
Prasiola is a genus of macroscopic green algae, found in a variety of habitats ranging from terrestrial, freshwater, to marine. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, ranging from the Arctic to the Antarctic.

The Trebouxiophyceae, also known as trebouxiophytes, are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Members of this class are single-celled, colonial, or multicellular and are found in freshwater or terrestrial habitats worldwide. Many taxa in the Trebouxiophyceae form symbiotic relationships with other organisms; in particular, the majority of phycobionts within lichens are trebouxiophytes. A number of taxa have also lost the ability to photosynthesize, and have evolved to become parasitic; examples include Prototheca and Helicosporidium.

Microthamniaceae is a family of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. It is the only family in the order Microthamniales.

Prasiolales is an order of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. Members of this order are ecologically widespread and are found in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial habitats from the Arctic to the Antarctic.

Botryococcaceae is a family of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae.

Chlorellaceae are a family of green algae in the order Chlorellales. About 250 species are currently accepted in the family. Members of the family are distributed worldwide and are common in a variety of freshwater, terrestrial and marine environments.

Prasiolaceae is a family of green algae in the order Prasiolales. Members of this family are found in freshwater, terrestrial, and marine habitats.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.
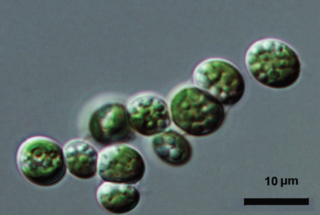
Elliptochloris is a genus of green algae in the order Prasiolales. Species of this genus are common and found in a variety of terrestrial habitats such as soils. Some species in the genus are photobiont partners in lichens. One species, E. marina, is a symbiont within two species of sea anemone, Anthopleura elegantissima and A. xanthogrammica. It seems to have a worldwide distribution.

Geminella is a genus of green algae in the phylum Chlorophyta. Once considered part of the order Ulotrichales, molecular phylogenetics have shown that Geminella and related genera form a well-supported clade within the class Trebouxiophyceae.
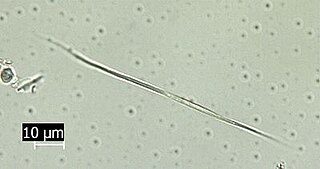
Koliella is a genus of green algae in the order Prasiolales. Members of this genus are found in freshwater plankton, but some are also found on snow and ice.
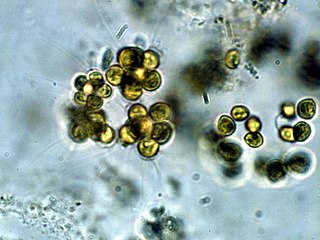
Micractinium is a genus of microscopic green algae in the family Chlorellaceae. Species of the genus Micractinium are found as phytoplankton, and are commonly found in freshwater habitats around the world. A few species are found as endosymbionts of ciliates. There is increasing interest in Micractinium due to its high growth rate and lipid production.

Microthamnion is a genus of green algae in the family Microthamniaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats around the world, preferably with low levels of pollution; it is typically attached to solid substrates.

Trentepohlia is a genus of filamentous chlorophyte green algae in the family Trentepohliaceae, living free on terrestrial supports such as tree trunks and wet rocks or symbiotically in lichens. The filaments of Trentepohlia have a strong orange colour caused by the presence of large quantities of carotenoid pigments which mask the green of the chlorophyll.

Watanabea is a genus of microscopic green algae in the family Watanabeaceae. It is widespread in terrestrial and freshwater habitats, including as a photobiont within lichens, but is apparently rare.
Symbiochloris reticulata is a species of green alga in the Trebouxiales. It is a known as a photobiont with several lichen species, like Lobaria pulmonaria, but also as a free-living soil alga as well. Phylogenetic analysis of rRNA sequence data revealed that the species shares a sister group relationship with two other green algae that lack motile stages, Chlorella saccharophila and C. luteoviridis.

The Klebsormidiaceae are a family containing five genera of charophyte green alga forming multicellular, non-branching filaments. The genus Chlorokybus was previously included as well, but this problematic and poorly known genus is now placed in a separate class Chlorokybophyceae.
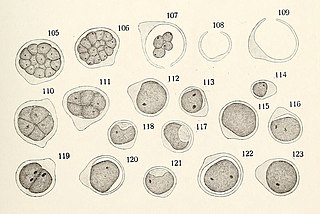
Trebouxiaceae is a family of green algae in the order Trebouxiales. Many species of Trebouxiaceae are found as symbionts associated with terrestrial lichens, although some genera are also found free-living.

Mucidosphaerium pulchellum, also known by its synonym Dictyosphaerium pulchellum, is a species of freshwater green algae, in the family Chlorellaceae.














