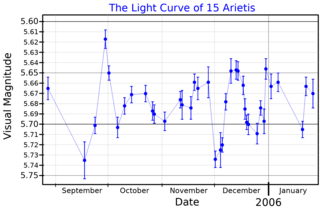
15 Arietis is a single variable star in the northern constellation of Aries. 15 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the variable star designation AV Arietis. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.74, which is just bright enough to be visible to the naked eye from dark suburban skies. An annual parallax shift of 5.84 mas corresponds to a physical distance of approximately 560 light-years from Earth. At that distance, the star's brightness is reduced by 0.33 in magnitude because of extinction from interstellar gas and dust.

RT Aurigae is a yellow supergiant variable star in the constellation Auriga, about 1,500 light years from Earth.

V382 Carinae, also known as x Carinae, is a yellow hypergiant in the constellation Carina. It is a G-type star with a mean apparent magnitude of +3.93, and a variable star of low amplitude.

2 Centauri is a single star in the southern constellation of Centaurus, located approximately 183 light-years from Earth. It has the Bayer designation g Centauri; 2 Centauri is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.19. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +41 km/s. The star is a member of the HR 1614 supercluster.
μ Normae, Latinised as Mu Normae, is a blue supergiant star of spectral type O9.7 Iab, located in the constellation of Norma.
Nu Herculis, Latinized from ν Herculis, is a binary and variable star in the constellation of Hercules. With an apparent magnitude of about 4.4, it is faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos spacecraft put it at a distance of about 860 light years.

RT Carinae, also known as CD-58 3538, is a red supergiant and a variable star, located 7,000 light years away in the constellation Carina. It is in the Carina Nebula. The average apparent magnitude of +8.55, too faint to be visible to the naked eye.

45 Draconis is a single star located in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco, around 3,500 light years from the Earth. 45 Draconis is the Flamsteed designation, while it has the Bayer designation of d Draconis. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78. Radial velocity measurements indicate it is moving closer to the Sun at the rate of −12.5 km/s.
106 Herculis is a variable star in the northern constellation Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. Based on its parallax, it is estimated to lie 383 light-years away from the Sun. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of -35 km/s.

19 Monocerotis is a single, variable star in the equatorial constellation of Monoceros, located approximately 1,220 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. It has the variable star designation V637 Monocerotis, while 19 Monocerotis is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.00. It is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +25 km/s.

Omicron1 Orionis is a binary star in the northeastern corner of the constellation Orion. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.7. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.01±0.71 mas, it is located approximately 650 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an interstellar absorption factor of 0.27 due to intervening dust.

72 Pegasi is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.97. The system is located approximately 550 light years away from the Sun, based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −25 km/s.

17 Persei is a single star in the northern constellation of Perseus, located about 390 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.53. This object is moving further from the Earth at a heliocentric radial velocity of +13 km/s.

30 Piscium is a solitary variable star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.37. Its calculated mid-value of antiposed parallax shift as the Earth moves around the Sun of very roughly 7.88 mas, makes it around 410 light years away. Its net movement in the present epoch is one of moving closer – radial velocity is −12 km/s.

KQ Puppis is a spectroscopic binary located about 2,700 light-years from Earth in the constellation Puppis. A red supergiant star and a B-type main-sequence star orbit each other every 27 years. Its apparent magnitude varies between 4.82 and 5.17, making it faintly visible to the naked eye.

HD 51799 is a class M1III star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.95 and it is approximately 860 light years away based on parallax.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8

9 Persei is a single variable star in the northern constellation Perseus, located around 4,300 light years away from the Sun. It has the Bayer designation i Persei; 9 Persei is the Flamsteed designation. This body is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of about 5.2. It is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −15.2 km/s. The star is a member of the Perseus OB1 association of co-moving stars.
η2 Pictoris, Latinised as Eta2 Pictoris, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Pictor. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.02. With an annual parallax shift of 7.8 mas as seen from the Earth, it is located around 418 light years from the Sun. It is a member of the HR 1614 moving group of stars that share a common motion through space.

QU Normae, also known as HR 6131, is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Norma. It is also a variable star, thought to be an α Cyg variable.