
Ara is a southern constellation between Scorpius, Telescopium, Triangulum Australe, and Norma. It was one of the Greek bulk described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union.

Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.

Cassiopeia is a constellation and asterism in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars.
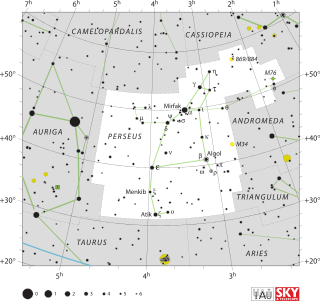
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.

Lacerta is one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Its name is Latin for lizard. A small, faint constellation, it was defined in 1687 by the astronomer Johannes Hevelius. Its brightest stars form a "W" shape similar to that of Cassiopeia, and it is thus sometimes referred to as 'Little Cassiopeia'. It is located between Cygnus, Cassiopeia and Andromeda on the northern celestial sphere. The northern part lies on the Milky Way.

The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745–46. Both the "Eagle" and the "Star Queen" refer to visual impressions of the dark silhouette near the center of the nebula, an area made famous as the "Pillars of Creation" imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula contains several active star-forming gas and dust regions, including the aforementioned Pillars of Creation. The Eagle Nebula lies in the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way.

Messier 103 is a small open cluster of many faint stars in Cassiopeia. It was discovered on 27 March 1781 by Pierre Méchain, but later added as Charles Messier's last deep-sky object in his catalogue.

NGC 457 is an open star cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia.

NGC 752 is an open cluster in the constellation Andromeda. The cluster was discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1783 and cataloged by her brother William Herschel in 1786, although an object that may have been NGC 752 was described by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654.

NGC 381 is an open cluster of stars in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia, located at a distance of approximately 3,120 light-years from the Sun. Credit for the discovery of this cluster was given to Caroline Herschel by her brother William in 1787, although she may never have actually seen it.

NGC 663 is a young open cluster in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It has an estimated 400 stars and spans about a quarter of a degree across the sky. It can reportedly be detected with the unaided eye, although a telescope is recommended for best viewing. The brightest members of the cluster can be viewed with binoculars. Although the listed visual magnitude is 7.1, several observers have reported higher estimates.

NGC 884 is an open cluster located 7640 light years away in the constellation of Perseus. It is the easternmost of the Double Cluster with NGC 869. NGC 869 and 884 are often designated h and χ Persei, respectively. The cluster is about 14 million years old. Located in the Perseus OB1 association, both clusters are located physically close to one another, only a few hundred light years apart. The clusters were first recorded by Hipparchus, thus have been known since antiquity.

NGC 6231 is an open cluster in the southern sky located half a degrees north of Zeta Scorpii. NGC 6231 is part of a swath of young, bluish stars in the constellation Scorpius known as the Scorpius OB1 association. The star Zeta1 is a member of this association, while its brighter apparent partner, Zeta2, is only 150 ly from Earth and so is not a member.

NGC 6755 is an open cluster of stars in the equatorial constellation of Aquila, positioned about 3° to the east of the star Delta Aquilae. It was discovered by the Anglo-German astronomer William Herschel on July 30, 1785 and is located at a distance of 8,060 light years from the Sun. NGC 6756 lies 30′ to the northeast of NGC 6755, with the pair forming a visual double cluster. However, they probably do not form a binary cluster system since they have different ages and are too distant from each other.

NGC 189 is an open cluster in the Cassiopeia constellation. It was discovered by Caroline Herschel on 27 September 1783, and independently rediscovered by John Herschel on 27 October 1829.

NGC 7790 is a young open cluster of stars located some 10,800 light years away from Earth in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. At this distance, the light from the cluster has undergone extinction from interstellar gas and dust equal to E(B – V ) = 0.51 magnitude in the UBV photometric system. NGC 7790 has a Trumpler class rating of II2m and the estimated age is 60–80 million years. It contains three cepheid variables: CEa Cas, CEb Cas, and CF Cas.

NGC 2129 is an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. It has an angular distance of 2.5 arcminutes and is approximately 2.2 ± 0.2 kpc from the Sun inside the Local spiral arm. At that distance, the angular size of the cluster corresponds to a diameter of about 10.4 light years. NGC 2129 is a very young cluster whose age has been estimated at 10 million years.

NGC 110 is an open star cluster located in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by the English astronomer John Herschel on October 29, 1831.

NGC 129 is an open cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1788. It is located almost exactly halfway between the bright stars Caph and γ Cassiopeiae. It is large but not dense and can be observed by binoculars, through which the most obvious component is a small triangle of stars of magnitude 8 and 9, located in the center of the cluster.

NGC 5617 is an open cluster in the constellation Centaurus. NGC 5617 forms a binary open cluster with Trumpler 22. It lies one degree west-northwest of Alpha Centauri.




















