The Miwok are members of four linguistically related Native American groups Indigenous to what is now Northern California, who traditionally spoke one of the Miwok languages in the Utian family. The word Miwok means people in the Miwok languages.
The Wintun are members of several related Native American peoples of Northern California, including the Wintu (northern), Nomlaki (central), and Patwin (southern). Their range is from approximately present-day Lake Shasta to San Francisco Bay, along the western side of the Sacramento River to the Coast Range. Each of these tribes speak one of the Wintuan languages. Linguistic and archaeological evidence suggests that the Wintun people probably entered the California area around 500 AD from what is now southern Oregon, introducing bow and arrow technology to the region. There has been carbon dating of several artifacts by UC Berkeley that dates back to around 10,000 years, and several of these artifacts have now been repatriated. Despite being a major influence on the region's history, there is still very little history on the Wintu due to centuries of genocide and displacement that still occur today along with continued destruction of sacred ceremonial and religious sites, often due to companies that ignore legal or ethical considerations.

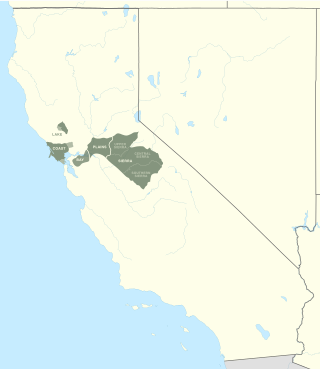
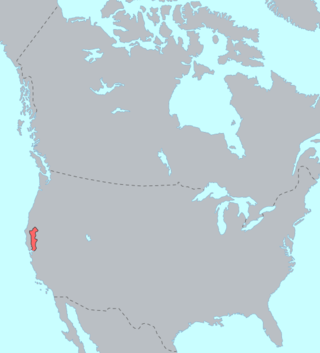
The Maidu are a Native American people of northern California. They reside in the central Sierra Nevada, in the watershed area of the Feather and American Rivers and in Humbug Valley. In Maiduan languages, maidu means "man".

The Spanish word ranchería, or rancherío, refers to a small, rural settlement. In the Americas the term was applied to native villages or bunkhouses. Anglo-Americans adopted the term with both these meanings, usually to designate the residential area of a rancho in the American Southwest, housing aboriginal ranch hands and their families. The term is still used in other parts of Spanish America; for example, the Wayuu tribes in northern Colombia call their villages rancherías.
The Graton Rancheria was a 15.45-acre (62,500 m2) property in the coastal hills of northern California, about two miles (3 km) northwest of Sebastopol. The site is about 1.5 miles (2.4 km) southwest of the hamlet of Graton, population 1,815 in 2000. The area is a few miles west of Santa Rosa, the largest of Sonoma County's nine cities and the County seat, population 147,595 in 2000. It was a former rancheria for Central Coast and Central valley tribes, including the Southern Pomo, a Hokan-speaking tribe, and Coast Miwok.
The Buena Vista Rancheria of Me-Wuk Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Miwok in Amador County, California. The Buena Vista Miwok are Sierra Miwok, an indigenous people of California.
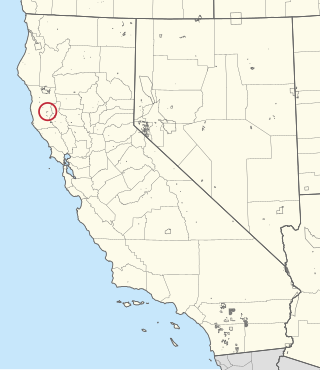
The Redwood Valley Rancheria is a federally recognized Indian tribe located in Redwood Valley, Mendocino County, California. The tribe is primarily composed of Pomo Indians. Redwood Valley Rancheria is a sovereign Indian tribe with the powers of self-governance.
The Big Lagoon Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe of Yurok and Tolowa Indians. They are located in Humboldt County, California, and their tribal headquarters is in Arcata, California.
The Big Sandy Rancheria of Mono Indians of California is a ranchería and federally recognized tribe of Western Mono Indians (Monache) located in Fresno County, California, United States. As of the 2010 Census the population was 118. In 1909, the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) bought 280 acres (110 ha) of land for the Big Sandy Band of Western Mono Indians.
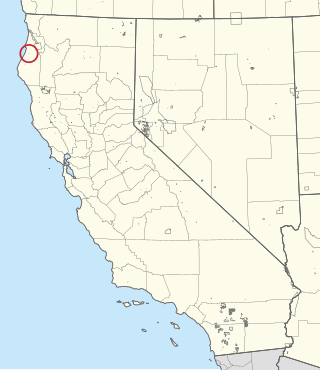
The Blue Lake Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe of Wiyot, Yurok, and Hupa Indians located northwest of the city of Blue Lake in Humboldt County, California on approximately 76 acres (0.31 km2). As of 2007, there were 53 enrolled members. As of the 2010 Census the population of Blue Lake Rancheria was 58.

The Elk Valley Rancheria is a ranchería and federally recognized tribe of Tolowa and Yurok people. It is located in the census-designated place of Bertsch-Oceanview, Del Norte County, California, just east of Crescent City. As of the 2010 Census, the population was 99.

The Sherwood Valley Rancheria of Pomo Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Pomo Indians in California.

The Cold Springs Rancheria of Mono Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Mono Native Americans. Cold Springs Rancheria is the tribe's reservation, which is located in Fresno County, California. As of the 2010 Census the population was 184.
The North Fork Rancheria of Mono Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Mono Native Americans. North Fork Rancheria is the name of the tribe's reservation, which is located in Madera County, California. Nium is their self-designation.
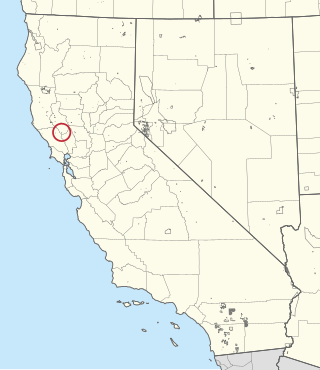
The Middletown Rancheria of Pomo Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Pomo Indians, as well as some Wappo and Lake Miwok Indians, in California, headquartered in Middletown, California.
The Susanville Indian Rancheria is a federally recognized ranchería of Native Americans in northeastern California whose people are from the Washoe, Achomawi, Mountain Maidu, Northern Paiute, and Atsugewi tribes.
The Cher-Ae Heights Indian Community of the Trinidad Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe with members who are descendants of Chetco, Hupa, Karuk, Tolowa, Wiyot, and Yurok people in Humboldt County, California. As of the 2010 Census the population was 132.












