
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

Sphaeropleales is an order of green algae that used to be called Chlorococcales. The order includes some of the most common freshwater planktonic algae such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. The Sphaeropleales includes vegetatively non-motile unicellular, colonial, or filamentous taxa. They have biflagellate zoospores with flagella that are directly opposed in direction : Sphaeroplea, Atractomorpha, Neochloris, Hydrodictyon, and Pediastrum. All of these taxa have basal body core connections. Motile cells generally lack cell walls or have only a very fine layer surrounding the cell membrane. Other common characteristics include a robust vegetative cell wall, cup-shaped chloroplasts with large pyrenoids, and relatively large nuclei.
The Palmellaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. Members of this group are typically found in atmophytic or terrestrial habitats, or as phycobionts associated with lichens; a few are found in fresh water.

Selenastraceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. Members of this family are common components of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats worldwide. A few species have been found in brackish and marine habitats, such as in the Baltic Sea.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.
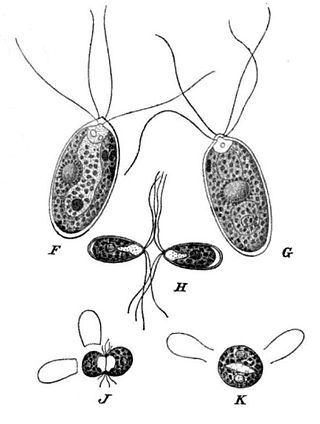
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.

Chloromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is closely related to the model green algae, Chlamydomonas, and traditionally has been distinguished mainly through the absence of a pyrenoid.

Cylindrocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.

Desmodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is the only chlorophyll-containing organism known to have caused human infections in immunocompetent individuals. All known cases involved open injuries occurring in fresh water.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.

Dictyosphaerium is a genus of green algae, in the family Chlorellaceae. It occurs in freshwater habitats around the world and is planktonic.

Golenkinia is a genus of green algae first described in 1894 by Robert Chodat. The genus is named for the Russian phycologist Mikhail Iljitsch Golenkin. Golenkinia species live in fresh water and are found around the world.

Lagerheimia is a genus of green algae in the family Oocystaceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats all over the world, although some species are rare and have only been recorded from Europe or the United States.
Planktosphaeria is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. It was first described by the phycologist Gilbert Morgan Smith in 1918, with Planktosphaeria gelatinosa as its type species. Species of Planktosphaeria are commonly found in freshwater plankton around the world.
Radiofilum is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is a freshwater genus; they are often found in soft, boggy or acidic waters.

Trebouxia is a unicellular green alga. It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions. It can either exist in a symbiotic relationship with fungi in the form of lichen or it can survive independently as a free-living organism alone or in colonies. Trebouxia is the most common photobiont in extant lichens. It is a primary producer of marine, freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems. It uses carotenoids and chlorophyll a and b to harvest energy from the sun and provide nutrients to various animals and insects.
Trichosarcina is a genus of green algae in the order Ulotrichales. Filoprotococcus was once regarded as a synonym. However, Filoprotococcus is now considered valid in its own right. Trichosarcina is considered to be of uncertain validity.

Tetrastrum is a genus of green algae (Chlorophyta). It is a common component of the phytoplankton of freshwater habitats, particularly eutrophic and alkaline waters.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.















