
Chiricahua is a band of Apache Native Americans.
The Apache are several Southern Athabaskan language–speaking peoples of the Southwest, the Southern Plains and Northern Mexico. They are linguistically related to the Navajo. They migrated from the Athabascan homelands in the north into the Southwest between 1000 and 1500 CE.

Sky islands are isolated mountains surrounded by radically different lowland environments. The term originally referred to those found on the Mexican Plateau and has extended to similarly isolated high-elevation forests. The isolation has significant implications for these natural habitats. The American Southwest region began warming up between c. 20,000 and 10,000 years BP and atmospheric temperatures increased substantially, resulting in the formation of vast deserts that isolated the sky islands. Endemism, altitudinal migration, and relict populations are some of the natural phenomena to be found on sky islands.

The Chiricahua Mountains massif is a large mountain range in southeastern Arizona which is part of the Basin and Range province of the west and southwestern United States and northwest Mexico; the range is part of the Coronado National Forest. The highest point, Chiricahua Peak, rises 9,759 feet (2,975 m) above sea level, approximately 6,000 feet (1,800 m) above the surrounding valleys. The range takes its name from the Chiricahua Apaches native to the region.

The Western Apache are a subgroup of the Apache Native American people, who live primarily in east central Arizona, in the United States and north of Mexico in the states of Sonora and Chihuahua. Most live within reservations. The Fort Apache Indian Reservation, San Carlos Apache Indian Reservation, Yavapai-Apache Nation, Tonto Apache, and the Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation are home to the majority of Western Apache and are the bases of their federally recognized tribes. In addition, there are numerous bands. The Western Apache bands call themselves Ndee (Indé). Because of dialectical differences, the Pinaleño/Pinal and Arivaipa/Aravaipa bands of the San Carlos Apache pronounce the word as Innee or Nnēē:.

The Madrean Sky Islands are enclaves of Madrean pine–oak woodlands, found at higher elevations in a complex of small mountain ranges in southern and southeastern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and northwestern Mexico. The sky islands are surrounded at lower elevations by the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts. The northern west–east perimeter of the sky island region merges into the higher elevation eastern Mogollon Rim and the White Mountains of eastern Arizona.
Mescalero-Chiricahua is a Southern Athabaskan language spoken by the Chiricahua and Mescalero people in Chihuahua and Sonora, México and in Oklahoma and New Mexico. It is related to Navajo and Western Apache and has been described in great detail by the anthropological linguist Harry Hoijer (1904–1976), especially in Hoijer & Opler (1938) and Hoijer (1946). Hoijer & Opler's Chiricahua and Mescalero Apache Texts, including a grammatical sketch and traditional religious and secular stories, has been converted into an online "book" available from the University of Virginia.

Apache Pass, also known by its earlier Spanish name Puerto del Dado, is a historic mountain pass in the U.S. state of Arizona between the Dos Cabezas Mountains and Chiricahua Mountains at an elevation of 5,110 feet (1,560 m). It is approximately 20 miles (32 km) east-southeast of Willcox, Arizona, in Cochise County.

The brown-backed solitaire is considered a thrush and is placed in the family Turdidae. It is a medium-sized bird about 21 centimeters long. It is a mostly grayish bird with brown flight feathers, a white eye ring and white rectrices (tail) feathers.

The Mexican fox squirrel is a species of tree squirrel found throughout the Sierra Madre Occidental of Mexico as far south as Jalisco — and northward into the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona, U.S.

Artemisia ludoviciana is a North American species of flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae, known by several common names, including silver wormwood, western mugwort, Louisiana wormwood, white sagebrush, lobed cud-weed, prairie sage, and gray sagewort.
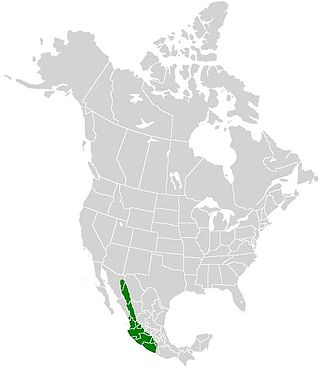
Parides alopius, the white-dotted cattleheart, is an endemic Mexican butterfly in the family Papilionidae. It has also strayed once into the United States in southeastern Arizona.

Neophasia menapia, the pine white, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is found in the western United States and in southern British Columbia, Canada.

Neophasia is a genus of pierid butterflies found in North America.

Catasticta nimbice, the pine white or Mexican dartwhite, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is found from Costa Rica north to Mexico. Rare strays can be found as far north as the Chisos Mountains of western Texas.
Stellaria porsildii is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common name Porsild's starwort. It is native to Arizona, where it can be found in the Chiricahua Mountains, and New Mexico, where it is known from one mountain.

Southern Athabaskan is a subfamily of Athabaskan languages spoken primarily in the Southwestern United States with two outliers in Oklahoma and Texas. The languages are spoken in the northern Mexican states of Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila and to a much lesser degree in Durango and Nuevo León. Those languages are spoken by various groups of Apache and Navajo peoples. Elsewhere, Athabaskan is spoken by many indigenous groups of peoples in Alaska, Canada, Oregon and northern California.
Apantesis allectans is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Douglas C. Ferguson in 1985. It is found in the Mexican states of Durango and Sonora and the Chiricahua Mountains of southern Arizona in the United States. The habitat consists of open montane pine forests.
Cirsium wheeleri is a North American species of plants in the tribe Cardueae within the family Asteraceae. Common names include Wheeler's thistle. It is native to northern Mexico and the southwestern United States.














