
NGC 500(also known as PGC 5013) is a type E-SO lenticular galaxy located in the Pisces constellation. It has an apparent size of .8 by .6 arcminutes and an apparent magnitude of 14.2. It was first discovered in 1850 by Bindon Blood Stoney during his time at Birr Castle in Ireland.

NGC 490, also occasionally referred to as PGC 4973 or GC 277, is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 85 million light-years from Earth and was discovered on December 6, 1850, by Irish engineer Bindon Blood Stoney. Although John Dreyer, creator of the New General Catalogue, credits the discovery to astronomer William Parsons, he notes that many of his claimed discoveries were made by one of his assistants. In the case of NGC 490, the discovery was made by Bindon Stoney, who discovered it along with NGC 486, NGC 492 and NGC 500 during his observation of NGC 488.

NGC 492, also occasionally referred to as PGC 4976 or GC 280, is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 590 million light-years from Earth and was discovered on December 6, 1850 by Irish engineer Bindon Blood Stoney. Although John Dreyer, creator of the New General Catalogue, credits the discovery to astronomer William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, he notes that many of his claimed discoveries were made by one of his assistants. In the case of NGC 492, the discovery was made by Bindon Stoney, who discovered it along with NGC 486, NGC 490 and NGC 500 during his observation of NGC 488 using Lord Rosse's 72" telescope.

NGC 493, also occasionally referred to as PGC 4979 or GC 281, is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Cetus. It is located approximately 90 million light-years from Earth and was discovered on December 20, 1786 by astronomer William Herschel. It was later also observed by his son, John Herschel. John Dreyer, creator of the New General Catalogue, described the galaxy as "very faint, large, much extended 60°" with "a little brighter middle".

NGC 494, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5035 or GC 282, is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 227 million light-years from Earth and was discovered on 22 November 1827 by astronomer John Herschel. John Dreyer, creator of the New General Catalogue, described the galaxy as "very faint, pretty large, extended, 3 faint stars to south".

NGC 495, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5037, UGC 920 or GC 278, is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 184 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 12 September 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 496, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5037, UGC 927 or GC 288, is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 250 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 12 September, 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 499, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5060, IC 1686 or GC 289, is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 197 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 12 September, 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 5774 is an intermediate spiral galaxy approximately 71 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Virgo. It was discovered by Irish engineer Bindon Stoney on April 26, 1851.

NGC 501, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5082 or GC 284, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 224 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 28 October 1856 by Irish astronomer R. J. Mitchell.

NGC 503, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5086 or GC 5169, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 265 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 13 August 1863 by German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest.

NGC 504, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5084 or UGC 935, is a lenticular galaxy located approximately 189 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 22 November 1827 by astronomer John Herschel. The object was listed twice in the General Catalogue, precursor of the New General Catalogue, as both GC 291 and GC 292.
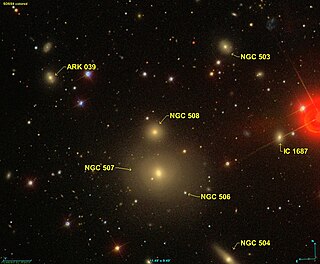
NGC 508, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5099 or UGC 939, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 247 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 12 September 1784 by British astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 511, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5103 or UGC 936, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 499 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 26 October 1876 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan.

NGC 512, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5132 or UGC 944, is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Andromeda. It is located approximately 217 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 17 November 1827 by astronomer John Herschel.

NGC 513, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5174 or UGC 953, is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Andromeda. It is located approximately 262 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 13 September 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 515, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5201 or UGC 956, is a lenticular galaxy located approximately 228 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 13 September 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 517, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5214 or UGC 960, is a lenticular galaxy located approximately 188 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 13 September 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 522, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5218 or UGC 970, is a spiral galaxy located approximately 122 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 25 September 1862 by astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest.

NGC 751 is an elliptical galaxy approximately 225 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Triangulum. It forms a close pair of interacting galaxies together with the nearby NGC 750 galaxy. The pair is listed as Arp 166 in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.




















