Related Research Articles

The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and its energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe.
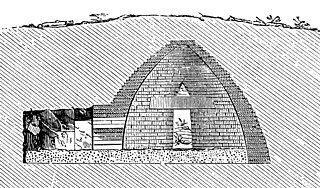
A beehive tomb, also known as a tholos tomb, is a burial structure characterized by its false dome created by corbelling, the superposition of successively smaller rings of mudbricks or, more often, stones. The resulting structure resembles a beehive, hence the traditional English name.

Pyrgos is an archaeological site of the Minoan civilization near Myrtos in the municipality of Ierapetra on the south coast of Crete. Pyrgos provides evidence of settlements along the southern Ierapetra Isthmus. This site has had a long history due to its valuable location and geography. It is located close to the Myrtos valley and has a harbor with a nearby mountain range providing its protection. The settlement includes a courtyard, many rooms, a country house and a tomb.


Therasia, also known as Thirasía, is an island in the volcanic island group of Santorini in the Greek Cyclades. It lies north-west of Nea Kameni, a small island formed in recent centuries by volcanic activity and thus marking the centre of the island group. Therasia is the second largest island of the group, the largest by far being Thera.

Pseira is an islet in the Gulf of Mirabello in northeastern Crete with the archaeological remains of Minoan and Mycenean civilisation.

Koumasa is the archaeological site of a prepalatial cemetery on Crete. The cemetery is located between the villages of Loukia and Koumasa near the southern border of the Mesara plain, right at the foothills of the Asterousia-Mountains. This Minoan archaeological site was first excavated by Stephanos Xanthoudides from 1904 to 1906, which was published in The vaulted tombs of Mesara. After another campaign within the years 1991 and 1992 by Alexandra Karetsou and Athanasia Kanta, the site is investigated by the University of Heidelberg supervised by Prof. Dr. Diamantis Panagiotopoulos.

Sacred caves and peak sanctuaries are characteristic holy places of ancient Minoan Crete. Most scholars agree that sacred caves were used by the Minoans for religious rites, and some for burial. While all peak sanctuaries have clay human figurines, only Idaeon, Trapeza and Psychro have them among the sacred caves. Clay body parts, also called votive body parts, common among peak sanctuaries, appear in no caves with the exception of a bronze leg in Psychro.
Apodoulou is the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan mansion or ceremonial building.

Mochlos is a modern, populated, and inhabited island in the Gulf of Mirabello in eastern Crete, and the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan settlement. There is evidence that Mochlos was not an island in Minoan times, but was attached to the mainland and acted as an eastern harbor.

Phourni is the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan cemetery in Crete, established in 2400 BC and lasted until 1200 BC. Phourni is Greek for "furnace, oven" and the name of the hill on which the cemetery is located. Phourni is located at 70100 Epano Archanes, Heraklion, Greece—located on a hill in north-central Crete. Phourni can be seen from Mount Juktas. It is a small hill situated northwest of Archanes, between Archanes and Kato Archanes. Phourni is reachable from a signed scenic path that starts at Archanes. It was an important site for Minoan burials. The burials consistently and proactively engaged the community of the Minoans. The largest cemetery in the Archanes area was discovered in 1957 and excavated for 25 years by Yiannis Sakellarakis, beginning in 1965. The 6600 sq m cemetery includes 26 funerary buildings of varying shapes and sizes. The necropolis of Phourni is of primary importance, both for the duration of its use and for the variety of its funerary monuments. All the pottery and much of the skeletal material was collected, unlike many other pre-palatial tombs. The cemetery was founded in the Ancient Minoan IIA, and continued to be used until the end of the Bronze Age. The occupation reached its peak during the Middle Minoan AI, just before the palaces of Knossos and Malia appeared. The proximity of Archanes to the important religious centres of Mount Iuktas probably contributed to the prominence of the site.

Kamilari is a village on the island of Crete, Greece, with 379 inhabitants. There is an archaeological site of an ancient Minoan cemetery nearby. The origin of the name 'Kamilari' is Byzantine. It is derived from the word 'kamilaris' or ‘Καμηλάρης’ meaning 'the one who rides a camel' Original owners of the name Kamilari live in Cyprus as Catholic Maronites and are quite active with investments and activities in the area of Kamilari.
Odigitria is the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan religious complex including two tholos tombs located near the modern Odigitria Monastery in the Asterousia mountains of southern Crete.

Armeni is the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan cemetery on Crete, roughly eight kilometers south of the modern town of Rethymnon.

Hagia Photia is an archaeological site of a fortified ancient Minoan building on eastern Crete. Sitia lies five kilometers to the west.

Nea Alikarnassos is a town and a former municipality in the Heraklion regional unit, Crete, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Heraklion, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 16.1 km2. Population 14,635 (2011). It is located on the north coast of the island and is served by the Nikos Kazantzakis International Airport. In the settlement of Prassas, the Minoan ruins of two houses were found.

Minoan religion was the religion of the Bronze Age Minoan civilization of Crete. In the absence of readable texts from most of the period, modern scholars have reconstructed it almost totally on the basis of archaeological evidence of such as Minoan paintings, statuettes, vessels for rituals and seals and rings. Minoan religion is considered to have been closely related to Near Eastern ancient religions, and its central deity is generally agreed to have been a goddess, although a number of deities are now generally thought to have been worshipped. Prominent Minoan sacred symbols include the bull and the horns of consecration, the labrys double-headed axe, and possibly the serpent.

Tell el-Dab'a is an archaeological site in the Nile Delta region of Egypt where Avaris, the capital city of the Hyksos, once stood. Avaris was occupied by Asiatics from the end of the 12th through the 13th Dynasty. The site is known primarily for its Minoan frescoes.

Minoan seals are impression seals in the form of carved gemstones and similar pieces in metal, ivory and other materials produced in the Minoan civilization. They are an important part of Minoan art, and have been found in quantity at specific sites, for example in Knossos, Mallia and Phaistos. They were evidently used as a means of identifying documents and objects.
Minoan Flying Dolphins (MFD) was a Greek passenger and freight ferry company.
References
- Swindale, Ian "Nea Roumata" Retrieved 11 February 2006