The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic.

Carbamoyl phosphate is an anion of biochemical significance. In land-dwelling animals, it is an intermediary metabolite in nitrogen disposal through the urea cycle and the synthesis of pyrimidines. Its enzymatic counterpart, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I, interacts with a class of molecules called sirtuins, NAD dependent protein deacetylases, and ATP to form carbamoyl phosphate. CP then enters the urea cycle in which it reacts with ornithine to form citrulline.
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2NCOOH. It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia NH3 and carbon dioxide CO2 at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate [NH4]+[NH2CO2]−. The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.
The enzyme carbamoyl-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.66) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosine-phosphate deaminase (EC 3.5.4.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allantoate deiminase (EC 3.5.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an amidase (EC 3.5.1.4, acylamidase, acylase (misleading), amidohydrolase (ambiguous), deaminase (ambiguous), fatty acylamidase, N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrates of this enzyme are an amide and H2O, whereas its two products are monocarboxylate and NH3.
In enzymology, an aminoacylase (EC 3.5.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-ureidopropionase (EC 3.5.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biuret amidohydrolase (EC 3.5.1.84) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a carboxymethylhydantoinase (EC 3.5.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, Nα-benzyloxycarbonylleucine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-benzyloxycarbonylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.58) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-L-amino-acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.87) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoylputrescine amidase (EC 3.5.1.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase (EC 3.5.1.59) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ureidosuccinase (EC 3.5.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
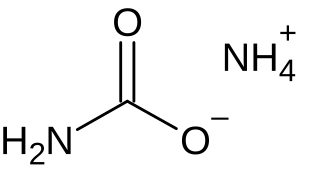
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.



