Related Research Articles

Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.

Endometrioid tumors are a class of tumor characterized by a resemblance to endometrium/ endometrial carcinoma, and over a third of cases have focal squamous differentiation.

Surface epithelial-stromal tumors are a class of ovarian neoplasms that may be benign or malignant. Neoplasms in this group are thought to be derived from the ovarian surface epithelium or from ectopic endometrial or Fallopian tube (tubal) tissue. Tumors of this type are also called ovarian adenocarcinoma. This group of tumors accounts for 90% to 95% of all cases of ovarian cancer; however is mainly only found in postmenopausal women with the exception of the United States where 7% of cases occur in women under the age of 40. Serum CA-125 is often elevated but is only 50% accurate so it is not a useful tumor marker to assess the progress of treatment. 75% of women with epithelial ovarian cancer are found within the advanced-stages; however younger patients are more likely to have better prognoses than older patients.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body.

Salivary gland tumours, also known as mucous gland adenomas or neoplasms, are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800 to 1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity. Patients with these types of tumours may be asymptomatic.
Large-cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of undifferentiated malignant neoplasms that lack the cytologic and architectural features of small cell carcinoma and glandular or squamous differentiation. LCC is categorized as a type of NSCLC which originates from epithelial cells of the lung.
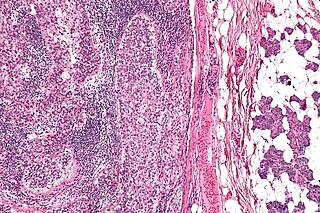
Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma is an uncommon malignant cutaneous tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebaceous glands in the skin and, therefore, may originate anywhere in the body where these glands are found. SGc can be divided into 2 types: periocular and extraocular. The periocular region is rich in sebaceous glands making it a common site of origin. The cause of these lesions in the vast majority of cases is unknown. Occasional cases may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome. SGc accounts for approximately 0.7% of all skin cancers, and the incidence of SGc is highest in Caucasian, Asian, and Indian populations. Due to the rarity of this tumor and variability in clinical and histological presentation, SGc is often misdiagnosed as an inflammatory condition or a more common neoplasm. SGc is commonly treated with wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, and the relative survival rates at 5 and 10 years are 92.72 and 86.98%, respectively.
Large cell lung carcinoma with rhabdoid phenotype (LCLC-RP) is a rare histological form of lung cancer, currently classified as a variant of large cell lung carcinoma (LCLC). In order for a LCLC to be subclassified as the rhabdoid phenotype variant, at least 10% of the malignant tumor cells must contain distinctive structures composed of tangled intermediate filaments that displace the cell nucleus outward toward the cell membrane. The whorled eosinophilic inclusions in LCLC-RP cells give it a microscopic resemblance to malignant cells found in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a rare neoplasm arising from transformed skeletal muscle. Despite their microscopic similarities, LCLC-RP is not associated with rhabdomyosarcoma.
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (Bas-SqCC) is an uncommon histological variant of lung cancer composed of cells exhibiting cytological and tissue architectural features of both squamous cell lung carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma.
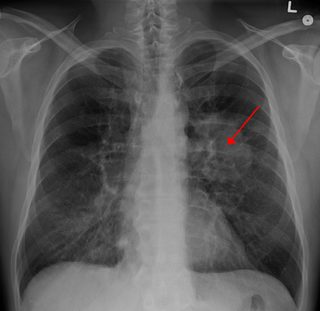
Lung tumors are neoplastic lung nodules. These include:
Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors are neuroendocrine tumors localized to the lung: bronchus or pulmonary parenchyma.

Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, often referred to as "islet cell tumours", or "pancreatic endocrine tumours" are neuroendocrine neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous system within the pancreas.
Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) is an indolent thyroid tumor that was previously classified as an encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, necessitating a new classification as it was recognized that encapsulated tumors without invasion have an indolent behavior, and may be over-treated if classified as a type of cancer.
References
- ↑ Neuroectodermal tumor entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E (2002). "Neuroectodermal Neoplasms of the Head and Neck with Emphasis on Neuroendocrine Carcinomas". Modern Pathology. 15 (3): 264–278. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880522 . ISSN 0893-3952. PMID 11904342.