Related Research Articles

The president of India is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the supreme commander of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office from 25 July 2022.

National Human Rights Commission of India is a statutory body constituted on 12 October 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Ordinance of 28 September 1993. It was given a statutory basis by the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993 (PHRA). The NHRC is responsible for the protection and promotion of human rights, which is defined by the act as "rights relating to life, liberty, equality and dignity of the individual guaranteed by the Constitution or embodied in the International Covenants and enforceable by courts in India".
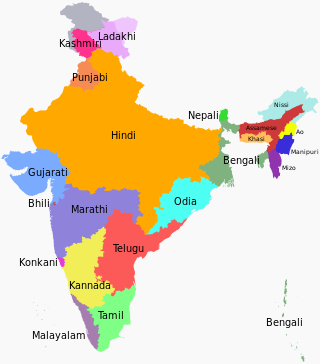
As of 2024, 22 languages have been classified as recognised languages under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. There is no designated national language of India.
The Other Backward Class (OBC) is a collective term used by the Government of India to classify communities that are "educationally or socially backward". It is one of several official classifications of the population of India, along with general castes, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. The OBCs were found to comprise 52% of the country's population by the Mandal Commission report of 1980 and were determined to be 41% in 2006 when the National Sample Survey Organisation took place. There is substantial debate over the exact number of OBCs in India; it is generally estimated to be sizable, but many believe that it is higher than the figures quoted by either the Mandal Commission or the National Sample Survey.

The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes.
India since its independence in 1947 has been a secular country. The secular values were enshrined in the constitution of India. India's first prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru is credited with the formation of the secular republic in the modern history of the country. With the Forty-second Amendment of the Constitution of India enacted in 1976, the Preamble to the Constitution asserted that India is a secular nation. However, the Supreme Court of India in the 1994 case S. R. Bommai v. Union of India established the fact that India was secular since the formation of the republic. The judgement established that there is separation of state and religion. It stated "In matters of State, religion has no place. Any State government which pursues nonsecular on policies or nonsecular course of action acts contrary to the constitutional mandate and renders itself amenable to action under Article 356". Furthermore, constitutionally, state-owned educational institutions are prohibited from imparting religious instructions, and Article 27 of the constitution prohibits using tax-payers money for the promotion of any religion.

The Union Public Service Commission is a constitutional body tasked with recruiting officers for All India Services and the Central Civil Services through various standardized examinations. In 2023, 1.3 million applicants competed for just 1,255 positions.

Katni officially Murwara is a city on the banks of the Katni River in Madhya Pradesh, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Katni District. It is in the Mahakoshal region of central India. The city is 90 km (56 mi) from the divisional headquarters of the region, Jabalpur.
Reservation is a system of affirmative action in India that was established during the British rule. Based on provisions in the Indian Constitution, it allows the Union Government and the States and Territories of India to allocate a specific percentage of reserved quotas or seats, in higher education admissions, employment, political bodies, etc., for "socially and economically backward citizens". Since its implementation, reservation has been a subject of debate and controversy over its impact, execution and effectiveness, significantly shaping the agendas of political parties and the actions of social groups.
The Fundamental Rights in India enshrined in part III of the Constitution of India guarantee civil liberties such that all Indians can lead their lives in peace and harmony as citizens of India. These rights are known as "fundamental" as they are the most essential for all-round development i.e., material, intellectual, moral and spiritual and protected by fundamental law of the land i.e. constitution. If the rights provided by Constitution especially the Fundamental rights are violated the Supreme Court and the High Courts can issue writs under Articles 32 and 226 of the Constitution, respectively, directing the State Machinery for enforcement of the fundamental rights.
The Directive Principles of State Policy of India are the guidelines to be followed by the government of India for the governance of the country. They are not enforceable by any court, but the principles laid down there are considered "Fundamental" in the governance of the country, which makes it the duty of the State to apply these principles in making laws to establish a just society in the country. The principles have been inspired by the Directive Principles given in the Constitution of Ireland which are related to socialjustice, economic welfare, foreign policy, and legal and administrative matters.
Linguistic rights are the human and civil rights concerning the individual and collective right to choose the language or languages for communication in a private or public atmosphere. Other parameters for analyzing linguistic rights include the degree of territoriality, amount of positivity, orientation in terms of assimilation or maintenance, and overtness.
The Ministry of Law and Justice in the Government of India is a cabinet ministry which deals with the management of the legal affairs, legislative activities and administration of justice in India through its three departments namely the Legislative Department and the Department of Legal Affairs and the Department of Justice respectively. The Department of Legal Affairs is concerned with advising the various Ministries of the Central Government while the Legislative Department is concerned with drafting of principal legislation for the Central Government. The ministry is headed by Cabinet Minister of Law and Justice Arjun Ram Meghwal appointed by the President of India on the recommendation of the Prime Minister of India. The first Law and Justice minister of independent India was Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, who served in the Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru's cabinet during 1947–51.

The National Commission for Minorities (NCM) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India, established in 1993. It is responsible to safeguard and protect the interests of minorities—Buddhists, Christians, Jains, Muslims, Sikhs, and Zoroastrians (Parsis).
National Commission for Religious and Linguistic Minorities, also called Ranganath Misra Commission, was constituted by Government of India on 29 October 2004 to look into various issues related to Linguistic and Religious minorities in India. It was chaired by former Chief Justice of India Justice Ranganath Misra, member of Rajya Sabha from 1998 to 2004. The commission submitted the report to the Government on 21 May 2007.

The Ministry of Minority Affairs is the ministry in the Government of India which was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and created on 29 January 2006. It is the apex body for the central government's regulatory and developmental programmes for the minority religious communities and minority linguistic communities in India, which include Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, Zoroastrians (Parsis) and Jains notified as minority religious communities in The Gazette of India under Section 2(c) of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992.

The National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) is a constitutional body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India. It was originally a statutory body established in 1993 through the National Commission for Backward Classes Act of 1993. In 2018, through the 102nd constitutional amendment, it was granted constitutional status under Article 338B of the Constitution of India.
Ordinances are laws that are promulgated by the President of India on the recommendation of the Union Cabinet, which will have the same effect as an Act of Parliament. They can only be issued when Parliament is not in session. They enable the Indian government to take immediate legislative action. Ordinances cease to operate either if Parliament does not approve of them within six weeks of reassembly, or if disapproving resolutions are passed by both Houses. It is also compulsory for a session of Parliament to be held within six months. A total of 679 ordinances have been issued from 1950-2014.

The West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education is the state government administered autonomous examining authority for affiliated and recognized madrasahs in West Bengal, India. Perhaps among the oldest post-secondary boards in India, it is the only madrasah board that is recognized by the Government of India. It is one of the parastatal organization of the Minority Affairs and Madrasah Education Department. The West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education is the West Bengal state government administered autonomous examining authority for the High Madrasah examination of West Bengal, India. It has come into force by the West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education Act-1994.
Article 30 is an article of the Constitution of India. It is included in Part 3 of the Constitution. Under which the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions is described. Article 30 protects the rights of minority communities to develop and manage educational institutions of their choice. All minorities, whether based on religion or language, have the right to develop and manage educational institutions of their choice.
References
- ↑ "No minority status to educational institutions on Linguistic basis". www.pib.nic.in. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ↑ "NCMEI". NCMEI. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- ↑ Wikisource:Constitution of India/Part III#Article 30 .7BRight of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.7D
- ↑ "Press Information Bureau English Releases". Pib.nic.in. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "About the National Commission for Minority Educational Institutions". National Commission for Minority Educational Institutions.