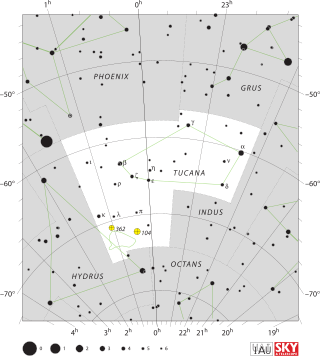
Tucana is a constellation of stars in the southern sky, named after the toucan, a South American bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived in the late sixteenth century by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Tucana first appeared on a 35-centimetre-diameter (14 in) celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Tucana, Grus, Phoenix and Pavo are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), or Nubecula Minor, is a dwarf galaxy near the Milky Way. Classified as a dwarf irregular galaxy, the SMC has a D25 isophotal diameter of about 5.78 kiloparsecs (18,900 light-years), and contains several hundred million stars. It has a total mass of approximately 7 billion solar masses. At a distance of about 200,000 light-years, the SMC is among the nearest intergalactic neighbors of the Milky Way and is one of the most distant objects visible to the naked eye.

The Wild Duck Cluster is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Scutum. It was discovered by Gottfried Kirch in 1681. Charles Messier included it in his catalogue of diffuse objects in 1764. Its popular name derives from the brighter stars forming a triangle which could resemble a flying flock of ducks. The cluster is located just to the east of the Scutum Star Cloud midpoint.

Messier 21 or M21, also designated NGC 6531 or Webb's Cross, is an open cluster of stars located to the north-east of Sagittarius in the night sky, close to the Messier objects M20 to M25. It was discovered and catalogued by Charles Messier on June 5, 1764. This cluster is relatively young and tightly packed. A few blue giant stars have been identified in the cluster, but Messier 21 is composed mainly of small dim stars. With a magnitude of 6.5, M21 is not visible to the naked eye; however, with the smallest binoculars it can be easily spotted on a dark night. The cluster is positioned near the Trifid nebula, but is not associated with that nebulosity. It forms part of the Sagittarius OB1 association.

Messier 18 or M18, also designated NGC 6613, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and included in his list of comet-like objects. From the perspective of Earth, M18 is situated between the Omega Nebula (M17) and the Small Sagittarius Star Cloud (M24).

Messier 69 or M69, also known NGC 6637, is a globular cluster in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It can be found 2.5° to the northeast of the star Epsilon Sagittarii and is dimly visible in 50 mm aperture binoculars. The cluster was discovered by Charles Messier on August 31, 1780, the same night he discovered M70. At the time, he was searching for an object described by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1751–2 and thought he had rediscovered it, but it is unclear if Lacaille actually described M69.

NGC 2022 is a planetary nebula in the equatorial constellation of Orion, located at a distance of 8.21 kilolight-years from the Sun. It was first observed by William Herschel on December 28, 1785, who described it as: considerably bright, nearly round, like a star with a large diameter, like an ill-defined planetary nebula. In medium-sized amateur telescopes it looks like a small grayish patch of light. It is not very bright but it is still easy to spot it in the eyepiece. Even in a telescope as small as 80mm it can just be seen using a narrowband filter such as an OIII filter as a 'fuzzy' star. The object has the shape of a prolate spheroid with a major to minor axis ratio of 1.2, an apparent size of 28″, and a halo extending out to 40″, which is about the angular diameter of Jupiter as seen from Earth.

R136 is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. When originally named it was an unresolved stellar object but is now known to include 72 class O and Wolf–Rayet stars within 5 parsecs of the centre of the cluster. The extreme number and concentration of young massive stars in this part of the LMC qualifies it as a starburst region.

NGC 602 is a young, bright open cluster of stars located in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), a satellite galaxy to the Milky Way. It is embedded in a nebula known as N90.

NGC 346 is a young open cluster of stars with associated nebula located in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) that appears in the southern constellation of Tucana. It was discovered August 1, 1826 by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop. J. L. E. Dreyer described it as, "bright, large, very irregular figure, much brighter middle similar to double star, mottled but not resolved". On the outskirts of the cluster is the multiple star system HD 5980, one of the brightest stars in the SMC.

NGC 290 is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Tucana. This cluster was discovered September 5, 1826 by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop. It lies some 200,000 light years away from the Sun in the Small Magellanic Cloud galaxy. The cluster is an estimated 30–63 million years old and is around 65 light years across.

NGC 5307 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Centaurus, positioned less than 3° to the northeast of the star Epsilon Centauri. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on April 15, 1836. The nebula is located at a distance of approximately 10.6 kilolight-years from the Sun. The central star, designated PNG 312.3+10.5, is a weak emission-line star, superficially similar to the WC subtype of Wolf–Rayet stars. It has a spectral class of O(H)3.5 V.

NGC 6884 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Cygnus, less than a degree to the southwest of the star Ο1 Cygni. It lies at a distance of approximately 12.5 kly from the Sun. The nebula was discovered on May 8, 1883, by American astronomer Edward C. Pickering.

AB8, also known as SMC WR8, is a binary star in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). A Wolf-Rayet star and a main sequence companion of spectral type O orbit in a period of 16.638 days. It is one of only nine known WO stars, the only Wolf-Rayet star in the SMC not on the nitrogen sequence, and the only Wolf-Rayet star in the SMC outside the main bar.

NGC 299 is an open cluster of stars in the main body of the Small Magellanic Cloud – a nearby dwarf galaxy. It is located in the southern constellation of Tucana, just under 200,000 light years distant from the Sun. The cluster was discovered on August 12, 1834 by English astronomer John Herschel.

NGC 376 is a young open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Tucana. It was discovered on September 2, 1826, by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop. Dreyer, a Danish/British astronomer, described it as a "globular cluster, bright, small, round." It is irregular in form, with a central spike.

NGC 1466 is the New General Catalogue designation for a globular cluster in the deep southern constellation of Hydrus. It is located in the outskirts of the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. The object was discovered November 26, 1834 by English astronomer John Herschel. John Dreyer described it as "pF, pS, iR, glbM, *7 f", meaning "pretty faint, pretty small, irregular round, gradually a little brighter middle, with a 7th magnitude star nearby". When using a small telescope, this is a "faint, small, unresolved and difficult" target with an angular size of 1.9 arc minutes. It has an integrated visual magnitude of 11.4.

NGC 2004 is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Dorado. It was discovered by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop on September 24, 1826. This is a young, massive cluster with an age of about 20 million years and 23,000 times the mass of the Sun. It has a core radius of 2.85 ± 0.46 pc (9.3 ± 1.5 ly). NGC 2004 is a member of the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.


















