
The politics of Libya has been in an uncertain state since the collapse of the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya in 2011 and a recent civil war and various jihadists and tribal elements controlling parts of the country.

Human rights in Libya is the record of human rights upheld and violated in various stages of Libya's history. The Kingdom of Libya, from 1951 to 1969, was heavily influenced by the British and Y.R.K companies. Under the King, Libya had a constitution. The kingdom, however, was marked by a feudal regime. Due to the previous colonial regime, Libya had a low literacy rate of 10%, a low life expectancy of 57 years, with many people living in shanties and tents. Illiteracy and homelessness were chronic problems during this era, when iron shacks dotted many urban centres in the country.

The National Front for the Salvation of Libya (NFSL) was a political opposition group active during the rule of the Gaddafi regime in Libya. It was formed in 1981 and called for major liberalising reforms such as democratic elections, a free press, and the separation of powers. During the 1980s, it pursued a campaign of armed opposition to the Gaddafi regime and made several coup attempts, the most notable being its 1984 armed assault on Gaddafi's Bab al-Azizia compound in Tripoli. After the failure of this and several other coup attempts the group largely abandoned militancy, and instead used peaceful tactics to promote reform in Libya; in 2005, the NFSL joined with six other groups to form the National Conference for the Libyan Opposition.

The Constitution of Kuwait was created by the Constitutional Assembly in 1961–1962 and signed into law on 11 November 1962 by the Emir, the Commander of the Military of Kuwait Sheikh Abdullah III Al-Salim Al-Sabah.

The Libyan civil war, also known as the First Libyan Civil War, was an armed conflict in 2011 in the North African country of Libya that was fought between forces loyal to Colonel Muammar Gaddafi and rebel groups that were seeking to oust his government. The war was preceded by protests in Zawiya on 8 August 2009 and finally ignited by protests in Benghazi beginning on Tuesday 15 February 2011, which led to clashes with security forces who fired on the crowd. The protests escalated into a rebellion that spread across the country, with the forces opposing Gaddafi establishing an interim governing body, the National Transitional Council.

Mustafa Abdul Jalil is a Libyan politician who was the Chairman of the National Transitional Council from 5 March 2011 until its dissolution on 8 August 2012. This position meant he was de facto head of state during a transitional period after the fall of Muammar Gaddafi's government in the Libyan Civil War, and until the handover of power to the General National Congress.
The international reactions to the Libyan Civil War were the responses to the series of protests and military confrontations occurring in Libya against the government of Libya and its de facto head of state Muammar Gaddafi.

The anti-Gaddafi forces, also known as the Libyan opposition or Libyan rebels, were Libyan groups that opposed and militarily defeated the government of Muammar Gaddafi during the First Libyan Civil War in 2011, killing him in the process. The Anti-Gaddafi forces were represented by the National Transitional Council and their National Liberation Army, which claimed to be the "only legitimate body representing the people of Libya and the Libyan state". These opposition forces included organized and armed militia groups, participants in the Libyan Civil War, Libyan diplomats who switched their allegiance from the Gaddafi-led government, and Libyan military units that switched sides to support the protesters.

The National Transitional Council (NTC) was a transitional government established in the 2011 Libyan civil war. The rebel forces overthrew the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya of Muammar Gaddafi. The NTC governed Libya for a period of ten months after the end of the war, holding elections to a General National Congress on 7 July 2012, and handing power to the newly elected assembly on 8 August.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1970 was a measure adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 26 February 2011. It condemned the use of lethal force by the government of Muammar Gaddafi against protesters participating in the Libyan Civil War, and imposed a series of international sanctions in response.

Abdul Hafiz Ghoga is a Libyan human rights lawyer who rose to prominence as the spokesman for the National Transitional Council, a body formed in Benghazi during the 2011 Libyan civil war. On 23 March 2011, he became the vice chairman of the council, serving in that post until he resigned on 22 January 2012 after protests against him.
Khamis Gaddafi was the seventh and youngest son of former Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi, and the military commander in charge of the Khamis Brigade of the Libyan Army. He was part of his father's inner circle. During the Libyan Civil War in 2011, he was a major target for opposition forces trying to overthrow his father.
Free speech in the media during the Libyan civil war describes the ability of domestic and international media to report news inside Libya free from interference and censorship during the civil war.
The outbreak of the Libyan Civil War was followed by accusations of human rights violations by rebel forces opposed to Muammar Gaddafi, Gaddafi's armed forces, and NATO. The alleged violations include rape, extrajudicial killings, ethnic cleansing, misconduct and bombings of civilians.
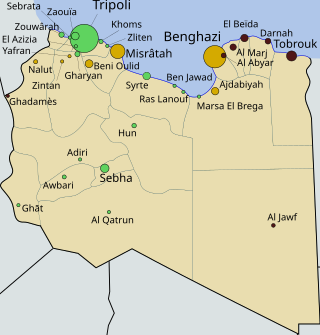
The Libyan Civil War began on 15 February 2011 as a chain of civil protests and later evolved into a widespread uprising against the regime of Muammar Gaddafi. On 25 February, most of eastern Libya was reported to be under the control of protesters and rebel forces. Gaddafi remained in control of the cities of Tripoli, Sirte and Sabha. By 15 March, however, Gaddafi's forces had retaken more than half a dozen lost cities. Except for most of Cyrenaica and a few Tripolitania cities the majority of cities had returned to Gaddafi government control.

The killing of Muammar Gaddafi took place on 20 October 2011 after the Battle of Sirte. Muammar Gaddafi, the deposed leader of Libya, was captured by NTC forces and executed shortly afterwards.

Ashour Ben Khayal, sometimes romanised Ben Hayal, is a Libyan diplomat and politician who was born in the Cyrenaican city of Derna in September 1939. He was named Foreign Minister on 22 November 2011 by Abdurrahim El-Keib in a surprise move, as the position was originally reported to be filled by Libya's deputy ambassador to United Nations Ibrahim Dabbashi. He was described as little-known prior to his appointment.
The following lists events that happened during 2011 in Libya.

Hisham Ben Ghalbon is a founding member and spokesman for Libyan Constitutional Union (LCU) and was an opponent of the regime of Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi since the mid 1970s when Ben Ghalbon was a student at the faculty of Engineering in the University of Tripoli.











