The legal status of transgender people varies greatly around the world. Some countries have enacted laws protecting the rights of transgender individuals, but others have criminalized their gender identity or expression. In many cases, transgender individuals face discrimination in employment, housing, healthcare, and other areas of life.

New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kenya face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Sodomy is a felony per Section 162 of the Kenyan Penal Code, punishable by 21 years' imprisonment, and any sexual practices are a felony under section 165 of the same statute, punishable by five years' imprisonment. On 24 May 2019, the High Court of Kenya refused an order to declare sections 162 and 165 unconstitutional. The state does not recognise any relationships between persons of the same sex; same-sex marriage is banned under the Kenyan Constitution since 2010. There are no explicit protections against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. Adoption is restricted to heterosexual couples only.
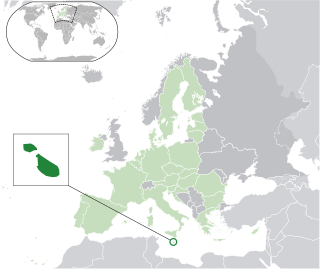
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Malta rank among the highest in the world. Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the rights of the LGBT community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity was legalized on 29 January 1973. The prohibition was already dormant by the 1890s.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in India face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT people. There are no legal restrictions against gay sex or gay expression within India. Same-sex couples have some limited cohabitation rights, colloquially known as live-in relationships. However, India does not currently provide for common law marriages, same-sex marriage, civil unions, guardianship or issue partnership certificates.
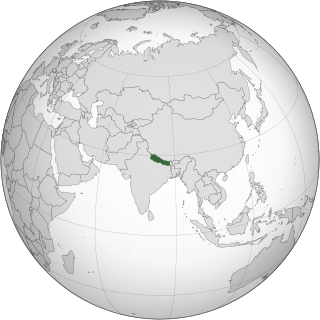
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Nepal have expanded in the 21st century, though much of Nepal's advancements on LGBT rights have come from the judiciary and not the legislature. Same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Nepal since 2007 after a ruling by the Supreme Court of Nepal.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in Tamil Nadu are the most progressive among all states of India. Tamil Nadu was the first state in India to introduce a transgender welfare policy, wherein transgender individuals can access free gender affirmation surgery in government hospitals and various other benefits and rights. The state was also the first to ban forced sex-selective surgeries on intersex infants, and also the first state to include an amendment in its state police guidelines that expects officers to abstain from harassing the LGBTQIA+ community and its members. The state also became the first to ban conversion therapy as well as the first to introduce LGBTQIA+ issues in school curricula.

Accessible India Campaign or Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan is a program which is set to be launched to serve the differently-able community of the country. The program comes with an index to measure the design of disabled-friendly buildings and human resource policies. The flagship program has been launched by the Prime Minister on 3 December 2015, the International Day of people with Disabilities. The initiative also in line with the Article 9 of the to which India is a signatory since 2007. The scheme also comes under Persons with Disabilities Act, 1995 under section 44, 45, 46 for equal Opportunities and protection of rights which provides non-discrimination in Transport to Persons with Disabilities.

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals, that, according to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies."

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals that, according to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". "Because their bodies are seen as different, intersex children and adults are often stigmatized and subjected to multiple human rights violations".
Transgender rights in Australia have legal protection under federal and state/territory laws, but the requirements for gender recognition vary depending on the jurisdiction. For example, birth certificates, recognised details certificates, and driver licences are regulated by the states and territories, while Medicare and passports are matters for the Commonwealth.

Transgender and non-binary people in New Zealand face discrimination in several aspects of their lives. The law is unclear on the legal status of discrimination based on gender identity, and also for intersex people.

Multiple countries legally recognize non-binary or third gender classifications. These classifications are typically based on a person's gender identity. In some countries, such classifications may only be available to intersex people, born with sex characteristics that "do not fit the typical definitions for male or female bodies."

Intersex rights in Malta since 2015 are among the most progressive in the world. Intersex children in Malta have world-first protections from non-consensual cosmetic medical interventions, following the passing into law of the Gender Identity, Gender Expression and Sex Characteristics Act in 2015. All Maltese intersex persons have protection from discrimination. Individuals who seek it can access simple administrative methods of changing sex assignment, with binary and non-binary forms of identification available.

Gopi Shankar Madurai is an Indian equal rights and Indigenous rights activist. Shankar was one of the youngest, and the first openly intersex and genderqueer statutory authority and one of the candidates to contest in 2016 Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly election. Shankar is also the founder of Srishti Madurai Student Volunteer Collective. Shankar's work inspired the Madras High Court to direct the Government of Tamil Nadu to order a ban on forced sex-selective surgeries on intersex infants. In December 2017, Shankar was elected to the executive board of ILGA Asia. In August 2020, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment appointed Shankar as the South Regional representative in the National Council for Transgender Persons.
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Act, 2017, often shortened to the HIV/AIDS Prevention Act, is an act of the Parliament of India that provides for controlling and preventing of HIV/AIDS and securing the rights of individuals diagnosed with HIV/AIDS. The bill for the act was introduced in the Rajya Sabha on 11 February 2014 and was referred to a Standing Committee on 24 February 2014, which submitted its report on 29 April 2015. After few amendments to the original 2014 bill, it was passed by the Rajya Sabh on 21 March 2017 and the Lok Sabha on 11 April 2017. It received Presidential assent on 20 April 2017, and became effective from 10 September 2018. The HIV/AIDS Prevention Act originated from a draft bill submitted by Lawyers Collective, a non-governmental organization, to the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) in 2006. The act penalises propagation of hate against HIV/AIDS affected persons, ensures the right of HIV/AIDS affected minors to shared household, protects non-disclosure of HIV/AIDS status in the absence of court order and mandates informed consent to disclose HIV/AIDS positive identity, inter alia. However, civil society organisations and HIV/AIDS affected persons criticised the act on certain legal language issues, as it mandates the state to provide HIV/AIDS affected persons with medical services "as far as possible". This aspect was absent from the draft bill submitted to NACO.
The Transgender Persons Act, 2019 is an act of the Parliament of India with the objective to provide for protection of rights of transgender people, their welfare, and other related matters. The act was introduced in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament, on 19 July 2019 by the Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment, Thawar Chand Gehlot, in light of the lapse of the Transgender Persons Bill, 2018. The 2019 act and the immediately preceding 2018 bill, were both preceded by a 2016 version. They were met with protests and criticism by some transgender people, lawyers, and activists in India. The 2016 bill was sent to a standing committee which submitted its report in July 2017. Following this, the Lok Sabha tabled and passed a newer version of the bill in December 2018. However, it did not incorporate many of the committee's recommendations. Although members of the opposition criticised the 2019 act and assured activists that they would not vote in favour of it, it was passed by the Lok Sabha on 5 August 2019 and by the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of the Parliament, on 26 November 2019. The president assented to it on 5 December 2019, upon which the act was published in the Gazette of India. It has been in effect since 10 January 2020 following a notification of the same in the Gazette on the same day.

Gender self-identification is the concept that a person's legal sex or gender is determined by their gender identity without any medical requirements, such as via statutory declaration.

S Sushma &Anr. versus Commissioner of Police&Ors.(2021) is a landmark decision of the Madras High Court that prohibited practice of "conversion therapy" by medical professionals in India. The court directed comprehensive measures to sensitize the society and various branches of the Union and State governments to remove prejudices against the queer community.

Arun Kumar &Anr. versus Inspector General of Registration&Ors. (2019) is a decision of the Madras High Court which recognised trans woman as a "bride" within the meaning of the Hindu Marriage Act 1955 and prohibited genital-normalizing surgery for intersex infants and children except on life-threatening situations.













