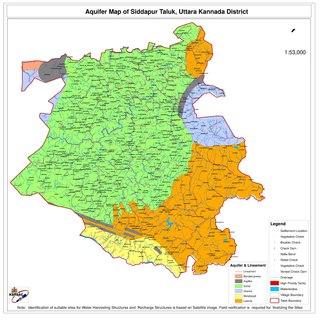
Siddapur or Siddhapura Taluk is the destination of world famous Jog Falls. It is a part of Uttara Kannada district, Karnataka, India and is located in the midst of forest areas of Western Ghats and it is also a part of Malenadu. The taluk is full of greenery, hills and arecanut gardens developed in the valleys’. The taluk headquarters is Siddapur. Sirsi is the nearest city,
Tarikere is a town, a taluk and is one of the two Subdivisional headquarter in the Chikmagalur district of Karnataka state, India. It is popularly known as gateway of Malnad because the Malnad area starts from here. The town's name is derived from the number of water tanks which surround it.

Karnataka, the sixth largest state in India, was ranked as the third most popular state in the country for tourism in 2014. It is home to 507 of the 3600 centrally protected monuments in India, second only to Uttar Pradesh. The State Directorate of Archaeology and Museums protects an additional 752 monuments and another 25,000 monuments are yet to receive protection.
Ulavi is a village in the Uttara Kannada district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Ulavi is a village about 75 kilometres (47 mi) from Karwar in Karnataka state, India.
Ambikanagar is a small project township approximately 16 km from bustling Dandeli city in the Haliyal taluk of Uttara Kannada district in Karnataka. Ambikanagar is soaked in the green pristine environs of the Western Ghats. The former name of Ambikanagar is believed to be Amga.
Yellapura is a town in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India. Arecanut is the primary crop grown in the villages surrounding the town. Approximately 90% of the population of Yellapura are farmers who grow Arecanut and paddy.
Joida is a town located in the Uttara Kannada district in the Indian state of Karnataka. The town is the headquarters of the eponymous taluk. Earlier it was known as Supa taluka but as Supa village got submerged due to dam built across river Kali, Joida taluka came into existence. Joida town has a Post office, branch of nationalised banks and a Police station.
Examba is a City and Municipal Council in the Belgaum district of the Indian state of karnataka.
Shelawadi or Shelavadi is a panchayat town in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Navalgund taluk of Dharwad district in Karnataka.
Nandikatta is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Mundgod taluk of Uttara Kannada district. It and its neighboring towns harbor the Drepung Tibetan Buhdist Monastery.
Agadi (Mundgod) is a village in the southern state of Karnataka in India. It is located in the Mundgod taluk and it is under kawar districts in Uttara Kannada.
Ajjihalli, Mundgod is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Mundgod taluk of Uttara Kannada district.

Attiveri Bird Sanctuary is a village in the Mundgod taluk of Uttara Kannada district in Karnataka. It is located 15 km away from Mundgod.

Karnataka is a state in India with rich archaeological and ecological heritage. The total geographical area of Karnataka is 191,976 square kilometres (74,122 sq mi) of which forest area is 37,550 square kilometres (14,500 sq mi) (19.58%).















