
Tampa is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the county seat of Hillsborough County. With an estimated population of 403,364 in 2023, Tampa is the 49th-most populous city in the country and the third-most populous city in Florida after Jacksonville and Miami.

Clearwater is a city and the county seat of Pinellas County, Florida, United States, west of Tampa and north of St. Petersburg. To the west of Clearwater lies the Gulf of Mexico and to the southeast lies Tampa Bay. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 117,292. It is the smallest of the three principal cities in the Tampa–St. Petersburg–Clearwater metropolitan area, most commonly referred to as the Tampa Bay area.

The Tampa Bay area is a major metropolitan area surrounding Tampa Bay on the Gulf Coast of Florida in the United States. It includes the main cities of Tampa, St. Petersburg, and Clearwater. It is the 17th-largest metropolitan area in the United States, with a population of 3,175,275 as of the 2020 U.S. census.

The 1993 Storm of the Century was a cyclonic storm, or nor'easter, that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on March 12, 1993. The cold weather, heavy snowfall, high winds and storm surge that the storm brought affected a very large area; at its height, it stretched from Canada to Honduras. The cyclone moved through the Gulf of Mexico and then through the eastern United States before moving on to eastern Canada. It eventually dissipated in the North Atlantic Ocean on March 15.
Bay News 9 is a cable news television network located in St. Petersburg, Florida. Owned by Charter Communications, it currently serves the Tampa Bay area including Hillsborough, Pinellas, Manatee, Polk, Pasco, Hernando, and Citrus counties. The station, which is exclusive to Spectrum customers, provides rolling news programming 24 hours a day, with the exception of some special programming, including a weekly political program, Political Connections.

The 1944 Cuba–Florida hurricane was a large Category 4 tropical cyclone on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale that caused widespread damage across the western Caribbean Sea and Southeastern United States in October 1944. It inflicted over US$100 million in damage and caused at least 318 deaths, the majority of fatalities occurring in Cuba. One study suggested that an equivalent storm in 2018 would rank among the costliest U.S. hurricanes. The full extent of the storm's effects remains unclear due to a dearth of conclusive reports from rural areas of Cuba. The unprecedented availability of meteorological data during the hurricane marked a turning point in the United States Weather Bureau's ability to forecast tropical cyclones.

It is very rare for snow to fall in the U.S. state of Florida, especially in the central and southern portions of the state. With the exception of the far northern areas of the state, most of the major cities in Florida have never recorded measurable snowfall, though trace amounts have been recorded, or flurries in the air observed few times each century. According to the National Weather Service, in the Florida Keys and Key West there is no known occurrence of snow flurries since the European colonization of the region more than 300 years ago. In Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and West Palm Beach there has been only one known report of snow flurries observed in the air in more than 200 years; this occurred in January 1977.

The 2007 Groundhog Day tornado outbreak was a localized but devastating tornado event that took place in central Florida early on February 2, 2007. Early morning temperatures had risen well above average for the season; combined with increased moisture and a powerful jet stream, this created enough instability and wind shear for thunderstorms to rotate and spawn tornadoes. Due to the conditions, a long-tracked supercell formed and produced three tornadoes over one hour and seventeen minutes. The supercell resulted in a 70-mile (110-kilometer) trail of damage.

The climate of the north and central parts of the U.S. state of Florida is humid subtropical. South Florida has a tropical climate. There is a defined rainy season from May through October when air-mass thundershowers that build in the heat of the day drop heavy but brief summer rainfall.

An extreme wind warning is an alert issued by the National Weather Service for areas on land that will experience sustained surface winds 100 knots or greater within one hour. As of 2024, it has only been used for the eyewalls of major hurricanes when they pass near-shore, and during and shortly after landfall, but it is also intended as a general "short-fused" warning for any immediate occurrence of such winds. Extreme wind warnings are issued for as precise of an area as possible, in like manner as a tornado warning, to provide guidance to the general public at the county and sub-county level when such winds pose a significant threat of casualties. They cannot be issued earlier than two hours before the onset of extreme winds.

The Tampa Bay area has a humid subtropical climate, closely bordering a tropical climate near the waterfront areas. There are two basic seasons in the Tampa Bay area, a hot and wet season from May through October, and a mild and dry season from November through April.
The National Weather Service Miami, Florida is a local weather forecast office of the National Weather Service (NWS) that serves six counties in South Florida – Broward, Collier, Glades, Hendry, Miami-Dade, and Palm Beach – as well as the mainland portion of Monroe County. This office was originally established in 1879 as a Signal Corps station near the Jupiter Inlet Light, before becoming a Weather Bureau Office (WBO) in 1891. The WBO at Jupiter was moved southward to Miami in 1911, due to the city's rapidly growing population. In 1930, a separate Weather Bureau Airport Station (WBAS) was established at the Miami Municipal Airport. The WBAS was later moved to the Miami International Airport in 1942 and remained there until ceasing operations in 1975.
The cold wave of January 1977 produced the only known trace of snow in the greater Miami area of Florida ever reported. It occurred following the passage of a strong cold front, in combination with a high-pressure area situated over the Mississippi River Valley. As a result, cold air moved far to the south across Florida, causing both snow flurries and record low temperatures. Most notably, the weather system brought snow flurries as far south as Homestead on January 19. No snow had ever been reported in southeastern Florida before or since. Damage was most significant to agriculture, as major losses occurred to citrus fruits and tender vegetables. Statewide, agricultural damage from the cold wave totaled to $350 million, and losses overall totaled to $2 billion. One fatality occurred due to an automobile accident in Central Florida, which was related to the cold wave.
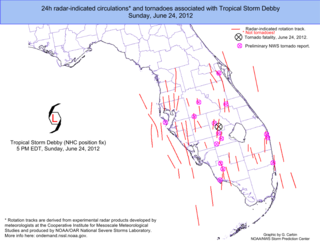
From June 23 to 26, 2012, Tropical Storm Debby produced a significant tornado outbreak across the Florida Peninsula. Throughout the entire event, 25 tornadoes touched down across the state, making the outbreak the second largest on record in Florida, behind only that spawned by Hurricane Agnes, which produced 28 tornadoes from June 18 to 19, 1972. At least ten of the tornadoes—the largest 24-hour total in South Florida since Hurricane Isbell produced eight in 1964—had been confirmed in four South Florida counties by the National Weather Service forecast office in Miami.

The passage of Hurricane Isaac generated a long-lived, nine-day tornado outbreak that affected the Central and Eastern United States from August 27 to September 4, 2012. The hurricane produced a total of 34 tornadoes, with the strongest being two EF2 tornadoes in Mississippi and Arkansas. There were 19 tornado watches were issued for Isaac over eight days and 171 tornado warnings were issued across 12 states, with 77 of them in Mississippi.

Tropical Storm Nestor was a large but short-lived and disorganized tropical cyclone which caused widespread tornadoes and heavy rain in the Southeastern United States during mid-October 2019. The sixteenth depression and fourteenth named storm of the erratic 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Nestor originated from a broad area of low pressure over the Western Caribbean. It emerged in the Gulf of Mexico and began to organize slightly, becoming Potential Tropical Cyclone Sixteen due to its threat to the Southeastern United States. It gained sufficient circulation to be designated Tropical Storm Nestor near the Florida Panhandle early on October 18, crawling to the northeast, and then finally transitioning into an extratropical cyclone due to strong shear from a nearby upper-level low before making landfall on the Florida Panhandle on October 19.















