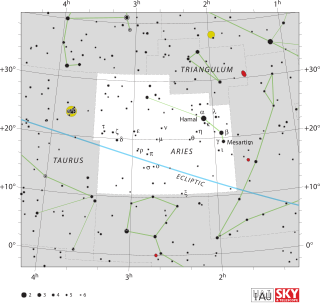
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is , representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.

Boötes is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from Latin Boōtēs, which comes from Greek Βοώτης Boṓtēs 'herdsman' or 'plowman'.

Corona Australis is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means "southern crown", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.
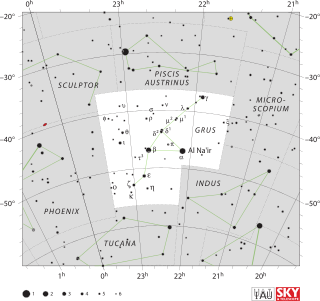
Grus is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a 35-centimetre-diameter (14-inch) celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

Hydrus is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm (14 in) diameter celestial globe published in late 1597 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted the brighter stars and gave their Bayer designations in 1756. Its name means "male water snake", as opposed to Hydra, a much larger constellation that represents a female water snake. It remains below the horizon for most Northern Hemisphere observers.
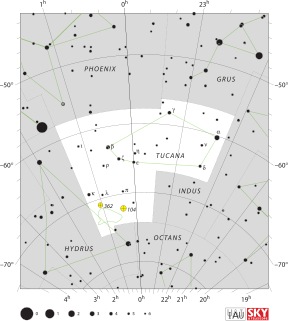
Tucana is a constellation of stars in the southern sky, named after the toucan, a South American bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived in the late sixteenth century by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Tucana first appeared on a 35-centimetre-diameter (14 in) celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Tucana, Grus, Phoenix and Pavo are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

Triangulum Australe is a small constellation in the far Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the southern triangle", which distinguishes it from Triangulum in the northern sky and is derived from the acute, almost equilateral pattern of its three brightest stars. It was first depicted on a celestial globe as Triangulus Antarcticus by Petrus Plancius in 1589, and later with more accuracy and its current name by Johann Bayer in his 1603 Uranometria. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756.
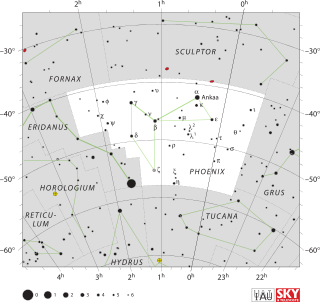
Phoenix is a minor constellation in the southern sky. Named after the mythical phoenix, it was first depicted on a celestial atlas by Johann Bayer in his 1603 Uranometria. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted the brighter stars and gave their Bayer designations in 1756. The constellation stretches from roughly −39° to −57° declination, and from 23.5h to 2.5h of right ascension. The constellations Phoenix, Grus, Pavo and Tucana, are known as the Southern Birds.

Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.
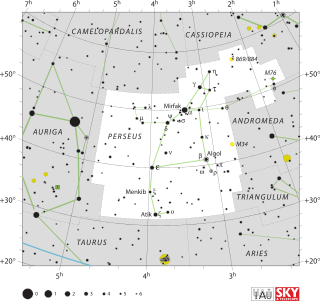
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, being named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.
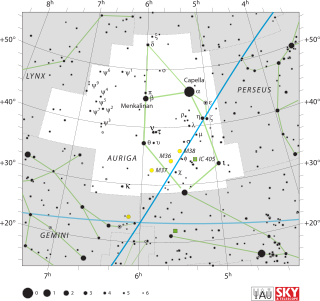
Auriga is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is north of the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra.

Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass, referring to the drafting tool used for drawing circles. Its brightest star is Alpha Circini, with an apparent magnitude of 3.19. Slightly variable, it is the brightest rapidly oscillating Ap star in the night sky. AX Circini is a Cepheid variable visible with the unaided eye, and BX Circini is a faint star thought to have been formed from the merger of two white dwarfs. Two sun-like stars have planetary systems: HD 134060 has two small planets, and HD 129445 has a Jupiter-like planet. Supernova SN 185 appeared in Circinus in 185 AD and was recorded by Chinese observers. Two novae have been observed more recently, in the 20th century.

Leo Minor is a small and faint constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the smaller lion", in contrast to Leo, the larger lion. It lies between the larger and more recognizable Ursa Major to the north and Leo to the south. Leo Minor was not regarded as a separate constellation by classical astronomers; it was designated by Johannes Hevelius in 1687.
59 Andromedae, abbreviated 59 And, is a sixth-magnitude binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. 59 Andromedae is the Flamsteed designation. As of 2017, the pair had an angular separation of 16.60″ along a position angle (PA) of 36°. Compare this to a separation of 15.3″ along a PA of 35°, as measured in 1783. The two stars have an estimated physical separation of 1,370 AU.

Tau Cygni, Latinised from τ Cygni, is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus, approximately 69 light years away from Earth. This visual binary system has a period of 49.6 years.

NGC 8 is an asterism of two completely unrelated stars in the constellation Pegasus, discovered on 29 September 1865 by Otto Wilhelm von Struve. It is approximately 2.7 arc minutes away from NGC 9.

Stein 2051 is a nearby binary star system, containing a red dwarf and a degenerate star, located in constellation Camelopardalis at about 18 ly from Earth.
EQ Pegasi is a nearby binary system of two red dwarfs. Both components are flare stars, with spectral types of M4Ve and M6Ve respectively, and a current separation between the components of 5.8 arcseconds. The system is at a distance of 20.4 light-years, and is 950 million years old.
















